Abstract
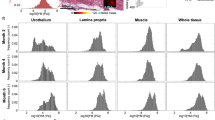
Spinal cord injuries (SCI) often lead to severe bladder dysfunctions. Our previous studies have demonstrated that following SCI, rat bladder wall tissue became hypertrophied, significantly more compliant, and changed its mechanical behavior from orthotropic to isotropic. In order to elucidate the link between the tissue microstructure and mechanical properties of the wall, we have developed a novel semi-automated image analysis method to quantify smooth muscle bundle orientation and mass fraction in the bladder wall tissues from normal and 10 day-post-SCI rats. Results of the present study revealed that there were significant (p < 0.05) increases in smooth muscle area fractions as well as significantly (p < 0.001) fewer cell nuclei per muscle area in the SCI groups compared to the normal groups. Furthermore, while the normal rat bladders exhibited predominant smooth muscle orientation only in the longitudinal direction, the SCI rat bladders exhibited smooth muscles oriented in both the circumferential and longitudinal directions. These results provide first evidence that bladder smooth muscle cells exhibit hypertrophy rather than hyperplasia and developed a second, orthogonal orientation of smooth muscle bundles following SCI. The results of the present study corroborate our previous mechanical anisotropy data and provide the basis for development of structure-based constitutive models for urinary bladder wall tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charlton, R. G., A. R. Morley, P. Chambers, and J. I. Gillespie. Focal changes in nerve, muscle and connective tissue in normal and unstable human bladder. BJU Int. 84(9):953–960, 1999.
Chaudhuri, S., H. Nguyen, R. M. Rangayyan, S. Walsh, and C. B. Frank. A Fourier Domain Directional Filtering Method for Analysis of Collagen Alignment in Ligaments. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. BME(34):509–518, 1987.
de Groat, W. C. A neurologic basis for the overactive bladder. Urology. 50(6A Suppl): 36–52, (discussion 53–56), 1997.
Deveaud, C. M., E. J. Macarak, U. Kucich, D. H. Ewalt, W. R. Abrams, and P. S. Howard. Molecular analysis of collagens in bladder fibrosis. J. Urol. 160(4):1518–1527, 1998.
Drake, M. J., B. P. Gardner, and A. F. Brading. Innervation of the detrusor muscle bundle in neurogenic detrusor overactivity. BJU Int. 91(7):702–710, 2003.
Drake, M. J., P. Hedlund, I. W. Mills, R. McCoy, G. McMurray, B. P. Gardner, K. E. Andersson, and A. F. Brading. Structural and functional denervation of human detrusor after spinal cord injury (In Process Citation). Lab Invest. 80(10):1491–1499, 2000.
Gabella, G., and B. Uvelius. Structural changes in the rat bladder after acute outlet obstruction. Scand. J. Urol Nephrol. Suppl. 201:32–37, 1999.
Gabella, G., and B. Uvelius. Urinary bladder of rat: fine structure of normal and hypertrophic musculature. Cell Tissue Res. 262(1):67–79, 1990.
Gloeckner, D. C. Tissue Biomechanics of the Urinary Bladder Wall: Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh, 2003, p. 258.
Gloeckner, D. C., M. S. Sacks, M. O. Fraser, G. T. Somogyi, W. C. de Groat, and M. B. Chancellor. Passive biaxial mechanical properties of the rat bladder wall after spinal cord injury. J. Urol. 167(5):2247–2252, 2002.
Hackler, R. H., M. K. Hall, and T. A. Zampieri. Bladder hypocompliance in the spinal cord injury population. J. Urol. 141(6):1390–1393, 1989.
Karlon, W. J., J. W. Covell, A. D. McCulloch, J. J. Hunter, and J. H. Omens. Automated measurement of myofiber disarray in transgenic mice with ventricular expression of ras. Anat. Rec. 252(4):612–625, 1998.
Kruse, M. N., B. Bennett, and W. C. De Groat, Effect of urinary diversion on the recovery of micturition reflexes after spinal cord injury in the rat. J. Urol. 151(4):1088–1091, 1994.
Mimata, H., F. Satoh, T. Tanigawa, Y. Nomura, and J. Ogata. Changes of rat urinary bladder during acute phase of spinal cord injury. Urol Int. 51(2):89–93, 1993.
Murakumo, M., T. Ushiki, K. Abe, K. Matsumura, Y. Shinno, and T. Koyanagi. Three-dimensional arrangement of collagen and elastin fibers in the human urinary bladder: A scanning electron microscopic study. J. Urol. 154(1):251–256, 1995.
Nagatomi, J., D. C. Gloeckner, M. Chancellor, R. D. DeGroat, and M. S. Sacks. Changes in the Biaxial Viscoelastic Response of the Urinary Bladder following Spinal Cord Injury. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 32(10):1409–1419, 2004.
Ogawa, T. Bladder deformities in patients with neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Urol Int. 47(Suppl 1):59–62, 1991.
Pitre, D. A., T. Ma, L. J. Wallace, and J. A. Bauer. Time-dependent urinary bladder remodeling in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model. Acta Diabetol. 39(1):23–27, 2002.
Sacks, M. S. Incorporation of experimentally-derived fiber orientation into a structural constitutive model for planar collagenous tissues. J. Biomech. Eng. 125(2):280–287, 2003.
Sacks, M. S., and D. C. Gloeckner. Quantification of the fiber architecture and biaxial mechanical behavior of porcine intestinal submucosa. J. Biomed. Mat. Res. 46:1–10, 1999.
Sacks, M. S., D. B. Smith, and E. D. Hiester. A small angle light scattering device for planar connective tissue microstructural analysis. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 25(4):678–689, 1997.
Shin, J. C., C. I. Park, H. J. Kim, and I. Y. Lee. Significance of low compliance bladder in cauda equina injury. Spinal Cord. 40(12):650–655, 2002.
Ushiki, T., and M. Murakumo. Scanning electron microscopic studies of tissue elastin components exposed by a KOH-collagenase or simple KOH digestion method. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 54(4):427–436, 1991.
Weld, K. J., M. J. Graney, and R. R. Dmochowski. Differences in bladder compliance with time and associations of bladder management with compliance in spinal cord injured patients. J. Urol. 163(4):1228–1233, 2000.
Yoo, T. S., M. J. Ackerman, W. E. Lorensen, W. Schroeder, V. V. Chalana, S. Aylward, D. Metaxes, and R. Whitaker. Engineering and Algorithm Design for an Image Processing API: A Technical Report on ITK - The Insight Toolkit. In: Proceedings of Medicine Meets Virtual Reality,edited by J. Westwood, Amsterdam: IOS Press, 2002, pp. 586– 592.
Yoshiyama, M., and W. C. de Groat. Effect of bilateral hypogastric nerve transection on voiding dysfunction in rats with spinal cord injury. Exp. Neurol. 175(1):191–197, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagatomi, J., Toosi, K.K., Grashow, J.S. et al. Quantification of Bladder Smooth Muscle Orientation in Normal and Spinal Cord Injured Rats. Ann Biomed Eng 33, 1078–1089 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-5776-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-5776-x