Abstract
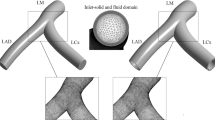
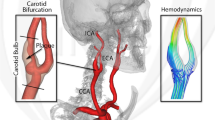
The present study presents a three-dimensional, unsteady supercomputer simulation of the coupled fluid–solid interaction problem associated with flow through a compliant model of the bifurcation of the common carotid artery into the internal and external carotid arteries. The fluid wall shear stress (WSS) and solid circumferential stress/strain (CS) are computed and analyzed for the first time using the complex ratio of CS to WSS (CS/WSS). This analysis reveals a large negative phase angle between CS and WSS (stress phase angle—SPA) on the outer wall of the carotid sinus where atherosclerotic plaques are localized. This finding is consistent with other measurements and computations of the SPA in coronary arteries and the aortic bifurcation that show large negative SPA correlating with sites of plaque location and in vitro studies of endothelial cells showing that large negative SPA induces pro-atherogenic gene expression and metabolite release profiles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anayiotos A. S., S. A. Jones, D. P. Giddens, S. Glagov, and C. K. Zarins. Shear stress at a compliant model of the human carotid bifurcation. Trans ASME J. Biomech. Eng. 116:98–106, 1994.
Atabek H. B., S. C. Ling, and D. J. Patel. Analysis of coronary flow fields in thoracotomized dogs. Circ. Eng. 107:307–315, 1975.
Bella J. N., M. J. Roman, R. Pini, J. E. Schwartz, T. G. Pickering, and R. B. Devereux. Assessment of arterial compliance by carotid midwall strain-stress relation in normotensive adults. Hypertension 33:787–792, 1999.
Bharadvaj B. K., R. F. Mabon, and D. P. Giddens. Steady flow in a model of the human carotid bifurcation part I—flow visualization. J. Biomech. 15:349–362, 1982.
Botnar R., G. Rappitsch, M. B. Scheidegger, D. Liepsch, K. Perktold, and P. Boesiger. Hemodynamics in the carotid artery bifurcation: A comparison between numerical simulations and in vitro MRI measurements. J. Biomech. 33:137–144, 2000.
Cebral J. R., P. J. Yim, R. Lohner, O. Soto, and P. L. Choyke. Blood flow modeling in carotid arteries with computational fluid dynamics and MR imaging. Acad. Radiol. 9:1286–1299, 2002.
Chien S. Molecular and mechanical bases of focal lipid accumulation in arterial wall. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 83:131–151, 2003.
Dai G., M. R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, S. Natarajan, Y. Zhang, S. Vaughn, B. R. Blackman, R. D. Kamm, G. Garcia-Cardeña, and M. A. Gimbrone, Jr. Distinct endothelial phenotypes evoked by arterial waveforms derived from atherosclerosis-susceptible and—resistant regions of human vasculature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101:14871–14876, 2004.
Dancu M. B., and J. M. Tarbell. Large negative stress phase angle (SPA) attenuates nitric oxide production in bovine aortic endothelial cells. Trans. ASME J. Biomech. Eng., in press.
Davies P. Flow-mediated endothelial mechanotransduction. Physiol. Rev. 75:519–560, 1995.
Delfino A., N. Stergioopulos, J. E. Moore Jr, and J. J. Meister. Residual strain effects on the stress field in a thick wall finite element model of the human carotid bifurcation. J. Biomech. 30:777–786, 1997.
He X., and D. N. Ku. Pulsatile flow in the human left coronary artery bifurcation: Average conditions. Trans. ASME J. Biomech. Eng. 118:74–82, 1996.
Holdworth D. W., C. J. D. Norley, R. Frayne, D. A. Steinman, and B. K. Rutt. Characterization of common carotid artery blood-flow waveforms in normal human subjects. Physiol. Meas. 20:219–240, 1999.
Hyun S., C. Kleinstreuer, and J. P. Archie Jr. Computational analysis of effects of external carotid artery flow and occlusion on adverse carotid bifurcation hemodynamics. J. Vasc. Surg. 37:1248–1254, 2003.
Joshi A. K., R. L. Leask, J. G. Myers, M. Ojha, J. Butany and C. R. Ethier. Intimal thickness is not associated with wall shear stress patterns in the human right coronary artery. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24:2408–2413, 2004.
Kaluzynski K., T. Powalowski, B. Lesniak, Z. Trawinski, T. Palko, and D. Liepsch. Studies of arterial input impedance in models of carotid artery. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 3:9–19, 2003.
Ku D. N., D. P. Giddens, C. K. Zarins, and S. Glagov. Pulsatile flow and atherosclerosis in the human carotid bifurcation. Positive correlation between plaque location and low oscillating shear stress. Arteriosclerosis 5:293–302, 1985.
Lee C. S., and J. M. Tarbell. Influence of vasoactive drugs on wall shear stress distribution in the abdominal aortic bifurcation: An in vitro study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 26:200–212, 1998.
Ma P. P., X. M. Li, and D. N. Ku. Convective mass transfer at the carotid bifurcation. J. Biomech. 30:565–571, 1997.
Maeda N., Y. Sawayama, M. Tatsukawa, K. Okada, N. Furusyo, M. Shigematsu, S. Kashiwagi, and J. Hayashi. Carotid artery lesions and atherosclerotic risk factors in Japanese hemodynamics patients. Atherosclerosis 169:183–192, 2003.
Milner J. S., J. A. Moore, B. K. Rutt, and D. A. Steinman. Hemodynamics of human carotid artery bifurcations: Computational studies with models reconstructed from magnetic resonance imaging of normal subjects. J. Vasc. Surg. 27:143–156, 1998.
Milnor W. R. Hemodynamics. Baltimore, MD: Williams and Wilkins, 1989, pp.167–181.
Moore J. A., D. A. Steinman, D. W. Holdworth, and C. R. Ethier. Accuracy of computational hemodynamics in complex arterial geometries reconstructed flow magnetic resonance imaging. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 27:32–41, 1999.
Ojha M., R. L. Leask, J. Butany, and K. W. Johnson. Distribution of intimal and medial thickening in the human right coronary artery: A study of 17 RCAs. Atherosclerosis 158:147–153, 2001.
Papathanasopoulou P., S. Zhao, U. Koehler, M. B. Robertson, Q. Long, P. Hoskins, X. Y. Xu, and I. Marshall. MRI measurement of time-resolved wall shear stress vectors in a carotid bifurcation model, and comparison with CFD predictions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 17:153–162, 2003.
Perktold K., and G. Rappitsch. Computer simulation of local blood flow and vessel mechanics in a compliant carotid artery bifurcation model. J. Biomech. 28:845–856, 1995.
Qiu Y., and J. M. Tarbell. Interaction between wall shear stress and circumferential strain affects endothelial cell biochemical production. J. Vasc. Res. 37:147–157, 2003.
Qiu Y., and J. M. Tarbell. Numerical simulation of pulsatile flow in a compliant curved tube model of a coronary artery. Trans. ASME J. Biomech. Eng. 122:77–85, 2000.
Ramnarine K. V., T. Hartshorne, Y. Sensier, M. Naylor, J. Walker, A. R. Naylor, R. B. Panerai, and D. H. Evans. Tissue Doppler imaging of carotid plaque wall motion: A pilot study. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 1:1–15, 2003.
Salzer R. S., M. J. Thubrikar, and R. T. Eppink. Pressure-induced mechanical stress in the carotid artery bifurcation: A possible correlation to atherosclerosis. J. Biomech. 28:1333–1340, 1995.
Schulz U. G. R., and P. M. Rothwell. Major variation in carotid bifurcation anatomy—a possible risk factor for plaque development. Stroke 32:2522–2529, 2001.
Selzer R. H., W. J. Mack, P. L. Lee, H. Kwong-Fu, and H. N. Hodis. Improved common carotid elasticity and intima-media thickness measurements from computer analysis of sequential ultrasound frames. Athrosclerosis 154:185–193, 2001.
Sitzer M., D. Puac, A. Buehler, D. A. Steckel, S. von Kegler, H. S. Markus, and H. Steinmetz. Internal carotid artery angle of origin: A novel risk factor for early carotid atherosclerosis. Stroke 34:950–955, 2003.
Stadler R. W., J. A. Taylor, and R. S. Lees. Comparison of B-mode, M-mode and Echo-tracking methods for measurement of the arterial distension waveform. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 23:879–887, 1997.
Steinman D. A., J. B. Thomas, H. M. Ladak, J. S. Milner, B. K. Rutt, and J. D. Spence. Reconstruction of carotid bifurcation hemodynamics and wall thickness using computational fluid dynamics and MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 47:149–159, 2002.
Sun Y., C. H. Lin, C. J. Lu, P. K. Yip, and R. C. Chen. Carotid atherosclerosis, intima media thickness and risk factors—an analysis of 1781 asymptomatic subjects in Taiwan. Atherosclerosis 164:89–94, 2002.
Thomas J. B., J. S. Milner, and D. A. Steinman. On the influence of vessel planarity on local hemodynamics at the human carotid bifurcation. Biorheology 39:443–448, 2002.
Urbina E. M., S. R. Srinivasan, R. Tang, M. G. Bond, L. Kieltyka, and G. S. Berenson. Impact of multiple coronary risk factors on the intima-media thickness of different segments of carotid artery in healthy young adults (The Bogalusa Heart Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 90:953–958, 2002.
Wang D. M., and J. M. Tarbell. Nonlinear analysis of oscillatory flow with a nonzero mean, in an elastic tube (artery). Trans. ASME J. Biomech. Eng. 117:127–135, 1995.
Younis H. F., M. R. Kaazempur-Mofrad, C. Chung, R. C. Chan, and R. D. Kamm. Computational analysis of the effects of exercise on hemodynamics in the carotid bifurcation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 13:995–1006, 2003.
Zarins C. K., D. P. Giddens, B. K. Bharadvaj, V. S. Sottiurai, R. F. Mabon, and S. Glagov. Carotid bifurcation atherosclerosis. Quantitative correlation of plaque localization with flow velocity profiles and wall shear stress. Circ. Res. 53:502–514, 1983.
Zhao S. Z., B. Ariff, Q. Long, A. D. Hughes, S. A. Thom, A. V. Stanton, and X. Y. Xu. Inter-individual variations in wall shear stress and mechanical stress distributions at the carotid artery bifurcation of healthy humans. J. Biomech. 35:1367–1377, 2002.
Zhao S. Z., X. Y. Xu, A. D. Hughes, S. A. Thom, A. V. Stanton, B. Ariff, and Q. Long. Blood flow and vessel mechanics in a physiologically realistic model of a human carotid arterial bifurcation. J. Biomech. 33:975–984, 2000.
Zulliger M. A., N. T. M. R. Kwak, T. Tsapikouni, and N. Stergiopulos. Effects of longitudinal stretch on VSM tone and distensibility of muscular conduit arteries. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 283:H2599–H2605, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tada, S., Tarbell, J.M. A Computational Study of Flow in a Compliant Carotid Bifurcation–Stress Phase Angle Correlation with Shear Stress. Ann Biomed Eng 33, 1202–1212 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-5630-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-5630-1