Abstract
Background: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a potent angiogenic factor that also has the ability to increase vascular permeability. Malignant ascites has significant morbidity, but the mechanism of its development is unknown. Because of the permeability-inducing properties of VEGF, we hypothesized that malignant ascites formation is associated with high levels of VEGF. The purpose of our study was to determine the role of VEGF in malignant ascites formation.
Methods: Ascites from 25 patients with gastric (n = 6), colon (n = 7), or ovarian (n = 12) cancers was collected by paracentesis or surgery. VEGF protein levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The effect of ascites on endothelial cell permeability was assessed by evaluating propidium iodide uptake by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) exposed to ascites. Neutralizing antibodies to VEGF added to ascites were used to determine the causal effect of VEGF in permeability induction.
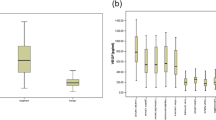
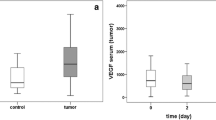
Results: VEGF protein levels were markedly increased in malignant ascites compared with levels in nonmalignant cirrhotic ascites (controls). VEGF protein levels in ovarian, gastric, and colon cancer ascites were found to be increased 45, 23, and 12 times, respectively, compared with levels in cirrhotic ascites. Malignant ascites from patients with colon and gastric cancer caused an increase in permeability in HUVECs in all cases. Neutralizing VEGF activity in colon cancer ascites decreased in-vitro HUVEC permeability in three of four cases.
Conclusions: VEGF protein levels are markedly elevated in malignant ascites. VEGF may play a role in malignant ascites formation by increasing endothelial cell permeability.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ferrara N, Houch KA, Jackeman LB, Winer J, Leung DW. The vascular endothelial growth factor family of polypeptides. J Cell Biochem 1991;47:211–218.
Collins PD, Connolly DT, Williams TJ. Characterization of the increase in vascular permeability induced by vascular permeability factor in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 1993;109:195–199.
Takahashi Y, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Cleary KR, Ellis LM. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, KDR, correlates with vascularity, metastasis, and proliferation of human colon cancer. Cancer Res 1995;55:3964–3968.
Takahashi Y, Tucker SL, Kitadai Y, Koura AN, Bucana CD, Cleary KR, Ellis LM. Vessel counts and VEGF expression as prognostic factors in node-negative colon cancer. Arch Surg 1997;132:541–546.
Takahashi Y, Cleary KR, Mai M, Kitadai Y, Bucana CD, Ellis LM. Significance of vessel count and vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor (KDR) in intestinal-type gastric cancer. Clin Ca Res 1996;2:1679–1684.
Aiello LP, Avery RL, Arrigg PG, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1480–1487.
Shifren JL, Tseng JF, Zaloudek CJ, et al. Ovarian steroid regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in the human endometrium: implications for angiogenesis during the menstrual cycle and in the pathogenesis of endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996;81:3112–3118.
Abromov Y, Barak V, Nisman B, Schenker JG. Vascular endothelial growth factor plasma levels correlate to the clinical picture in severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Fertil Steril 1997;67:261–265.
Koch AE, Harlow LA, Haines GK, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor. A cytokine modulating endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 1994;152:4149–4156.
Brown LF, Berse B, Jackman RW, Tognazzi K, Manseau EJ, Dvorak HF, Senger DR. Increased expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in kidney and bladder carcinomas. Am J Pathol 1993;143:1255–1262.
Brown LF, Berse B, Jackman RW, Tognazzi K, Manseau EJ, Senger DR, Dvorak HF. Expression of vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) and its receptors in adenocarcinomas of the gastrointestinal tract. Cancer Res 1993;53:4727–4735.
Boocock CA, Charnock-Jones DS, Sharkey AM, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors flt and KDR in ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 1995;87:506–516.
Garrison RN, Kaelin LD, Galloway RH, Heuser LS. Malignant ascites. Clinical and experimental observations. Ann Surg 1986;203:644–651.
Roberts JM, Edep ME, Goldfien A, Taylor RN. Sera from preeclamptic women specifically activate human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro: morphological and biochemical evidence. Am J Reprod Immunol 1992;27(3–4):101–108.
Andus T, Gross V, Holstege A, Weber M, Ott M, Gerok W, Scholmerich J. Evidence for the production of high amounts of interleukin-6 in the peritoneal cavity of patients with ascites. J Hepatol 1992;15:378–381.
Behammer W, Kluge M, Ruschoff J, Mannel DN. Tumor necrosis factor effects on ascites formation in an experimental tumor model. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1996;16:403–408.
Nagy JA, Herzberg KT, Masse EM, Zientara GP, Dvorak HF. Exchange of macromolecules between plasma and peritoneal cavity in ascites tumor-bearing, normal, and serotonin-injected mice. Cancer Res 1989;49:5448–5458.
Adamsen S, Jonsson P, Brodin B, Lindberg B, Jorpes P. Measurement of fibronectin concentration in benign and malignant ascites. Eur J Surg 1991;157:325–328.
Jungst D, Xie Y, Gerbes AL. Pathophysiology of elevated ascites fluid cholesterol in malignant ascites. Increased ascites to serum relation of proteins and lipoproteins in patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis as compared to patients with cirrhosis of the liver. J Hepatol 1992;14:244–248.
Lee CM, Changchien CS, Shyu WC, Liaw YF. Serum-ascites albumin concentration gradient and ascites fibronectin in the diagnosis of malignant ascites. Cancer 1992;70:2057–2060.
Kountouras J. Value of ascitic fluid ferritin in the differential diagnosis of malignant ascites. Anticancer Res 1993;13:2441–2445.
Andus T, Gross V, Holstege A, et al. High concentrations of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors in ascites. Hepatology 1992;16:749–755.
Rath U, Kaufmann M, Schmid H, et al. Effect of intraperitoneal recombinant human tumour necrosis factor alpha on malignant ascites. Eur J Cancer 1991;27:121–125.
Bezwoda WR, Seymour L, Dansey R. Intraperitoneal recombinant interferon-alpha 2b for recurrent malignant ascites due to ovarian cancer. Cancer 1989;64:1029–1033.
Marincola FM, Schwartzentruber DJ. Malignant ascites. In: De-Vita VT, Hellman J, Rosenberg SA (eds). Cancer: Principles and Practice of Oncology. 5th ed. Vol. 2. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven, 1997:2598–2606.
Parsons SL, Watson SA, Steele RJ. Phase I/II trial of batimastat, a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, in patients with malignant ascites. Eur J Surg Oncol 1997;23:526–531.
Mori H, Itoh N, Yamada Y, Tamaya T. Induction of endogenous tumor necrosis factor by OK-432 in ovarian cancer patients with ascites. Biotherapy 1989;1(3):123–131.
Luo JC, Yamaguchi S, Shinkai A, Shitara K, Shibuya M. Significant expression of vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor in mouse ascites tumors. Cancer Res 1998;58:2652–2660.
Yeo KT, Wang HH, Nagy JA, et al. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) in guinea pig and human tumor and inflammatory effusions. Cancer Res 1993;53:2912–2918.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zebrowski, B.K., Liu, W., Ramirez, K. et al. Markedly Elevated Levels of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Malignant Ascites. Ann Surg Oncol 6, 373–378 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10434-999-0373-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10434-999-0373-0