Abstract
Background: Stereotactic radiosurgery is an alternative to resection or to radiotherapy alone for patients with brain metastases. Outcomes after radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases specifically from breast cancer have not been defined.
Methods: We retrospectively studied survival and tumor control for all patients with brain metastases from breast cancer who underwent gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery at the University of Pittsburgh. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to determine which prognostic factors significantly affected survival.
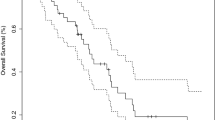
Results: Thirty patients underwent radiosurgery between 1990 and 1997. A total of 58 metastases were treated. The median length of survival for all patients was 13 months from radiosurgery and 18 months from diagnosis of brain metastases. The tumor control rate on follow-up imaging was 93%. On multivariate analysis, the only factor that correlated with longer survival was the absence of multiple brain metastases. Age, presence of systemic disease, previous whole brain radiation, location, and total tumor volume did not significantly affect survival. Four patients had tumors with evidence of radiation-induced edema after radiosurgery but did not require resection. Two patients underwent delayed resection for tumor growth after radiosurgery.
Conclusions: Stereotactic radiosurgery is an effective treatment for brain metastases from breast cancer and is associated with a low complication rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
DiStefano A, Yap Y, Hortobagyi GN, Blumenschein GR. The natural history of breast cancer patients with brain metastases. Cancer 1979;44:1913–8.
Adler JR, Cox RS, Kaplan I, Martin DP. Stereotactic radiosurgical treatment of brain metastases. J Neurosurg 1992;76:444–9.
Alexander E, Moriarty TM, Davis RB, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for the definitive, non-invasive treatment of brain metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 1995;87:34–40.
Caron JL, Souhami L, Podgorsak EB. Dynamic stereotactic radiosurgery in the palliative treatment of cerebral metastatic tumors. J Neurooncol 1992;12:173–9.
Coffey RJ, Flickinger JC, Bissonette DJ, Lunsford LD. Radiosur-gery for solitary brain metastases using the cobalt-60 gamma unit: methods and results in 24 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1991;20:1287–95.
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD, et al. A multi-institutional experience with stereotactic radiosurgery for solitary brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1994;28:797–802.
Kihlstrom L, Karlsson B, Lindquist C. Gamma knife surgery for cerebral metastases: complications for survival based on 16 years experience. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 1993;61(Supp l):45–50.
Mehta MP, Rozental JM, Levin AB, et al. Defining the role of radiosurgery in the management of brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1992;24:619–25.
Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 1958;53:457–81.
Cox DR. Regression models and life tables. J R Stat Soc 1972;74:187–220.
Cairncross JG, Kim J-H, Posner JB. Radiation therapy for brain metastases. Ann Neurol 1980;7:529–41.
Kamby C, Soerenson PS. Characteristics of patients with short and long survivals after detection of intracranial metastases from breast cancer. J Neurooncol 1988;6:37–55.
West J, Maor M. Intracranial metastases: behavioral patterns related to primary site and results of treatment by whole brain irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1980;6:111–5.
Zimm S, Wampler GL, Stablein D, Hazra T, Young HF. Intracerebral metastases in solid tumor patients: natural history and results of treatment. Cancer 1981;48:384–94.
Boogerd W, Dalesio O, Bais EM, van der Sande JJ. Response of brain metastases from breast cancer to systemic chemotherapy. Cancer 1992;69:972–80.
Rosner D, Nemoto T, Lane W. Chemotherapy induces regression of brain metastases in breast carcinoma. Cancer 1986;58:832–9.
Salvati M, Cervoni L, Innocenzi G, Bardella L. Prolonged stabilization of multiple and single brain metastases from breast cancer with tamoxifen: report of three cases. Tumori 1993;79:359–62.
Patchell RA, Cirrincione C, Thaler HT, Galicich JH, Kim JH, Posner JB. Single brain metastases: surgery plus radiation or radiation alone. Neurology 1986;36:447–53.
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, et al. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med 1990;322:494–500.
Vecht CJ, Haaxma-Reiche H, Noordijk EM, et al. Treatment of single brain metastases: radiotherapy alone or combined with neurosurgery? Ann Neurol 1993;33:583–90.
Wronski M, Arbit E, McCormick B. Surgical treatment of 70 patients with brain metastases from breast carcinoma. Cancer 1997;80:1746–54.
Pieper DR, Hess KR, Sawaya RE. Role of surgery in the treatment of brain metastases in patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 1997;4:481–90.
Nieder C, Walter K, Nestle U, Schnabel K. Ten years disease-free survival after solitary brain metastases from breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 1996;122:570–2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Firlik, K.S., Kondziolka, D., Flickinger, J.C. et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases From Breast Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 7, 333–338 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10434-000-0333-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10434-000-0333-1