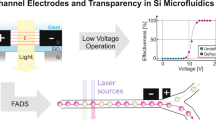
Abstract
Nowadays nanofluidic devices have a great potential in biosensing and DNA sequencing applications. This work is aimed at development of the technique for fabrication of arrays of nanochannels in silicon-glass chips by focused ion beam milling. The use of lithography with charged particles (electrons and ions) paves the way for the fabrication of micro- and nanochannels and pores as well as functional nanostructures of a more complex shape in nanofluidic devices. In this study, a technique for fabrication of microfluidic chips with a system of nanochannels connecting two independent volumes (2 half cells) was developed. It was shown experimentally that the focused ion beam etching time has an influence on both the width of the created nanochannels and their depth. We suggested using anodic bonding of a silicon wafer with the net of micro- and nanochannels with a glass plate for encapsulation of such devices that provide their long lifetime of microfluidic devices. To determine the functionality of the produced devices we studied the ionic conductivity of the produced nanochannels experimentally and using a theoretical approach. Analyzing the results, we determined the effective diameter of the nanochannels and the surface charge density inside the channel which were 20 nm and 1.5 mC/m\({}^2\), respectively. The proposed technique allows to create ensembles of channels with a predefined width and depth. Such systems can find wide application in studies of the transport phenomena of both ions and various molecules in nanofluidic devices.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arab J, Adhale P, Mishra DK, Dixit P (2019) Micro array hole formation in glass using electrochemical discharge machining. Procedia Manuf 34:349–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2019.06.174
Bardand LA, Faulkner R (1980) Electrochemical methods, fundamentals and applications. Wiley, NewYork
Chen Y (2015) Nanofabrication by electron beam lithography and its applications: a review. Microelectron Eng 135:57–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2015.02.042
Chen X, Zhang L (2018) Review in manufacturing methods of nanochannels of bio-nanofluidic chips. Sens Actuat B: Chem 254:648–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.139
de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Merkoçi A (2012) Nanochannels preparation and application in biosensing. ACS Nano 6(9):7556–7583. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn301368z
Esfandiar A, Radha B, Wang FC, Yang Q, Hu S, Garaj S, Nair RR, Geim AK, Gopinadhan K (2017) Size effect in ion transport through Angstrom-scale slits. Science 358(6362):511–513. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan5275
Evstrapov A, Mukhin I, Bukatin A, Kukhtevich I (2012) Ion and electron beam assisted fabrication of nanostructures integrated in microfluidic chips. Nucl Inst Methods Phys Res Sect B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 282:145–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2011.08.035
Favre I, Moczydlowski E, Schild L (1996) On the structural basis for ionic selectivity among Na+, K+, and Ca2+ in the voltage-gated sodium channel. Biophys J 71(6):3110–3125. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79505-X
Guan W, Reed MA (2012) Electric field modulation of the membrane potential in solid-state ion channels. Nano Lett 12(12):6441–6447. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl303820a
Guo LJ (2007) Nanoimprint lithography: methods and material requirements. Adv Mater 19(4):495–513. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200600882
Han W, Chen X (2019) Nano-electrokinetic ion enrichment of highly viscous fluids in micro-nanochannel. Chem Eng Process Process Intensif 143:107626
Han W, Chen X (2020) Nano-electrokinetic ion enrichment in a micro-nanofluidic preconcentrator with nanochannel’s cantor fractal wall structure. Appl Nanosci 10(1):95–105
Han W, Chen X (2020) A novel design of nanochannel structure in a micro-nanofluidic preconcentrator for electrokinetic ion enrichment. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 42(1):1–9
Han W, Chen X (2020) A review: applications of ion transport in micro-nanofluidic systems based on ion concentration polarization. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 95(6):1622–1631
Hao Z, Zhang Q, Xu X, Zhao Q, Wu C, Liu J, Wang H (2020) Nanochannels regulating ionic transport for boosting electrochemical energy storage and conversion: a review. Nanoscale 12(30):15923–15943. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR02464C
Hou G, Peng Z, Tian Y, Zhang H, Jiang L (2013) Applications of polymer single nanochannels in biosensors. Chin Sci Bull 58(13):1473–1482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-5788-0
Kanda Y, Matsuda K, Murayama C, Sugaya J (1990) The mechanism of field-assisted silicon-glass bonding. Sens Actuat A: Phys 23(1–3):939–943. https://doi.org/10.1016/0924-4247(90)87064-P
Kowalczyk SW, Blosser TR, Dekker C (2011) Biomimetic nanopores: learning from and about nature. Trends Biotechnol 29(12):607–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.07.006
Kurita R, Niwa O (2016) Microfluidic platforms for DNA methylation analysis. Lab Chip 16(19):3631–3644. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6LC00829A
Le T, Shimizu H, Morikawa K (2020) Advances in label-free detections for nanofluidic analytical devices. Micromachines 11(10):885. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11100885
Li G, Wang L (2004) Influence of bonding parameters on electrostatic force in anodic wafer bonding. Thin Solid Films 462–463:334–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2004.05.084
Ma T, Balanzat E, Janot J-M, Balme S (2019) Single conical track-etched nanopore for a free-label detection of OSCS contaminants in heparin. Biosens Bioelectron 137:207–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.05.005
Ma T, Balanzat E, Janot J-M, Balme S (2019) Nanopore functionalized by highly charged hydrogels for osmotic energy harvesting. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(13):12578–12585. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b01768
Ma T, Janot J, Balme S (2020) Track-etched nanopore/membrane: from fundamental to applications. Small Methods 4(9):2000366. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202000366
McDonald JC, Whitesides GM (2002) Poly(dimethylsiloxane) as a material for fabricating microfluidic devices. Acc Chem Res 35(7):491–499. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar010110q
Medina-Sánchez M, Miserere S, Cadevall M, Merkoçi A (2016) Enhanced detection of quantum dots labeled protein by simultaneous bismuth electrodeposition into microfluidic channel. Electrophoresis 37(3):432–437. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201500288
Menard LD, Ramsey JM (2011) Fabrication of sub-5 nm nanochannels in insulating substrates using focused ion beam milling. Nano Lett 11(2):512–517. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl103369g
Mills KL, Huh D, Takayama S, Thouless MD (2010) Instantaneous fabrication of arrays of normally closed, adjustable, and reversible nanochannels by tunnel cracking. Lab Chip 10(12):1627. https://doi.org/10.1039/c000863j
Mirkin MV, Amemiya S (2015) Nanoelectrochemistry. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Mokkapati VRSS, Di Virgilio V, Shen C, Mollinger J, Bastemeijer J, Bossche A (2011) DNA tracking within a nanochannel: device fabrication and experiments. Lab Chip 11(16):2711. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1lc20075e
Mukhin I, Fadeev I, Zhukov M, Dubrovskii V, Golubok A (2015) Framed carbon nanostructures: synthesis and applications in functional SPM tips. Ultramicroscopy 148:151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultramic.2014.10.008
Nam S-W, Lee M-H, Lee S-H, Lee D-J, Rossnagel SM, Kim K-B (2010) Sub-10-nm nanochannels by self-sealing and self-limiting atomic layer deposition. Nano Lett 10(9):3324–3329. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl100999e
Nelder JA, Mead R (1965) A simplex method for function minimization. Comp J 7(4):308–313
Noakes MT, Brinkerhoff H, Laszlo AH, Derrington IM, Langford KW, Mount JW, Bowman JL, Baker KS, Doering KM, Tickman BI, Gundlach JH (2019) Increasing the accuracy of nanopore DNA sequencing using a time-varying cross membrane voltage. Nat Biotechnol 37(6):651–656. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0096-0
O’Brien MJ, Bisong P, Ista LK, Rabinovich EM, Garcia AL, Sibbett SS, Lopez GP, Brueck SRJ (2003) Fabrication of an integrated nanofluidic chip using interferometric lithography. J Vac Sci Technol B: Microelectron Nanometer Struct 21(6):2941. https://doi.org/10.1116/1.1625964
Ou X, Chen P, Huang X, Li S, Liu B (2020) Microfluidic chip electrophoresis for biochemical analysis. J Sep Sci 43(1):258–270. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201900758
Ouyang W, Han J (2019) Universal amplification-free molecular diagnostics by billion-fold hierarchical nanofluidic concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci 116(33):16240–16249. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1904513116
Payandeh J, Gamal El-Din TM, Scheuer T, Zheng N, Catterall WA (2012) Crystal structure of a voltage-gated sodium channel in two potentially inactivated states. Nature 486 (7401) 135–139. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11077. http://www.nature.com/articles/nature11077
Peng R, Li D (2016) Fabrication of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) nanofluidic chips with controllable channel size and spacing. Lab Chip 16(19):3767–3776. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6LC00867D
Picallo CB, Gravelle S, Joly L, Charlaix E, Bocquet L (2013) Nanofluidic osmotic diodes: theory and molecular dynamics simulations. Phys Rev Lett 111(24):2444501. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.244501
Ramsden JJ (2016) Nanotechnology, Elsevier. https://www.elsevier.com/books/nanotechnology/ramsden/978-0-323-39311-9. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/C20140039123
Ryzhkov II, Vyatkin AS, Medvedeva MI (2019) Modelling of electrochemically switchable ion transport in nanoporous membranes with conductive surface. J Siberian Federal Univ Math Phys 579–589 https://doi.org/10.17516/1997-1397-2019-12-5-579-589. http://www.journal.sfu-kras.ru/en/article/125576
Ryzhkov II, Lebedev DV, Solodovnichenko VS, Minakov AV, Simunin MM (2018) On the origin of membrane potential in membranes with polarizable nanopores. J Membr Sci 549:616–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.073
Ryzhkov II, Vyatkin AS, Mikhlina EV (2020) Modelling of conductive nanoporous membranes with switchable ionic selectivity. Membr Membr Technol 2(1):10–19. https://doi.org/10.1134/S2517751620010072
Shi X, Verschueren DV, Dekker C (2018) Active delivery of single DNA molecules into a plasmonic nanopore for label-free optical sensing. Nano Lett 18(12):8003–8010. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04146
Siria A, Poncharal P, Biance A-L, Fulcrand R, Blase X, Purcell ST, Bocquet L (2013) Giant osmotic energy conversion measured in a single transmembrane boron nitride nanotube. Nature 494(7438):455–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11876
Sparreboom W, van den Berg A, Eijkel JCT (2009) Principles and applications of nanofluidic transport. Nat Nanotechnol 4(11):713–720. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2009.332
Tagliazucchi M, Szleifer I (2015) Transport mechanisms in nanopores and nanochannels: can we mimic nature? Mater Today 18(3):131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2014.10.020
van Kan JA, Zhang C, Perumal Malar P, van der Maarel JRC (2012) High throughput fabrication of disposable nanofluidic lab-on-chip devices for single molecule studies. Biomicrofluidics 6(3):036502. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4740231. http://aip.scitation.org/doi/10.1063/1.4740231
Wang P, Wang M, Liu F, Ding S, Wang X, Du G, Liu J, Apel P, Kluth P, Trautmann C, Wang Y (2018) Ultrafast ion sieving using nanoporous polymeric membranes. Nat Commun 9(1):569. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-02941-6
Wang Y, Yang Q, Wang Z (2015) The evolution of nanopore sequencing, Front Genet 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2014.00449. http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fgene.2014.00449/abstract
Wu W, Walmsley RG, Li W-D, Li X, Williams RS (2012) Nanoimprint lithography with 60 nm overlay precision. Appl Phys A 106(4):767–772. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-012-6775-z
Xia D, Yan J, Hou S (2012) Fabrication of nanofluidic biochips with nanochannels for applications in DNA analysis. Small 8(18):2787–2801. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201200240
Xu Y, Matsumoto N (2015) Flexible and in situ fabrication of nanochannels with high aspect ratios and nanopillar arrays in fused silica substrates utilizing focused ion beam. RSC Adv 5(62):50638–50643. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA06306J
Xu Z, Zhu Z, Li N, Tian Y, Jiang L (2018) Continuous in situ extraction toward multiphase complex systems based on superwettable membrane with micro-/nanostructures. ACS Nano 12(10):10000–10007. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b04328
Yazda K, Tahir S, Michel T, Loubet B, Manghi M, Bentin J, Picaud F, Palmeri J, Henn F, Jourdain V (2017) Voltage-activated transport of ions through single-walled carbon nanotubes. Nanoscale 9(33):11976–11986. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR02976D
Zhang H, Xu Y, Fohlerova Z, Chang H, Iliescu C, Neuzil P (2019) LAMP-on-a-chip: revising microfluidic platforms for loop-mediated DNA amplification. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 113:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.01.015
Zhou J (2011) Controllable fabrication of enclosed micro/nanochannels via polymethyl methacrylate pattern as sacrificial template and capillary effect. J Micro/Nanolithogr MEMS, MOEMS 10(4):049701. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3665215. http://nanolithography.spiedigitallibrary.org/article.aspx?doi=10.1117/1.3665215
Zhu Z, Wang D, Tian Y, Jiang L (2019) Ion/molecule transportation in nanopores and nanochannels: from critical principles to diverse functions. J Am Chem Soc 141(22):8658–8669. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b00086
Acknowledgements
The reported study was funded by RFBR according to the research Project No 19-08-00823 and the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Russia (Project No. 075-15-2019-1896). The development of a technique for measuring the conductivity of ion channels was carried out the financial support of the Russian Science Foundation (Project No. 19-79-00095). The authors also express their gratitude to the resource center of SPBU “Optical and Laser Materials Research” and “Interdisciplinary Resource Centre for Nanotechnology”. A.S. Bukatin and I.S. Mukhin thanks for financial support in the formation of microfluidic chips the Russian Science Foundation (Project No. 20-74-10117).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DL conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing and original draft preparation, visualization, project administration, funding acquisition. GM investigation. IR software, formal analysis, theoretical model. AM resources, sample synthesis. KS resources, sample synthesis. VS AFM investigation. MP writing and original draft preparation. IT supervision. PA investigation. AE methodology, validation. AB validation, review and editing, funding acquisition. IM project administration, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebedev, D., Malyshev, G., Ryzhkov, I. et al. Focused ion beam milling based formation of nanochannels in silicon-glass microfluidic chips for the study of ion transport. Microfluid Nanofluid 25, 51 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-021-02450-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-021-02450-x