Abstract
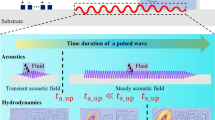
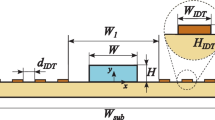
A new computational method was developed to simulate a two-dimensional Eckart acoustic streaming field in an ultrasonic heptagonal chamber actuated by multiple acoustic transducers with different associated frequencies and acoustic incident pressures. Simulation was conducted using the superposition of multiple spatial gradients of the Reynolds stresses and the second mean sound pressures at different frequencies. The developed method extends beyond the capabilities of the conventional method that is restricted to uniform frequency and incident pressure. Various acoustic streaming patterns can be feasibly generated by tuning the frequency and incident pressure of each individual transducer. The implementation of multiple acoustic transducers offers flexibility to control acoustic flows in microfluidic devices for various applications. Furthermore, the developed simulation method for acoustic streaming fields provides an optimization tool for the frequency, incident pressure and location of each transducer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed D, Mao X, Shi J, Juluri BK, Huang TJ (2009) A millisecond micromixer via single-bubble-based acoustic streaming. Lab Chip 9(18):2738–2741
Bernassau AL, Glynne-Jones P, Gesellchen F, Riehle M, Hill M, Cumming DRS (2014) Controlling acoustic streaming in an ultrasonic heptagonal tweezers with application to cell manipulation. Ultrasonics 54(1):268–274
Beyer RT (1965) Nonlinear acoustics. In: Mason WP (ed) Physical acoustics, vol 2B. Academic Press, New York, pp 231–263
Beyer RT (1997) The parameter B/A. In: Hamilton MF, Blackstock DT (eds) Nonlinear acoustics: theory and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 25–39
Boluriaan S, Morris PJ (2003) Acoustic streaming: from Rayleigh to today. Int J Aeroacoust 2(3):255–292
Bruus H, Dual J, Hawkes J, Hill M, Laurell T, Nilsson J, Radel S, Sadhal S, Wiklund M (2011) Forthcoming Lab on a Chip tutorial series on acoustofluidics: acoustofluidics—exploiting ultrasonic standing wave forces and acoustic streaming in microfluidic systems for cell and particle manipulation. Lab Chip 11(21):3579–3580
Collins DJ, Ma Z, Ai Y (2016) Highly localized acoustic streaming and size-selective submicrometer particle concentration using high frequency microscale focused acoustic fields. Anal Chem 88(10):5513–5522
Collins DJ, Ma Z, Han J, Ai Y (2017) Continuous micro-vortex-based nanoparticle manipulation via focused surface acoustic waves. Lab Chip 17(1):91–103
Devendran C, Gralinski I, Nield A (2014) Separation of particles using acoustic streaming and radiation forces in an open microfluidic channel. Microfluidics Nanofluidics 17(5):879–890
Eckart C (1948) Vortices and streams caused by sound waves. Phys Rev 73(1):68–76
Evander M, Nilsson J (2012) Acoustofluidics 20: applications in acoustic trapping. Lab Chip 12(22):4667–4676
Evander M, Johansson L, Lilliehorn T, Piskur J, Lindvall M, Johansson S, Almqvist M, Laurell T, Nilsson J (2007) Noninvasive acoustic cell trapping in a microfluidic perfusion system for online bioassays. Anal Chem 79(7):2984–2991
Freegard T (2012) Introduction to the physics of waves. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gadkari SA, Nayfeh TH (2008) Micro fabrication using electro deposition and ultrasonic acoustic liquid manipulation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39(1):107–117
Gogate PR, Sutkar VS, Pandit AB (2011) Sonochemical reactors: important design and scale up considerations with a special emphasis on heterogeneous systems. Chem Eng J 166(3):1066–1082
Gopi KR, Nagarajan R (2008) Advances in nanoalumina ceramic particle fabrication using sonofragmentation. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol 7(5):532–537
Hahn P (2015) Numerical simulation tools for the design and the analysis of acoustofluidic devices. Dissertation, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zürich
Hahn P, Leibacher I, Baasch T, Dual J (2015) Numerical simulation of acoustofluidic manipulation by radiation forces and acoustic streaming for complex particle. Lab Chip 15(22):4302–4313
Hammarström B, Laurell T, Nilsson J (2012) Seed particle-enabled acoustic trapping of bacteria and nanoparticles in continuous flow systems. Lab Chip 12(21):4296–4304
Hu JH (2014) Ultrasonic micro/nano manipulations. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore
Hu JH, Tay C, Cai YM, Du JL (2005) Controlled rotation of sound-trapped small particles by an acoustic needle. Appl Phys Lett 87(9):094104–094104-3
Kinsler LE, Frey AR, Coppens AB, Sanders JV (1999) Fundamentals of acoustics. Hamilton Press, Te Rapa
Kotas CW, Yoda M, Rogers PH (2008) Steady streaming flows near spheroids oscillated at multiple frequencies. Exp Fluids 45(2):295–307
Laurell T, Peterssona F, Nilssona A (2007) Chip integrated strategies for acoustic separation and manipulation of cells and particles. Chem Soc Rev 36(3):492–506
Lei J, Glynne-Jones P, Hill M (2013) Acoustic streaming in the transducer plane in ultrasonic particle manipulation devices. Lab Chip 13(11):2133–2143
Lighthill J (1978) Acoustic streaming. J Sound Vib 61(3):391–418
Lilliehorn T, Simu U, Nilsson M, Almqvist M, Stepinski T, Laurell T, Nilsson J, Johansson S (2005) Trapping of microparticles in the near field of an ultrasonic transducer. Ultrasonics 43(5):293–303
Liu HL, Hsieh CM (2009) Single-transducer dual-frequency ultrasound generation to enhance acoustic cavitation. Ultrason Sonochem 16(3):431–438
Liu X, Wu J (2009) Acoustic microstreaming around an isolated encapsulated microbubble. J Acoust Soc Am 125(3):1319–1330
Lutz BR, Chen J, Schwartz DT (2006) Hydrodynamic Tweezers: 1. Noncontact trapping of single cells using steady streaming microeddies. Anal Chem 78(15):5429–5435
Martin KH, Lindsey BD, Ma J, Lee M, Li S, Foster FS, Jiang X, Dayton PA (2014) Dual-frequency piezoelectric transducers for contrast enhanced ultrasound imaging. Sensors 14(11):20825–20842
Miles CA, Morley MJ, Hudson WR, Mackey BM (1995) Principles of separating micro-organisms from suspensions using ultrasound. J Appl Microbiol 78(1):47–54
Murry EJ (1971) Multiple frequency ultrasonic method and apparatus for improved cavitation, emulsification and mixing. US Patent, US3614069
Neild A, Oberti S, Radziwill G, Dual J (2007) Simultaneous positioning of cells into two-dimensional arrays using ultrasound. Biotechnol Bioeng 97(5):1335–1339
Nyborg WL (1958) Acoustic streaming near a boundary. J Acoust Soc Am 30(4):329–339
Oberti S, Neild A, Dual J (2007) Manipulation of micrometer sized particles within a micromachined fluidic device to form two-dimensional patterns using ultrasound. J Acoust Soc Am 121(2):778–785
Schwarz T, Hahn P, Petit-Pierre G, Dual J (2015) Rotation of fibers and other non-spherical particles by the acoustic radiation torque. Microfluidics Nanofluidics 18(1):65–79
Shilton RJ, Travagliati M, Beltram F, Cecchini M (2014) Nanoliter-droplet acoustic streaming via ultra high frequency surface acoustic waves. Adv Mater 26(29):4941–4946
Sritharan K, Strobl CJ, Schneider MF, Wixforth A, Guttenberg Z (2006) Acoustic mixing at low Reynold’s numbers. Appl Phys Lett 88(5):054102–054102-3
Suri C, Takenaka K, Yanagida H, Kojima Y, Koyama K (2002) Chaotic mixing generated by acoustic streaming. Ultrasonics 40(1–8):393–396
Tang Q, Hu JH (2015a) Diversity of acoustic streaming in a rectangular acoustofluidic field. Ultrasonics 58:27–34
Tang Q, Hu JH (2015b) Analyses of acoustic streaming field in the probe-liquid-substrate system for nanotrapping. Microfluidics Nanofluidics 19(6):1395–1408
Urban MW, Fatemi M, Greenleaf JF (2010) Modulation of ultrasound to produce multifrequency radiation force. J Acoust Soc Am 127(3):1228–1238
Wiklund M, Green R, Ohlin M (2012) Acoustofluidics 14: applications of acoustic streaming in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 12(14):2438–2451
Wunenburger R, Carrier V, Garrabos Y (2002) Periodic order induced by horizontal vibrations in a two-dimensional assembly of heavy beads in water. Phys Fluids 14(7):2350–2359
Xu L, Neild A, Ng TW, Shao FF (2009) Continuous particle assembly in a capillary cell. Appl Phys Lett 95(15):153501–153501-3
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the State Key Lab of Mechanics and Control of Mechanical Structures (0314G01) in China and National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, Grant No. 2015CB057501).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the topical collection “2016 International Conference of Microfluidics, Nanofluidics and Lab-on-a-Chip, Dalian, China” guest edited by Chun Yang, Carolyn Ren and Xiangchun Xuan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Q., Hu, J., Qian, S. et al. Eckart acoustic streaming in a heptagonal chamber by multiple acoustic transducers. Microfluid Nanofluid 21, 28 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1871-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1871-1