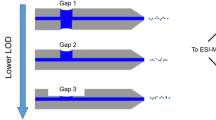
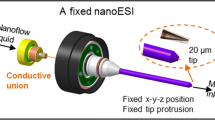
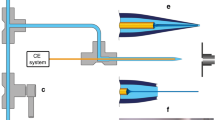
Abstract
In this work we shed light on the microfluidics of a miniaturized liquid bridge that forms the central part of a so-called “capillary gap sampler,” a novel device for rapid and seamless injection of nanoliter sample volumes into an electrospray ionization mass spectrometer (ESI-MS). Parameters relevant for sample flush-out at the liquid bridge and in the spray capillary were identified by systematic variation of the capillary dimensions, the linear buffer flow rate (2.1–34 mm/s) and molecular weight of the analytes (0.5–30 kDa). We found that a reduction in capillary wall thickness by a factor of 1.6 significantly influences analyte peak shapes, leads to an inversion of the relationship between peak width and analyte molecular weight, and allows a fivefold decrease in peak width for large molecules down to 5 s. The results could be verified and explained by simulations, in which the presence of diffusion-controlled “dead zones” at the liquid bridge and dispersion in the spray tip that depend on analyte molecular weight were identified as key factors relevant for the sample flush-out process. The merging of simulations and experimental data gives useful hints toward the re-design of a spray tip as built-in ESI-MS interface for an optimized gap sampler performance.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aris R (1956) On the dispersion of a solute in a fluid flowing through a tube. Proc R Soc Lond A 235:67–77. doi:10.1098/rspa.1956.0065
Choi J, Terazima M (2002) Denaturation of a protein monitored by diffusion coefficients: myoglobin. J Phys Chem B 106:6587–6593. doi:10.1021/jp0256802
Feng X, Liu X, Luo Q, Liu B-F (2008) Mass spectrometry in systems biology: an overview. Mass Spectrom Rev 27:635–660. doi:10.1002/mas.20182
Feng X, Liu B-F, Li J, Liu X (2014) Advances in coupling microfluidic chips to mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Rev 34:535–557. doi:10.1002/mas.21417
Gao D, Liu H, Jiang Y, Lin J-M (2013) Recent advances in microfluidics combined with mass spectrometry: technologies and applications. Lab Chip 13:3309–3322. doi:10.1039/c3lc50449b
Gasilova N, Yu Q, Qiao L, Girault HH (2014) On-chip spyhole mass spectrometry for droplet based microfluidics. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53:4408–4412. doi:10.1002/anie.201310795
Gerhardt G (2011) Microfluidics-based separations technology for the analytical laboratory. Chromatogr Today 4:6–8
Gerhardt G, Adams RN (1982) Determination of diffusion coefficients by flow injection analysis. Anal Chem 54:2618–2620. doi:10.1021/ac00251a054
Jian W, Romm MV, Edom RW, Miller VP, LaMarr WA, Weng N (2011) Evaluation of a high-throughput online solid phase extraction–tandem mass spectrometry system for in vivo bioanalytical studies. Anal Chem 83:8259–8266. doi:10.1021/ac202017c
Jin D-Q, Zhu Y, Fang Q (2014) Swan probe: a nanoliter-scale and high-throughput sampling interface for coupling electrospray ionization mass spectrometry with microfluidic droplet array and multiwell plate. Anal Chem 86:10796–10803. doi:10.1021/ac503014k
Koster S, Verpoorte E (2007) A decade of microfluidic analysis coupled with electrospray mass spectrometry: an overview. Lab Chip 7:1394–1412. doi:10.1039/B709706A
Mayr LM, Bojanic D (2009) Novel trends in high-throughput screening. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:580–588. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2009.08.004
Neu V, Steiner R, Müller S, Fattinger C, Zenobi R (2013) Development and characterization of a capillary gap sampler as new microfluidic device for fast and direct analysis of low sample amounts by ESI-MS. Anal Chem 85:4628–4635. doi:10.1021/ac400186t
Nge PN, Rogers CI, Woolley AT (2013) Advances in microfluidic materials, functions, integration, and applications. Chem Rev 113:2550–2583. doi:10.1021/cr300337x
O’Brien JT, Williams ER, Holman H-YN (2015) Ambient infrared laser ablation mass spectrometry (AIRLAB-MS) of live plant tissue with plume capture by continuous flow solvent probe. Anal Chem 87:2631–2638. doi:10.1021/ac503383p
Oh KW, Ahn CH (2006) A review of microvalves. J Micromech Microeng 16:R13–R39. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/16/5/R01
Ohla S, Belder D (2012) Chip-based separation devices coupled to mass spectrometry. Curr Opin Chem Biol 16:453–459. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2012.05.180
Ovchinnikova OS, Kertesz V, Van Berkel GJ (2011) Combining laser ablation/liquid phase collection surface sampling and high-performance liquid chromatography—electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 83:1874–1878. doi:10.1021/ac200051y
Park S-G, Murray KK (2012) Infrared laser ablation sample transfer for on-line liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 47:1322–1326. doi:10.1002/jms.3096
Pei J, Li Q, Kennedy RT (2010) Rapid and label-free screening of enzyme inhibitors using segmented flow electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 21:1107–1113. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2010.02.013
Riveros-Moreno V, Wittenberg JB (1972) The self-diffusion coefficients of myoglobin and hemoglobin in concentrated solutions. J Biol Chem 47:895–901
Roach PJ, Laskin J, Laskin A (2010) Nanospray desorption electrospray ionization: an ambient method for liquid-extraction surface sampling in mass spectrometry. Analyst 135:2233–2236. doi:10.1039/c0an00312c
Růžička J (1992) The second coming of flow-injection analysis. Anal Chim Acta 261:3–10. doi:10.1016/0003-2670(92)80169-8
Sun S, Slaney TR, Kennedy RT (2012) Label free screening of enzyme inhibitors at femtomole scale using segmented flow electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 84:5794–5800. doi:10.1021/ac3011389
Van Berkel GJ, Kertesz V (2015) An open port sampling interface for liquid introduction atmospheric pressure ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 29:1749–1756. doi:10.1002/rcm.7274
Van Berkel GJ, Kertesz V, King RC (2009) High-throughput mode liquid microjunction surface sampling probe. Anal Chem 81:7096–7101. doi:10.1021/ac901098d
Volný M, Rolfs J, Hakimi B, Fryčák P, Schneider T, Liu D, Yen G, Chiu DT, Tureček F (2014) Nanoliter segmented-flow sampling mass spectrometry with online compartmentalization. Anal Chem 86:3647–3652. doi:10.1021/ac500365r
Wissler EH (1969) On the applicability of the Taylor–Aris axial diffusion model to tubular reactor calculations. Chem Eng Sci 24:527–539. doi:10.1016/0009-2509(69)85024-4
Yin H, Killeen K, Brennen R, Sobek D, Werlich M, van de Goor T (2005) Microfluidic chip for peptide analysis with an integrated HPLC column, sample enrichment column, and nanoelectrospray tip. Anal Chem 77:527–533. doi:10.1021/ac049068d
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Janos Vörös for fruitful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neu, V., Dörig, P., Fattinger, C. et al. Characterization of a miniaturized liquid bridge for nL sample infusion: a comparative study of sample flush-out behavior using flow simulations and direct ESI-MS analysis. Microfluid Nanofluid 20, 62 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1732-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1732-3