Abstract
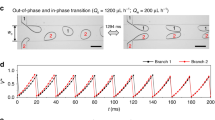
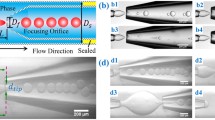
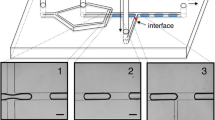
We quantitatively characterize the perturbed droplet generation in co-flow microfluidics with mechanical vibration by estimating the fluctuations in the flow rate of inner fluid. We show the variation of generation frequency and uniformity of droplets as the frequency and amplitude of vibration. Synchronized droplet generation occurs in certain range of the vibration frequency that is predicted by our model. Besides, we scale the droplet size by incorporating the effects of vibration, inner and outer flows. The vibration is found to be capable of promoting the dripping, suppressing the jetting and even shifting the jetting into the dripping when the jet length is sufficiently short. The delayed dripping–jetting transition is characterized in a phase diagram by taking vibration into consideration. Our results unveil the mechanism of mechanically perturbed droplet generation and provide valuable guidelines for practical applications of vibration-enhanced droplet generation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abate AR, Weitz DA (2008) Single-layer membrane valves for elastomeric microfluidic devices. Appl Phys Lett 92:243509
Abate AR, Romanowsky MB, Agresti JJ, Weitz DA (2009) Valve-based flow focusing for drop formation. Appl Phys Lett 94:023503
Anna SL, Mayer HC (2006) Microscale tipstreaming in a microfluidic flow focusing device. Phys Fluids 18:121512
Anna SL, Bontoux N, Stone HA (2003) Formation of dispersions using “flow focusing” in microchannels. Appl Phys Lett 82:364
Augustin MA, Hemar Y (2009) Nano-and micro-structured assemblies for encapsulation of food ingredients. Chem Soc Rev 38:902–912
Batchelor G (1967) An introduction to fluid dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Chan HF, Zhang Y, Ho Y-P, Chiu Y-L, Jung Y, Leong KW (2013) Rapid formation of multicellular spheroids in double-emulsion droplets with controllable microenvironment. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep03462
Chong ZZ, Tor SB, Loh NH, Wong TN, Gañán-Calvo AM, Tan SH, Nguyen N-T (2015) Acoustofluidic control of bubble size in microfluidic flow-focusing configuration. Lab Chip 15:996–999
Christopher G, Anna S (2007) Microfluidic methods for generating continuous droplet streams. J Phys D Appl Phys 40:R319–R336
Collins DJ, Neild A, deMello A, Liu A-Q, Ai Y (2015) The Poisson distribution and beyond: methods for microfluidic droplet production and single cell encapsulation. Lab Chip 15:3439–3459
deMello AJ (2006) Control and detection of chemical reactions in microfluidic systems. Nature 442:394–402
Ding Y, i Solvas XC, deMello A (2015) “V-junction”: a novel structure for high-speed generation of bespoke droplet flows. Analyst 140:414–421
Dittrich PS, Manz A (2006) Lab-on-a-chip: microfluidics in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:210–218
Driessen T, Sleutel P, Dijksman F, Jeurissen R, Lohse D (2014) Control of jet breakup by a superposition of two Rayleigh–Plateau-unstable modes. J Fluid Mech 749:275–296
Erb RM, Obrist D, Chen PW, Studer J, Studart AR (2011) Predicting sizes of droplets made by microfluidic flow-induced dripping. Soft Matter 7:8757–8761
Evans HM, Surenjav E, Priest C, Herminghaus S, Seemann R, Pfohl T (2009) In situ formation, manipulation, and imaging of droplet-encapsulated fibrin networks. Lab Chip 9:1933–1941
Fan J, Zhang YX, Wang LQ (2010) Formation of nanoliter bubbles in microfluidic T-junctions. NANO 5:175–184
García F, González H, Castrejón-Pita J, Castrejón-Pita A (2014) The breakup length of harmonically stimulated capillary jets. Appl Phys Lett 105:094104
Garstecki P, Gitlin I, DiLuzio W, Whitesides GM, Kumacheva E, Stone HA (2004) Formation of monodisperse bubbles in a microfluidic flow-focusing device. Appl Phys Lett 85:2649–2651
Guillot P, Colin A, Utada AS, Ajdari A (2007) Stability of a jet in confined pressure-driven biphasic flows at low Reynolds numbers. Phys Rev Lett 99:104502
Guillot P, Colin A, Ajdari A (2008) Stability of a jet in confined pressure-driven biphasic flows at low Reynolds number in various geometries. Phys Rev E 78:016307
Haber C (2006) Microfluidics in commercial applications; an industry perspective. Lab Chip 6:1118–1121
Hong J, Choi M, Edel JB, deMello AJ (2010) Passive self-synchronized two-droplet generation. Lab Chip 10:2702–2709
Khan IU, Stolch L, Serra CA, Anton N, Akasov R, Vandamme TF (2015) Microfluidic conceived pH sensitive core–shell particles for dual drug delivery. Int J Pharm 478:78–87
Khoshmanesh K, Almansouri A, Albloushi H, Yi P, Soffe R, Kalantar-zadeh K (2015) A multi-functional bubble-based microfluidic system. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep09942
Kim SH, Shim JW, Yang SM (2011) Microfluidic multicolor encoding of microspheres with nanoscopic surface complexity for multiplex immunoassays. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:1171–1174
Kim JH, Jeon TY, Choi TM, Shim TS, Kim S-H, Yang S-M (2013) Droplet microfluidics for producing functional microparticles. Langmuir 30:1473–1488
Kobayashi I, Nakajima M, Nabetani H, Kikuchi Y, Shohno A, Satoh K (2001) Preparation of micron-scale monodisperse oil-in-water microspheres by microchannel emulsification. J Am Oil Chem Soc 78:797–802
Kong TT, Liu Z, Song Y, Wang LQ, Shum HC (2013) Engineering polymeric composite particles by emulsion-templating: thermodynamics versus kinetics. Soft Matter 9:9780–9784
Kong TT, Wang LQ, Wyss HM, Shum HC (2014) Capillary micromechanics for core–shell particles. Soft Matter 10:3271–3276
Lee W, Walker LM, Anna SL (2009) Role of geometry and fluid properties in droplet and thread formation processes in planar flow focusing. Phys Fluids 21:032103
Li J, Mittal N, Mak SY, Song Y, Shum HC (2015) Perturbation-induced droplets for manipulating droplet structure and configuration in microfluidics. J Micromech Microeng 25:084009
Meier G, Klöpper A, Grabitz G (1992) The influence of kinematic waves on jet break down. Exp Fluids 12:173–180
Moon B-U, Jones SG, Hwang DK, Tsai SSH (2015) Microfluidic generation of aqueous two-phase system (ATPS) droplets by controlled pulsating inlet pressures. Lab Chip 15:2437–2444
Nakano M, Komatsu J, Matsuura S-i, Takashima K, Katsura S, Mizuno A (2003) Single-molecule PCR using water-in-oil emulsion. J Biotechnol 102:117–124
Nguyen N-T et al (2007) Thermally mediated droplet formation in microchannels. Appl Phys Lett 91:084102
Patravale VB, Mandawgade SD (2008) Novel cosmetic delivery systems: an application update. Int J Cosmet Sci 30:19–33
Sauret A, Shum HC (2012) Forced generation of simple and double emulsions in all-aqueous systems. Appl Phys Lett 100:154106
Sauret A, Spandagos C, Shum HC (2012) Fluctuation-induced dynamics of multiphase liquid jets with ultra-low interfacial tension. Lab Chip 12:3380–3386
Schmid L, Franke T (2013) SAW-controlled drop size for flow focusing. Lab Chip 13:1691–1694
Schmid L, Franke T (2014) Acoustic modulation of droplet size in a T-junction. Appl Phys Lett 104:133501
Song H, Chen DL, Ismagilov RF (2006) Reactions in droplets in microfluidic channels. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:7336–7356
Stone HA, Stroock AD, Ajdari A (2004) Engineering flows in small devices: microfluidics toward a lab-on-a-chip. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 36:381–411
Sugiura S, Nakajima M, Seki M (2002) Prediction of droplet diameter for microchannel emulsification. Langmuir 18:3854–3859
Tan SH, Maes F, Semin B, Vrignon J, Baret J-C (2014a) The microfluidic jukebox. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep04787
Tan SH, Semin B, Baret J-C (2014b) Microfluidic flow-focusing in ac electric fields. Lab Chip 14:1099–1106
Umbanhowar PB, Prasad V, Weitz DA (2000) Monodisperse emulsion generation via drop break off in a coflowing stream. Langmuir 16:347–351
Utada AS, Fernandez-Nieves A, Stone HA, Weitz DA (2007) Dripping to jetting transitions in coflowing liquid streams. Phys Rev Lett 99:094502
Wang LQ, Zhang YX, Cheng L (2009) Magic microfluidic T-junctions: valving and bubbling. Chaos Soliton Fractals 39:1530–1537
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368–373
Zhang YX, Wang LQ (2011) Nanoliter-droplet breakup in confined T-shaped junctions. Curr Nanosci 7:471–479
Zhang YX, Jiang W, Wang LQ (2010) Microfluidic synthesis of copper nanofluids. Microfluid Nanofluid 9:727–735
Zhao C-X (2013) Multiphase flow microfluidics for the production of single or multiple emulsions for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 65:1420–1446
Zhou H, Yao S (2014) A facile on-demand droplet microfluidic system for lab-on-a-chip applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 16:667–675
Zhu PA, Kong TT, Kang ZX, Tian XW, Wang LQ (2015) Tip-multi-breaking in capillary microfluidic devices. Sci Rep. doi:10.1038/srep11102
Ziemecka I, van Steijn V, Koper GJM, Rosso M, Brizard AM, van Esch JH, Kreutzer MT (2011) Monodisperse hydrogel microspheres by forced droplet formation in aqueous two-phase systems. Lab Chip 11:620–624
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Ho Cheung Shum for the generous use of mechanical vibrator. The financial support from the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (GRF 17211115, GRF17207914, GRF HKU717613E, GRF HKU718111E) and the University of Hong Kong (URC 201511159108, 201411159074 and 201311159187) is gratefully acknowledged. The work is also supported in part by the Zhejiang Provincial, Hangzhou Municipal and Lin’an County Governments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MOV 966 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (MOV 1136 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (MOV 1335 kb)
Supplementary material 4 (MOV 777 kb)
Supplementary material 5 (MOV 1700 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, P., Tang, X. & Wang, L. Droplet generation in co-flow microfluidic channels with vibration. Microfluid Nanofluid 20, 47 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1717-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1717-2