Abstract
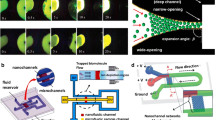
This paper presents a Nafion-film-based micro–nanofluidic device for concurrent DNA preconcentration and separation. The principle of the device is based on the combination of (a) ion concentration polarization phenomenon at the junction of the microchannel and the nanochannels in the Nafion film to form opposing electrophoretic and electroosmotic forces acting on the DNAs and (b) end-labeled-free solution electrophoresis to harness the charge-to-mass ratio for molecular differentiation. The experiments successfully demonstrated concurrent preconcentration and separation of DNA mixture in free solution within 240 s, yielding concentration ratios up to 1,150× and separation resolution of 1.85. The effect of applied electric field on the concentration and separation performance was also investigated. The device can be used as a key sample preparation element in conjunction with micro- or nano-fluidic sensors for microTAS functionality.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abgrall P, Nguyen NT (2008) Nanofluidic devices and their applications. Anal Chem 80(7):2326–2341
Auroux P-A, Iossifidis D, Reyes DR, Manz A (2002) Micro total analysis systems. 2. Analytical standard operations and applications. Anal Chem 74(12):2637–2652
Buel E, LaFountain M, Schwartz M, Walkinshaw M (2001) Evaluation of capillary electrophoresis performance through resolution measurements. J Forensic Sci 46(2):341–345
Cheow LF, Ko SH, Kim SJ, Kang KH, Han J (2010) Increasing the sensitivity of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using multiplexed electrokinetic concentrator. Anal Chem 82(8):3383–3388
Dhopeshwarkar R, Sun L, Crooks RM (2005) Electrokinetic concentration enrichment within a microfluidic device using a hydrogel microplug. Lab Chip 5(10):1148–1154
Haynes RD, Meagher RJ, Won J-I, Bogdan FM, Barron AE (2005) Comblike, monodisperse polypeptoid drag-tags for DNA separations by end-labeled free-solution electrophoresis (ELFSE). Bioconjugte Chem 16(4):929–938
Kim T, Meyhöfer E (2008) Nanofluidic concentration of selectively extracted biomolecule analytes by microtubules. Anal Chem 80(14):5383–5390
Lee JH, Song Y-A, Han J (2008a) Multiplexed proteomic sample preconcentration device using surface-patterned ion-selective membrane. Lab Chip 8(4):596–601
Lee JH, Song Y-A, Tannenbaum SR, Han J (2008b) Increase of reaction rate and sensitivity of low-abundance enzyme assay using micro/nanofluidic preconcentration chip. Anal Chem 80(9):3198–3204
Mani A, Zangle TA, Santiago JG (2009) On the propagation of concentration polarization from microchannel− nanochannel interfaces part I: analytical model and characteristic analysis. Langmuir 25(6):3898–3908
Mayer P, Slater GW, Drouin G (1994) Theory of DNA sequencing using free-solution electrophoresis of protein-DNA complexes. Anal Chem 66(10):1777–1780
Meagher RJ, Thaitrong N (2012) Microchip electrophoresis of DNA following preconcentration at photopatterned gel membranes. Electrophoresis 33(8):1236–1246
Meagher RJ, Won JI, McCormick LC, Nedelcu S, Bertrand MM, Bertram JL, Drouin G, Barron AE, Slater GW (2005) End-labeled free-solution electrophoresis of DNA. Electrophoresis 26(2):331–350
Meagher RJ, Won J-I, Coyne JA, Lin J, Barron AE (2008) Sequencing of DNA by free-solution capillary electrophoresis using a genetically engineered protein polymer drag-tag. Anal Chem 80(8):2842–2848
Plecis A, Schoch RB, Renaud P (2005) Ionic transport phenomena in nanofluidics: experimental and theoretical study of the exclusion-enrichment effect on a chip. Nano Lett 5(6):1147–1155
Prakash S, Piruska A, Gatimu EN, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV, Shannon MA (2008) Nanofluidics: systems and applications. IEEE Sens J 8(5):441–450
Ren H, Karger AE, Oaks F, Menchen S, Slater GW, Drouin G (1999) Separating DNA sequencing fragments without a sieving matrix. Electrophoresis 20(12):2501–2509
Reyes DR, Iossifidis D, Auroux P-A, Manz A (2002) Micro total analysis systems. 1. Introduction, theory, and technology. Anal Chem 74(12):2623–2636
Shen M, Yang H, Sivagnanam V, Gijs MAM (2010) Microfluidic protein preconcentrator using a microchannel-integrated Nafion strip: experiment and modeling. Anal Chem 82(24):9989–9997
Sparreboom W, Van Den Berg A, Eijkel JCT (2009) Principles and applications of nanofluidic transport. Nat Nanotechnol 4(11):713–720
Wang Y-C, Han J (2008) Pre-binding dynamic range and sensitivity enhancement for immuno-sensors using nanofluidic preconcentrator. Lab Chip 8(3):392–394
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442(7101):368–373
Won J-I, Meagher RJ, Barron AE (2005) Protein polymer drag-tags for DNA separations by end-labeled free-solution electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 26(11):2138–2148
Xia Y, Whitesides GM (1998) Soft lithography. Annu Rev Mater Sci 28(1):153–184
Zangle TA, Mani A, Santiago JG (2009) On the propagation of concentration polarization from microchannel− nanochannel interfaces part II: numerical and experimental study. Langmuir 25(6):3909–3916
Zangle TA, Mani A, Santiago JG (2010) Theory and experiments of concentration polarization and ion focusing at microchannel and nanochannel interfaces. Chem Soc Rev 39(3):1014–1035
Acknowledgments
This research is sponsored by NIH/NHGRI under grant number 5R44HG004290-03. We would like to thank Prof. Jongyoon Han of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, and Biological Engineering at Massachusetts Institute of Technology for guidance on the project and Prof. James W. Schneider of Chemical Engineering at Carnegie Mellon University for help discussion about the ELFSE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, H., Wang, Y., Garson, C. et al. Nafion-film-based micro–nanofluidic device for concurrent DNA preconcentration and separation in free solution. Microfluid Nanofluid 17, 693–699 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1357-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1357-3