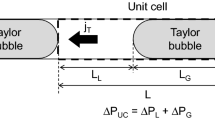
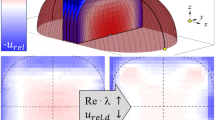
Abstract
The effect of fluid properties and operating conditions on the generation of gas–liquid Taylor flow in microchannels has been investigated experimentally and numerically. Visualisation experiments and 2D numerical simulations have been performed to study bubble and slug lengths, liquid film hold-up and bubble velocities. The results show that the bubble and slug lengths increase as a function of the gas and liquid flow rate ratios. The bubble and slug lengths follow the model developed by Garstecki et al. (Lab chip 6:437–446, 2006) and van Steijn et al. (Chem Eng Sci 62:7505–7514, 2007), however, the model coefficients appear to be dependent on the liquid properties and flow conditions in some cases. The ratio of the bubble velocity to superficial two-phase velocity is close to unity, which confirms a thin liquid film under the assumption of a stagnant liquid film. Numerical simulations confirm the hypothesis of a stagnant liquid film and provide information on the thickness of the liquid film.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A :
-
Cross-section area (m2)
- C :
-
Color function (VOF) (−)
- d :
-
Diameter (m)
- f :
-
Break-up frequency (s−1)
- \(\mathbf{F_\sigma}\) :
-
Capillary force (Pa/m)
- k :
-
Constant (−)
- \(l_{1,\infty}\) :
-
norms in the spurious currents evaluation (m/s)
- L :
-
Length (m)
- m :
-
Constant (−)
- \(\mathbf{n}\) :
-
Normal to the interface (−)
- P :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- Q :
-
Flow rate (m3/s)
- r :
-
Radius (m)
- U :
-
Velocity (m/s)
- W :
-
Dimensionless velocity (−)
- w :
-
Width (m)
- x, y :
-
Axis in 2D simulations (−)
- α:
-
Volume fraction (−)
- β1,2 :
-
Constant (−)
- δ:
-
Liquid film thickness (m)
- δ I :
-
Dirac distribution (interface) (−)
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Fraction of area (−)
- λ1,2 :
-
Constant (−)
- μ:
-
Dynamic viscosity (Pa . s)
- ρ:
-
Density (kg/m3)
- σ:
-
Surface tension (N/m)
- \(\varvec{\Upsigma}\) :
-
Viscous stress tensor (Pa)
- B:
-
Bubble
- ch:
-
Channel
- G:
-
Gas phase (air)
- h:
-
Hydraulic
- in:
-
Gas inlet
- L:
-
Liquid phase
- S:
-
Slug
- SC:
-
Spurious currents
- TP:
-
Two-phase
- Bo TP :
-
Bond number \( Bo \;=\; {\frac{(\rho_{\rm{L}} - \rho_{\rm{G}}) d_{\rm h}^2 g}{\sigma}} \)
- Ca TP :
-
Capillary number \( Ca \;=\; {\frac{\mu_{\rm L} U_{\rm TP}} {\sigma}} \)
- Re TP :
-
Reynolds number \( Re \;=\; {\frac{\rho_{\rm L} U_{\rm TP} d_{\rm h}}{\mu_{\rm L}}} \)
- We TP :
-
Weber number \( We \;=\; {\frac{\rho_{\rm L} U_{\rm TP}^2 d_{\rm h}}{\sigma}} \)
References
Akbar MK, Plummer DA, Ghiaasiaan SM (2003) On gas–liquid two-phase flow regimes in microchannels. Int J Multiph Flow 29:855–865
Aussillous P, Quéré D (2000) Quick deposition of a fluid on the wall of a tube. Phys Fluids 12(10):2367
Bonometti T, Magnaudet J (2007) An interface-capturing method for incompressible two-phase flows. Validation and application to bubble dynamics. Int J Multiph Flow 33:109–133
Brackbill J, Kothe DB, Zemach C (1992) A continuum method for modeling surface tension. J Comput Phys 100:335–354
Bretherton FP (1961) The motion of long bubbles in tubes. J Fluid Mech 10:166
de Lózar A, Juel A, Hazel AL (2008) The steady propagation of an air finger into a rectangular tube. J Fluid Mech 614:173–195
De Menech M, Garstecki P, Jousse F, Stone HA (2008) Transition from squeezing to dripping in a microfluidic T-shaped junction. J Fluid Mech 595:141–161
Dupont J-B, Legendre D (2010) Numerical simulation of static and sliding drop with contact angle hysteresis. J Comput Phys 229:2453–2478
Fouilland TS, Fletcher DF, Haynes BS (2010) Film and slug behaviour in intermittent slugannular microchannel flows. Chem Eng Sci 65:5344–5355
Francois MM, Cummins SJ, Dendy ED, Kothe DB, Sicilian JM, Williams MW (2006) A balanced-force algorithm for continuous and sharp interfacial surface tension models within a volume tracking framework. J Comput Phys 213:141–173
Garstecki P, Fuerstman MJ, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2006) Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction—scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab chip 6:437–446
Giavedoni MD, Saita FA (1997) The axisymmetric and plane cases of a gas phase steadily displacing a Newtonian liquid—a simultaneous solution of the governing equations. Phys Fluids 9(8):2428
Guillot P, Colin A (2005) Stability of parallel flows in a microchannel after a T junction. Phys Rev E 72:066301
Gupta A, Kumar R (2010) effect of geometry on droplet formation in the squeezing regime in a microfluidics T-junction. Microfluid Nanofluid 8:799–812
Gupta R, Fletcher DF, Haynes BS (2009) On the CFD modelling of Taylor flow in microchannels. Chem Eng Sci 64:2941–2950
Gupta R, Fletcher DF, Haynes BS (2010) CFD modelling of heat and mass transfer in the Taylor flow regime. Chem Eng Sci 65:2094–2107
Han Y, Shikazono N (2009a) Measurement of the liquid film thickness in micro tube slug flow. Int J Heat Fluid Fl 35:842–853
Han Y, Shikazono N (2009b) Measurement of the liquid film thickness in micro square channel. Int J Multiph Flow 30:896–903
Haverkamp V, Ehrfeld W, Gebauer K, Hessel V, Lowe H, Richter T, Wille C (1999) The potential of micromixers for contacting of disperse liquid phases. Fresen J Anal Chem 364:617–624
Hazel AL, Heil M (2002) The steady propagation of a semi infinite bubble into a tube of elliptical or rectangular cross-section. J Fluid Mech 470:91–114
Kreutzer MT, Kapteijn F, Moulijn JA, Heiszwolf JJ (2005a) Multiphase monolith reactors: chemical reaction engineering of segmented flow in microchannels. Chem Eng Sci 60:5895–5916
Kreutzer MT, Kapteijn F, Moulijn JA, Heiszwolf JJ (2005b) Inertial and interfacial effects on pressure drop of Taylor flow in capillaries. AIChE J 51:2428–2440
Lafaurie B, Nardone C, Scardovelli R, Zaleski S, Zanetti G (1994) Modelling merging and fragmentation in multiphase flow with SURFER. J Comput Phys 113:134–147
Leclerc A, Philippe R, Houzelot V, Schweich D, de Bellefon C (2010) Gas–liquid Taylor flow in square microchannels: New inlet geometries and interfacial area tuning. Chem Eng J 165:290–300
Leung SSY, Liu Y, Fletcher DF, Haynes BS (2010) Heat transfer in well-characterised Taylor flow. Chem Eng Sci. doi:10.1016/j.ces.2010.09.014
Liu D, Wang S (2008) Hydrodynamics of Taylor flow in noncircular capillaries. Chem Eng Process 47:2098–2106
Pohorecki R, Kula K (2008) A simple mechanism of bubble and slug formation in Taylor flow in microchannels. Chem Eng Res Des 86:997–1001
Qian D, Lawal A (2006) Numerical study on gas and liquid slugs for Taylor flow in a T-junction microchannel. Chem Eng Sci 61:7609–7625
Renardy Y, Renardy M (2002) PROST: a parabolic reconstruction of surface tension for the volume-of-fluid method. J Comput Phys 183:400–421
Sarrazin F, Bonometti T, Loubière K, Prat L, Gourdon C, Magnaudet J (2006) Experimental and numerical study of droplets hydrodynamics in microchannels. AIChE J 52:4061–4070
Scardovelli R, Zaleski S (1999) Direct numerical simulation of free-surface and interfacial flow. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 31:567–303
Sobieszuk P, Cyganski P, Pohorecki R (2008) Volumetric liquid side mass transfer coefficient in a gas–liquid microreactor. Chem Process Eng 29:651–661
van Steijn V, Kreutzer MT, Kleijn CR (2007) μ-PIV study of the formation of segmented flow in microfluidic T-junction. Chem Eng Sci 62:7505–7514
Taha T, Cui ZF (2006) CFD modelling of slug flow inside square capillaries. Chem Eng Sci 61:665–675
Taylor GI (1961) Deposition of a viscous fluid on the wall of a tube. J Fluid Mech 10:161–165
Triplett KA, Ghiaasiaan SM, Abdel-Khalik SI, Sadowsli DL (1999) Gas–liquid two-phase flow in microchannels. Part i: two-phase flow patterns. Int J Multiph Flow 25:377–394
Völkel N (2009) Design and characterization of gas–liquid microreactors, PhD Thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse, France
Waelchli S, von Rohr PR (2006) Two-phase flow characteristics in gas–liquid microreactors. Int J Multiph Flow 32:791–806
Wong H, Radke CJ, Morris S (1995) The motion of long bubbles in polygonal capillaries Part 1:Thin films. J Fluid Mech 292:71–94
Yue J, Chen G, Yuan Q, Luo L, Gonthier Y (2007) Hydrodynamics and mass transfer characteristics in gas–liquid flow through a rectangular microchannel. Chem Eng Sci 62:2096–2108
Yue J, Luo L, Gonthier Y, Chen G, Yuan Q (2008) An experimental investigation of gas–liquid two-phase flow in single microchannel contactors. Chem Eng Sci 63:4189–4202
Yun J, Lei Q, Zhang S, Shen S, Yao K (2010) Slug flow characteristics of gas-miscible liquids in a rectangular microchannel with cross and T-shaped junctions. Chem Eng Sci 65:5256–5263
Acknowledgments
This work was financed by the French “Agence Nationale de la Recherche” in the framework of the project MIGALI no. ANR-09-BLAN-0381-01. We also acknowledge the support for this project from the CNRS research federation FERMaT, such as the CALMIP project for providing computational resources.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abadie, T., Aubin, J., Legendre, D. et al. Hydrodynamics of gas–liquid Taylor flow in rectangular microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 12, 355–369 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0880-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0880-8