Abstract
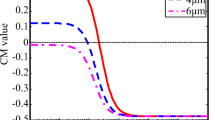
The dynamics of DNA molecules in highly confined nanoslits under varying electric fields are studied using dissipative particle dynamics method, and our results show that manipulation of the electrical field can strongly influence DNA mobility. The mobility of DNA μ scales with electric field E as \( \mu = \mu^{\text{H}} - k_{1} e^{{ - E/E_{c} }} . \) And the data points for different DNA lengths finally approach each other in strong fields, which suggest that the sensitivity to chain length is almost lost. To explain the unusual field-dependent phenomena, we analyze the time evolution of DNA configurations under different fields. For strong driving potentials when the system is dominated by the electric driving force, the DNA chains are more likely to hold coiled configurations. For weak driving potential when the random diffusion forces dominate, we see frequent dynamic transitions between stretched and coiled configuration, which may increase the drag resistance, therefore reduce the mobility.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abgrall P, Nguyen NT (2008) Nanofluidic devices and their applications. Anal Chem 80:2326–2341
Baldessari F, Santiago JG (2006) Electrophoresis in nanochannels: brief review and speculation. J Nanobiotechnol 4:12
Balducci A, Mao P, Han J, Doyle PS (2006) Double-stranded DNA diffusion in slitlike nanochannels. Macromolecules 39:6273–6281
Brahmassandra SN, Durke DT, Mastrangelo CH, Burns MA (2001) Mobility, diffusion and dispersion of single-stranded DNA in sequencing gels. Electrophoresis 22:1046–1062
Chu B, Wang Z (1991) DNA electrophoretic mobility and deformation in agarose gels. J Non Cryst Solids 131:685–692
Cross JD, Strychalski EA, Craighead HG (2007) Size-dependent DNA mobility in nanochannels. J Appl Phys 102:024701
Duong-Hong D, Wang J, Liu GR et al (2008a) Dissipative particle dynamics simulations of electroosmotic flow in nano-fluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:219–225
Duong-Hong D, Han J, Wang J et al (2008b) Realistic simulation of combined DNA electrophoretic flow and EOF in nano-fluidic devices. Electrophoresis 29:4880–4886
Eijkel JCT, van den Berg A (2004) Nanofluidics: what is it and what can we expect from it? Microfluid Nanofluid 1:249–267
Fu J, Yoo J, Han J (2006) Molecular sieving in periodic free-energy landscapes created by patterned nanofilter arrays. Phys Rev Lett 97:018103.1
Fu J, Schoch RB, Stevens AL et al (2007) A patterned anisotropic nanofluidic sieving structure for continuous-flow separation of DNA and proteins. Nat Nanotechnol 2:121–128
Groot RD, Warren PB (1997) Dissipative particle dynamics: bridging the gap between atomistic and mesoscopic simulation. J Chem Phys 107:4423–4435
Han J, Craighead HG (2000) Separation of long DNA molecules in a microfabricated entropic trap array. Science 288:1026–1029
Han J, Turner SW, Craighead HG (1999) Entropic trapping and escape of long DNA molecules at submicron size constriction. Phys Rev Lett 83:1688–1691
Hoogerbrugge PJ, Koelman JMVA (1992) Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics. Europhys Lett 19:155
Hunter RJ (1981) Zeta potential in colloid science: principles and applications. Academic, New York
Jo K, Dhingra DM, Odijk T, Pablo J, Graham MD et al (2007) A single-molecule barcoding system using nanoslits for DNA analysis. PNAS 104:2673–2678
Kasiteropoulou D, Karakasidis TE, Liakopoulos A (2011) Dissipative particle dynamics investigation of parameters affecting planar nanochannel flows. Mater Sci Eng B. doi:10.1016/j.mseb.2011.01.023
Kumar A, Asako Y, Abu-Nada E, Krafczyk M, Faghri M (2009) From dissipative particle dynamics scales to physical scales: a coarse-graining study for water flow in microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:467–477
Lumpkin J, Dejardin P, Zimm BH (1985) Theory of gel electrophoresis of DNA. Biopolymers 24:1573–1593
Meller A, Vivon L, Branton D (2001) Voltage-driven DNA translocations through a nanopore. Phys Rev Lett 86:3435–3438
Pan H, Ng TY, Li H, Moeendarbary E (2010) Dissipative particle dynamics simulation of entropic trapping for DNA separation. Sens Actuators A 157:328–335
Pennathur S, Santiago J (2005) Electrokinetic transport in nanochannels: 2. Experiments. Anal Chem 77:6782–6789
Perkins TT, Smith DE, Larson RG, Chu S (1995) Stretching of a single tethered polymer in a uniform flow. Science 268:83–87
Salieb-Beugelaar GB, Teapal J et al (2008) Field-dependent DNA mobility in 20 nm high nanoslits. Nano Lett 8:1785–1790
Stein D, van der Heyden FHJ et al (2006) Pressure-driven transport of confined DNA polymers in fluidic channels. PNAS 103:15853–15858
Streek M, Schmid F, Duong TT, Ros A (2004) Mechanisms of DNA separation in entropic trap arrays: a Brownian dynamics simulation. J Biotechnol 112:79–89
Symeonidis V, Karniadakis GE, Caswell B (2005) Dissipative particle dynamics simulations of polymer chains: scaling laws and shearing response compared to DNA experiments. Phys Rev Lett 95:076001
Acknowledgment
This study is funded by Singapore-MIT Alliance (Computational Engineering Program).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, K., Chen, YZ., Han, J. et al. Dissipative particle dynamics simulation of field-dependent DNA mobility in nanoslits. Microfluid Nanofluid 12, 157–163 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0859-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0859-5