Abstract
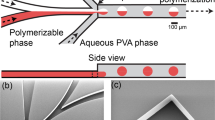
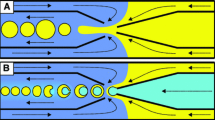
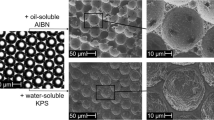
We present a microfluidic cross-flowing system for producing biphasic emulsion droplets and non-spherical polymer microparticles. Microfluidic channels on a glass chip comprise a Y-shaped channel so as to form a two-phase organic stream of photocurable and non-curable phases, and a T-junction to generate phase-separated droplets in a cross-flowing aqueous stream. The biphasic droplets at equilibrium formed a Janus configuration (partial engulfing) or a core–shell configuration (complete engulfing) consistent with minimizing the interfacial free energies among the three liquid phases, according to the three spreading coefficients. When silicone oil was used as the non-curable phase, monodisperse Janus droplets were generated reproducibly in a one-step process; for e.g., the mean particle size was 119 μm with a coefficient of variation (CV) of 1.9%. Subsequent UV-initiated polymerization yielded monodisperse particles with controlled convex/concave structures, which were tunable through variation of the ratio of the flow rates between the two organic phases. In contrast, when perfluorocarbon fluid, which is more hydrophobic than silicone oil, was used as the non-curable phase, monodisperse core–shell droplets were generated in a two-step regime, leading to the synthesis of cross-linked polymeric shells with a pore on their surfaces. We also investigated how the asymmetric flow configuration influenced droplet formation at the T-junction.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2D:
-
Two dimensional
- 3D:
-
Three dimensional
- Ca :
-
Capillary number
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- D h :
-
Hydraulic diameter
- DRIE:
-
Deep reactive ion etching
- f b :
-
Rate of droplet breakup
- HDDA:
-
1,6-hexanediol diacrylate
- M w :
-
Molecular weight
- PFC:
-
Perfluorocarbon fluid
- PTFE:
-
Poly(tetrafluoroethylene)
- PVA:
-
Polyvinyl alcohol
- Q c :
-
Volumetric flow rate of the continuous phase
- Q d :
-
Total volumetric flow rate of the photocurable and non-curable phases
- Q m :
-
Volumetric flow rate of the photocurable monomer (HDDA)
- Q p :
-
Volumetric flow rate of the perfluorocarbon fluid
- Q s :
-
Volumetric flow rate of the silicone oil
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- S i :
-
Spreading parameter
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet
- v :
-
Flow velocity
- wt%:
-
Weight percent
- γ :
-
Interfacial tension or surface tension
- γ 12 :
-
Interfacial tension at the interface 12
- γ 23 :
-
Interfacial tension at the interface 23
- γ 31 :
-
Interfacial tension at the interface 31
- η :
-
Fluid viscosity
- η m :
-
Viscosity of the photocurable monomer (HDDA)
- η s :
-
Viscosity of the silicone oil
- η p :
-
Viscosity of the perfluorocarbon fluid
- ρ m :
-
Density of the photocurable monomer (HDDA)
- ρ s :
-
Density of the silicone oil
- ρ p :
-
Density of the perfluorocarbon fluid
References
Anna SL, Bontoux N, Stone HA (2003) Formation of dispersions using “flow focusing” in microchannels. Appl Phys Lett 82:364–366
Bong KW, Pregibon DC, Doyle PS (2009) Lock release lithography for 3D and composite microparticles. Lab Chip 9:863–866
Brooks CF, Fuller GG, Frank CW, Robertson CR (1999) An interfacial stress rheometer to study rheological transitions in monolayers at the air–water interface. Langmuir 15:2450–2459
Chen CH, Shah RK, Abate AR, Weitz DA (2009) Janus particles templated from double emulsion droplets generated using microfluidics. Langmuir 25:4320–4323
Chou CS, Kowalski A, Rokowski JM, Schaller EJ (1987) Nonspherical acrylic latices. J Coat Technol 59:93–102
Christopher GF, Noharuddin NN, Taylor JA, Anna SL (2008) Experimental observations of the squeezing-to-dripping transition in T-shaped microfluidic junctions. Phys Rev E 78:036317
De Menech M, Garstecki P, Jousse F, Stone HA (2008) Transition from squeezing to dripping in a microfluidic T-shaped junction. Fluid Mech 595:141–161
Dendukuri D, Tsoi K, Hatton TA, Doyle PS (2005) Controlled synthesis of nonspherical microparticles using microfluidics. Langmuir 21:2113–2116
Dendukuri D, Pregibon DC, Collins J, Hatton TA, Doyle PS (2006) Continuous-flow lithography for high-throughput microparticle synthesis. Nat Mater 5:365–369
Dendukuri D, Hatton TA, Doyle PS (2007) Synthesis and self-assembly of amphiphilic polymeric microparticles. Langmuir 23:4669–4674
Donev A, Cisse I, Sachs D, Variano EA, Stillinger FH, Connelly R, Torquato S, Chaikin PM (2004) Improving the density of jammed disordered packings using ellipsoids. Science 303:990–993
Fernández-Nieves A, Cristobal G, Garcés-Chávez V, Spalding GC, Dholakia K, Weitz DA (2005) Optically anisotropic colloids of controllable shape. Adv Mater 17:680–684
Garstecki P, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2005) Mechanism for flow-rate controlled breakup in confined geometries: a route to monodisperse emulsions. Phys Rev Lett 94:164501
Garstecki P, Fuerstman MJ, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2006) Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junctions–scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab Chip 6:437–446
Glotzer SC, Solomon MJ (2007) Anisotropy of building blocks and their assembly into complex structures. Nat Mater 6:557–562
Gracias DH, Tien J, Breen TL TL, Hsu C, Whitesides GM (2000) Forming electrical networks in three dimensions by self-assembly. Science 289:1170–1172
Gross GA, Hamann C, Günther M, Köhler JM (2007) Formation of polymer and nanoparticle doped polymer minirods by use of the microsegmented flow principle. Chem Eng Technol 30:341–346
Gupta A, Kumar R (2009) Effect of geometry on droplet formation in the squeezing regime in a microfluidic T-junction. Microfluid Nanofluid. doi:10.1007/s10404-009-0513-7
Gupta A, Murshed SMS, Kumar R (2009) Droplet formation and stability of flows in a microfluidic T-junctions. Appl Phys Lett 94:164107
Hwang DK, Dendukuri D, Doyle PS (2008) Microfluidic-based synthesis of non-spherical magnetic hydrogel microparticles. Lab Chip 8:1640–1647
Im SH, Jeong U, Xia Y (2005) Polymer hollow particles with controllable holes in their surfaces. Nat Mater 4:671–675
Lao KL, Wang JH, Lee GB (2009) A microfluidic platform for formation of double-emulsion droplets. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:709–719
Lu Y, Yin Y, Xia Y (2001) Three-dimensional photonic crystals with non-spherical colloids as building blocks. Adv Mater 13:415–420
Malloggi F, Pannacci N, Attia R, Monti F, Mary P, Willaime H, Tabeling P (2009) Monodisperse colloids synthesized with nanofluidic technology. Langmuir doi:10.1021/la9028047
Minami H, Kobayashi H, Okubo M (2005) Preparation of hollow polymer particles with a single hole in the shell by SaPSeP. Langmuir 21:5655–5658
Nie Z, Zu S, Seo M, Lewis PC, Kumacheva E (2005) Polymer particles with various shapes and morphologies produced in continuous microfluidic reactors. J Am Chem Soc 127:8058–8063
Nie Z, Li W, Seo M, Xu S, Kumacheva E (2006) Janus and ternary particles generated by microfluidic synthesis: design, synthesis, and self-assembly. J Am Chem Soc 128:9408–9412
Nisisako T (2008) Microstructured devices for preparing controlled multiple emulsions. Chem Eng Technol 31:1091–1098
Nisisako T, Torii T (2007) Formation of biphasic Janus droplets in a microfabricated channel for the synthesis of shape-controlled polymer microparticles. Adv Mater 19:1489–1493
Nisisako T, Torii T (2008) Microfluidic large-scale integration on a chip for mass production of monodisperse droplets and particles. Lab Chip 8:287–293
Nisisako T, Torii T, Higuchi T (2002a) Droplet formation in a microchannel network. Lab Chip 2:24–26
Nisisako T, Torii T, Higuchi T (2002b) Preparation of picoliter-sized reaction/analysis chambers for droplet-based chemical and biochemical systems. In: Baba Y et al (eds) Micro total analysis system 2002, vol 1. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 362–364
Nisisako T, Torii T, Higuchi T (2004a) Novel microreactors for functional polymer beads. Chem Eng J 101:23–29
Nisisako T, Torii T, Higuchi T (2004b) Separation of satellite droplets using branch microchannel configuration. In: Laurell T et al (eds) Micro total analysis system 2004, vol 1. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 312–314
Nisisako T, Torii T, Takahashi T, Takizawa Y (2006) Synthesis of monodisperse bicolored Janus particles with electrical anisotropy using a microfluidic co-flow system. Adv Mater 18:1152–1156
Okubo M, Katsuta Y, Matsumoto T (1980) Rupture of anomalous composite-particles prepared by seeded emulsion polymerization. J Polym Sci Polym Lett Ed 18:481–486
Okubo M, Fujibayashi T, Terada A (2005) Synthesis of micron-sized, monodisperse polymer particles of disc-like and polyhedral shapes by seeded dispersion polymerization. Colloid Polym Sci 283:793–798
Pannacci N, Bruus H, Bartolo D, Etchart I, Lockhart T, Hennequin Y, Willaime H, Tabeling P (2008) Equilibrium and nonequilibrium states in microfluidic double emulsions. Phys Rev Lett 101:164502
Prasad N, Perumal J, Choi CH, Lee CS, Kim DP (2009) Generation of monodisperse inorganic-organic Janus microspheres in a microfluidic device. Adv Funct Mater 19:1656–1662
Serra CA, Chang Z (2008) Microfluidic-assisted synthesis of polymer particles. Chem Eng Technol 31:1099–1115
Shepherd RF, Conrad JC, Rhodes SK, Link DR, Marquez M, Weitz DA, Lewis JA (2006) Microfluidic assembly of homogeneous and Janus colloid-filled hydrogel granules. Langmuir 22:8618–8622
Shepherd RF, Panda P, Bao Z, Sandhage KH, Hatton TA, Lewis JA, Doyle PS (2008) Stop-flow lithography of colloidal, glass, and silicon microcomponents. Adv Mater 20:4734–4739
Thorsen T, Roberts RW, Arnold FH, Quake SR (2001) Dynamic pattern formation in a vesicle-generating microfluidic device. Phys Rev Lett 86:4163–4166
Tice JD, Song H, Lyon AD, Ismagilov RF (2003) Formation of droplets and mixing in multiphase microfluidics at low values of the Reynolds and the Capillary numbers. Langmuir 19:9127–9133
Torza S, Mason SG (1969) Coalescence of two immiscible liquid drops. Science 163:813–814
Xu S, Nie Z, Seo M, Lewis P, Kumacheva E, Stone HA, Garstecki P, Weibel DB, Gitlin I, Whitesides GM (2005) Generation of monodisperse particles using microfluidics: control over size, shape, and composition. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:724–728
Yang SM, Kim SH, Lim JM, Yi GR (2008) Synthesis and assembly of structured colloidal particles. J Mater Chem 18:2177–2190
Zhao CX, Middelberg APJ (2009) Microfluidic mass-transfer control for the simple formation of complex multiple emulsions. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:7208–7211
Zhao LB, Pan L, Zhang K, Guo SS, Liu W, Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhao XZ, Chan HLW (2009) Generation of Janus alginate hydrogel particles with magnetic anisotropy for cell encapsulation. Lab Chip 9:2981–2986
Zheng B, Tice JD, Ismagilov RF (2004) Formation of droplets of alternating composition in microfluidic channels and applications to indexing of concentrations in droplet-based assays. Anal Chem 76:4977–4982
Acknowledgments
TN gratefully acknowledges the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (MEXT) in Japan (Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) No. 19710114 and No. 21710124), Hosokawa Particle Technology Foundation, and Yazaki Memorial Foundation for Science & Technology for their support of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nisisako, T., Hatsuzawa, T. A microfluidic cross-flowing emulsion generator for producing biphasic droplets and anisotropically shaped polymer particles. Microfluid Nanofluid 9, 427–437 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0559-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0559-6