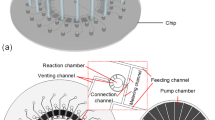
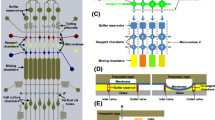
Abstract
We present a combinatorial dilution device using a three-layer microfluidic network that can produce systematic variations of buffer and additive solutions in a combinatorial fashion for high throughput screening and optimization. A proof-of-concept device providing seven combinations (ABC/D, AB/D, BC/D, AC/D, A/D, B/D, and C/D) of three additive samples (A, B, and C) into a buffer solution (D) has been demonstrated. Such combinations are often used in simplex-centroid mixture DOE (design of experiments), useful techniques to minimize the experimental efforts at maximal information output with systematic variations of large-scale components. Based on mathematical and electrical modeling and computational fluid dynamic simulation, the device has been designed, fabricated, and characterized.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assay Guidance Manual Version 5.0. (2008) Eli Lilly and Company and NIH Chemical Genomics Center. http://www.ncgc.nih.gov/guidance/manual_toc.html
Breslauer DN, Lee PJ et al (2006) Microfluidics-based systems biology. Mol Biosyst 2(2):97–112
Campbell K, Groisman A (2007) Generation of complex concentration profiles in microchannels in a logarithmically small number of steps. Lab Chip 7(2):264–272
Cooksey GA, Sip CG et al (2009) A multi-purpose microfluidic perfusion system with combinatorial choice of inputs, mixtures, gradient patterns, and flow rates. Lab Chip 9(3):417–426
Dertinger SKW, Chiu DT et al (2001) Generation of gradients having complex shapes using microfluidic networks. Anal Chem 73(6):1240–1246
Dittrich PS, Manz A (2006) Lab-on-a-chip: microfluidics in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(3):210–218
Garcia-Egido E, Spikmans V et al (2003) Synthesis and analysis of combinatorial libraries performed in an automated micro reactor system. Lab Chip 3(2):73–76
Greve F, Seemann L et al (2007) A hybrid microsystem for parallel perfusion experiments on living cells. J Micromech Microeng 17(8):1721–1730
Hattori K, Sugiura S et al (2009) Generation of arbitrary monotonic concentration profiles by a serial dilution microfluidic network composed of microchannels with a high fluidic-resistance ratio. Lab Chip. doi:10.1039/b816995k
Holden MA, Kumar S et al (2003) Generating fixed concentration arrays in a microfluidic device. Sens Actuators B 92(1–2):199–207
Irimia D, Geba DA et al (2006) Universal microfluidic gradient generator. Anal Chem 78(10):3472–3477
Islam RS, Tisi D et al (2007) Framework for the rapid optimization of soluble protein expression in Escherichia coli combining microscale experiments and statistical experimental design. Biotechnol Prog 23(4):785–793
Ismagilov RF, Ng JMK et al (2001) Microfluidic arrays of fluid–fluid diffusional contacts as detection elements and combinatorial tools. Anal Chem 73(21):5207–5213
Jacobson SC, McKnight TE et al (1999) Microfluidic devices for electrokinetically driven parallel and serial mixing. Anal Chem 71(20):4455–4459
Jeon NL, Dertinger SKW et al (2000) Generation of solution and surface gradients using microfluidic systems. Langmuir 16(22):8311–8316
Kang JH, Um E et al (2009) Fabrication of a poly(dimethylsiloxane) membrane with well-defined through-holes for three-dimensional microfluidic networks. J Micromech Microeng 19:045027 (6 pp)
Kikutani Y, Horiuchi T et al (2002) Glass microchip with three-dimensional microchannel network for 2 × 2 parallel synthesis. Lab Chip 2(4):188–192
Kikutani Y, Ueno M et al (2005) Continuous-flow chemical processing in three-dimensional microchannel network for on-chip integration of multiple reactions in a combinatorial mode. QSAR Comb Sci 24(6):742–757
Kim C, Lee K et al (2008) A serial dilution microfluidic device using a ladder network generating logarithmic or linear concentrations. Lab Chip 8(3):473–479
Kirsten G, Maier WF (2004) Strategies for the discovery of new catalysts with combinatorial chemistry. Appl Surf Sci 223(1–3):87–101
Lee K, Kim C et al (2009) Generalized serial dilution module for monotonic and arbitrary microfluidic gradient generators. Lab Chip 9(5):709–717
Liu MC, Ho D et al (2008) Monolithic fabrication of three-dimensional microfluidic networks for constructing cell culture array with an integrated combinatorial mixer. Sens Actuators B 129(2):826–833
Maier WF, Stowe K et al (2007) Combinatorial and high-throughput materials science. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(32):6016–6067
Muteki K, MacGregor JF et al (2007) Mixture designs and models for the simultaneous selection of ingredients and their ratios. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 86(1):17–25
Narasimhan B, Mallapragada SK, Porter MD (2007) Combinatorial materials science. Wiley, New York
Neils C, Tyree Z et al (2004) Combinatorial mixing of microfluidic streams. Lab Chip 4(4):342–350
Pereira SRM, Clerc F et al (2007) Optimisation methodologies and algorithms for research on catalysis employing high-throughput methods: comparison using the selox benchmark. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 10(2):149–159
Schudel BR, Choi CJ, Cunningham BT, Kenis PJA (2009) Microfluidic chip for combinatorial mixing and screening of assays. Lab Chip 9:1676–1680
Singh B, Dahiya M et al (2005) Optimizing drug delivery systems using systematic “design of experiments”. Part II: retrospect and prospects. Crit Rev Therap Drug Carr Syst 22(3):215–294
Smith CG, O’Donnell JT (2006) The process of new drug discovery and development. Informa Health Care, New York
Timbrell JA (2000) Principles of biochemical toxicology. Taylor & Francis, London
Tye H (2004) Application of statistical ‘design of experiments’ methods in drug discovery. Drug Discov Today 9(11):485–491
Walker GM, Monteiro-Riviere N et al (2007) A linear dilution microfluidic device for cytotoxicity assays. Lab Chip 7(2):226–232
Webster DC (2008) Combinatorial and high-throughput methods in macromolecular materials research and development. Macromol Chem Phys 209(3):237–246
Yang K, EI-Haik BS (2008) Design for six sigma: a roadmap for product development, McGraw-Hill Professional, New York
Yu ZTF, Kamei KI et al (2009) Integrated microfluidic devices for combinatorial cell-based assays. Biomed Microdevices 11(3):547–555
Acknowledgments
This research was supported in part by the Intelligent Microsystem Center, which is carrying out one of the 21st Century’s Frontier R&D Projects sponsored by the Korea Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K., Kim, C., Jung, G. et al. Microfluidic network-based combinatorial dilution device for high throughput screening and optimization. Microfluid Nanofluid 8, 677–685 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0500-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0500-z