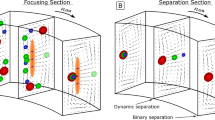
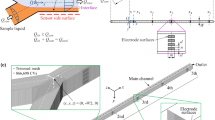
Abstract
Focusing particles into a tight stream is usually a necessary step prior to separating and sorting them. We present herein a proof-of-concept experiment of a novel particle focusing technique in DC electrokinetic flow through a planar serpentine microchannel. This focusing stems from the cross-stream dielectrophoretic motion induced within the channel turns. The observed particle focusing behavior is consistent with the predicted particle trajectories from a numerical modeling.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JL (1989) Colloidal transport by interfacial forces. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 21:61–99
Ateya DA, Erickson JS, Howell PB Jr, Hilliard LR et al (2008) The good, the bad, the tiny: a review of microflow cytometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1485–1498
Chang CC, Huang ZY, Yang RJ (2007) Three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing in two-layer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 17:1479–1486
Cheng IF, Chang HC, Hou D, Chang HC (2007) An integrated dielectrophoretic chip for continuous bioparticle filtering, focusing, sorting, trapping, and detecting. Biomicrofluidics 1:021503
Choi C, Park JK (2008) Sheathless Hydrophoretic particle focusing in a microchannel with exponentially increasing obstacle arrays. Anal Chem 80:3035–3039
Choi S, Song S, Choi C, Park JK (2007) Sheathless focusing of microbeads and blood cells based on hydrophoresis. Small 4:634–641
Chung TD, Kim HC (2007) Recent advances in miniaturized microfluidic flow cytometry for clinical use. Electrophoresis 28:4511–4520
Cummings EB, Singh AK (2003) Dielectrophoresis in Microchips Containing Arrays of Insulating Posts: Theoretical and Experimental Results. Anal Chem 75:4724–4731
Di Carlo D, Irimia D, Tompkins RG, Toner M (2007) Continuous inertial focusing, ordering, and separation of particles in microchannels. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:18892–18897
Di Carlo D, Edd JF, Irimia D, Tompkins RG, Toner M (2008) Equilibrium separation and filtration of particles using differential inertial focusing. Anal Chem 80:2204–2211
Duffy DC, McDonald JC, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (1998) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem 70:4974–4984
Ermolina I, Morgan H (2005) The electrokinetic properties of latex particles: comparison of electrophoresis and dielectrophoresis. J Colloid Interf Sci 285:419–428
Fu LM, Yang RJ, Lee GB (2003) Electrokinetic focusing injection methods on microfluidic devices. Anal Chem 75:1905–1910
Hawkins BG, Smith AE, Syed YA, Kirby BJ (2007) Continuous-flow particle separation by 3D insulative dielectrophoresis using coherently shaped, DC-biased, AC electric fields. Anal Chem 79:7291–7300
Huh D, Gu W, Kamotani Y, Grotgerg JB, Takayama S (2005) Microfluidics for flow cytometric analysis of cells and particles. Physiol Meas 26:R73–R98
Kang K, Kang Y, Xuan X, Li D (2006a) Continuous separation of microparticles by size with DC-dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 27:694–702
Kang K, Xuan X, Kang Y, Li D (2006b) Effects of the DC-dielectrophoretic force on particle trajectories in microchannels. J Appl Phys 99:064702
Kohlheyer D, Unnikrishnan S, Besselink GAJ, Schlautmann S, Schasfoort RBM (2008) A microfluidic device for array patterning by perpendicular electrokinetic focusing. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:557–564
Lee GB, Chang CC, Huang SB, Yang RJ (2006) The hydrodynamic focusing effect in rectangular microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 16:1024–1032
Lewpiriyawong N, Yang C, Lam YC (2008) Dielectrophoretic manipulation of particles in a modified microfluidic H filter with multi-insulating blocks. Biomicrofluidics 2:034105
Lin CH, Lee GB, Fu LM, Hwey BH (2004) Vertical focusing device utilizing dielectrophoretic force and its application on microflow cytometer. J Microelectromech Syst 13:923–932
Mao XL, Waldeisen JR, Huang TJ (2007) “Microfluidic drifting”—implementing three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing with a single-layer planar microfluidic device. Lab Chip 7:1260–1262
Morgan H, Green NG (2002) AC Electrokinetic: Colloids and Nanoparticles. Research Studies Press, Hertfordshire, UK
Pamme N (2007) Continuous flow separations in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7:1644–1659
Santiago JG (2001) Electroosmotic flows in microchannels with finite inertial and pressure forces. Anal Chem 73:2353–2365
Seo J, Lean MH, Kole A (2007a) Membrane-free microfiltration by asymmetric inertial migration. Appl Phys Lett 91:033901
Seo J, Lean MH, Kole A (2007b) Membraneless microseparation by asymmetry in curvilinear laminar flows. J Chromatogr A 1162:126–131
Shi J, Mao X, Ahmed D, Colletti A, Huang TJ (2008) Focusing microparticles in a microfluidic channel with standing surface. Lab Chip 8:221–223
Shilov VN, Delgadob AV, González-Caballero F, Horno J, López-García JJ, Grosse C (2000) Polarization of the electrical double layer. Time evolution after application of an electric field. J Colloid Interf Sci 232:141–148
Simonnet C, Groisman A (2006) High-throughput and high-resolution flow cytometry in molded microfluidic devices. Anal Chem 78:5653–5663
Takahashi T, Ogata S, Nishizawa M, Matsue T (2003) A valveless switch for microparticle sorting with laminar flow streams and electrophoresis perpendicular to the direction of fluid stream. Electrochem Commun 5:175–177
Thamida SK, Chang HC (2002) Nonlinear electrokinetic ejection and entrainment due to polarization at nearly insulated wedges. Phys Fluid 14:4315–4328
Thwar PK, Linderman JJ, Burns MA (2007) Electrodeless direct current dielectrophoresis using reconfigurable field-shaping oil barriers. Electrophoresis 28:4572–4581
Tornay R, Braschler T, Demierre N, Steitz B et al (2008) Dielectrophoresis-based particle exchanger for the manipulation and surface functionalization of particles. Lab Chip 8:267–273
Tsai CG, Hou HH, Fu LM (2008) An optimal three-dimensional focusing technique for micro-flow cytometers. Microfluid Nanofluid 5:827–836
Voldman J (2006) Electrical forces for microscale cell manipulation. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:425–454
Xuan X, Li D (2005) Focused electrophoretic motion and selected electrokinetic dispensing of particles and cells in cross-microchannels. Electrophoresis 26:3552–3560
Xuan X, Xu B, Li D (2005) Accelerated particle electrophoretic motion and separation in converging-diverging microchannels. Anal Chem 77:4323–4328
Xuan X, Raghibizadeh S, Li D (2006) Wall effects on electrophoretic motion of spherical polystyrene particles in a rectangular poly(dimethylsiloxane) microchannel. J Colloid Interf Sci 296:743–748
Yang RJ, Chang CC, Huang SB, Lee GB (2005) A new focusing model and switching approach for electrokinetic flow inside microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 15:2141–2148
Yu C, Vykoukal J, Vykoukal DM, Schwartz JA et al (2005) A three-dimensional dielectrophoretic particle focusing channel for microcytometry applications. J Microelectromech Syst 14:480–487
Zhao Y, Fujimoto BS, Jeffries GDM, Schiro PG, Chiu DT (2007) Optical gradient flow focusing. Opt Express 15:6167–6176
Acknowledgments
The support from Clemson University through a start-up package and a Research Equipment Fund to Xuan is gratefully acknowledged. The support from the State Key Laboratory of Nonlinear Mechanics in China is also gratefully appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, J., Tzeng, TR.J., Hu, G. et al. DC dielectrophoretic focusing of particles in a serpentine microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 7, 751 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0432-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0432-7