Abstract
Purpose
The first aim of this study was to evaluate changes in the stiffness of the medial gastrocnemius muscle (GM) after a botulinum toxin A (BoNT-A) injection in children with cerebral palsy (CP) using shear wave elastography (SWE). We also wanted to investigate the usability of SWE for evaluating spasticity in a clinical setting. The second aim of this study was to show how treatment of the gastrocnemius muscle spasticity caused a change in the elasticity of the anterior tibial (TA) muscle.
Methods
Twenty-four pediatric patients diagnosed with a spastic type of CP, who were scheduled to receive a BoNT-A injection in the gastrocnemius muscle, were included in the study. There was a total of 43 lower extremities to evaluate, and muscle stiffness was measured before the injection and a month post injection using SWE. The physiatrist evaluated muscle spasticity using the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS) and the Modified Tardieu Scale at about the same time.
Results
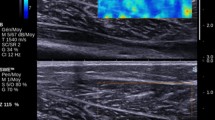
SWE values of the GM (pre-BoNT-A: 45.9 ± 6.5 kPa, post-BoNT-A: 25.0 ± 5.7 kPa) decreased significantly post BoNT-A injection (P < 0.01). SWE measurements of the GM had positive correlations with MAS, V1X, V3X, and R2-R1 (P < 0.01); and negative correlations with R2 and R1 (P < 0.05). SWE values of the TA muscle (pre: 36.9 ± 7.9 kPa, post: 28.4 ± 5.2 kPa) decreased significantly (P < 0.01).
Conclusion
Quantitative measurement of muscle stiffness using SWE may provide important information for the evaluation of spasticity and treatment efficiency in pediatric CP patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenbaum P, Paneth N, Leviton A, et al. A report: the definition and classification of cerebral palsy April 2006. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007;109:8–14.
Cans C, Dolk H, Platt M, et al. Recommendations from the SCPE collaborative group for defining and classifying cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007;49:35–8.
Krigger KW. Cerebral palsy: an overview. Am Fam Physician. 2006;73:91–100.
Yam WKL, Leung MSM. Interrater reliability of Modified Ashworth Scale and Modified Tardieu Scale in children with spastic cerebral palsy. J Child Neurol. 2006;21:1031–5.
Fosang AL, Galea MP, McCoy AT, et al. Measures of muscle and joint performance in the lower limb of children with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2003;45:664–70.
Numanoglu A, Gunel MK. Intraobserver reliability of modified Ashworth scale and modified Tardieu scale in the assessment of spasticity in children with cerebral palsy. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2012;46:196–200.
Mackey AH, Walt SE, Lobb G, et al. Intraobserver reliability of the modified Tardieu scale in the upper limb of children with hemiplegia. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2004;46(4):267–72.
Graham HK, Aoki KR, Autti-Rämö I, et al. Recommendations for the use of botulinum toxin type A in the management of cerebral palsy. Gait Posture. 2000;11:67–79.
Kahraman A, Seyhan K, Değer Ü, et al. Should botulinum toxin A injections be repeated in children with cerebral palsy? A systematic review. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2016;58:910–7.
Öztürk M, Sayinbatur B. Real-time ultrasound elastography of the Achilles tendon in patients with cerebral palsy: is there a correlation between strain ratio and biomechanical indicators? J Med Ultrasonics. 2018;45:143–8.
Bilgici MC, Bekci T, Ulus Y, et al. Quantitative assessment of muscle stiffness with acoustic radiation force impulse elastography after botulinum toxin A injection in children with cerebral palsy. J Med Ultrasonics. 2018;45:137–41.
Brandenburg JE, Eby SF, Song P, et al. Feasibility and reliability of quantifying passive muscle stiffness in young children by using shear wave ultrasound elastography. J Ultras Med. 2015;34:663–70.
Shiina T, Nightingale KR, Palmeri ML, et al. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: part 1: basic principles and terminology. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:1126–47.
Lee SS, Gaebler-Spira D, Zhang L-Q, et al. Use of shear wave ultrasound elastography to quantify muscle properties in cerebral palsy. Clin Biomech. 2016;31:20–8.
Scholtes VA, Becher JG, Beelen A, et al. Clinical assessment of spasticity in children with cerebral palsy: a critical review of available instruments. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2006;48:64–73.
Bilgici MC, Bekci T, Ulus Y, et al. Quantitative assessment of muscular stiffness in children with cerebral palsy using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) ultrasound elastography. J Med Ultrasonics. 2018;45:295–300.
Brandenburg JE, Eby SF, Song P, et al. Ultrasound elastography: the new frontier in direct measurement of muscle stiffness. Arch Phys Med. 2014;95:2207–19.
Eby SF, Song P, Chen S, et al. Validation of shear wave elastography in skeletal muscle. J Biomech. 2013;46:2381–7.
Brandenburg JE, Eby SF, Song P, et al. Quantifying passive muscle stiffness in children with and without cerebral palsy using ultrasound shear wave elastography. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2016;58:1288–94.
Vola E, Albano M, Di Luise C, et al. Use of ultrasound shear wave to measure muscle stiffness in children with cerebral palsy. J ultrasound. 2018;21:241–7.
Kwon DR, Park GY, Lee SU, et al. Spastic cerebral palsy in children: dynamic sonoelastographic findings of medial gastrocnemius. Radiology. 2012;263:794–801.
Vasilescu D, Vasilescu D, Dudea SM, et al. Sonoelastography contribution in cerebral palsy spasticity treatment assessment, preliminary report: a systematic review of the literature apropos of seven patients. Med Ultrason. 2010;12:306–10.
Park G-Y, Kwon DR. Sonoelastographic evaluation of medial gastrocnemius muscles intrinsic stiffness after rehabilitation therapy with botulinum toxin a injection in spastic cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med. 2012;93:2085–9.
Boyaci A, Tutoglu A, Boyaci N, et al. Changes in spastic muscle stiffness after botulinum toxin A injections as part of rehabilitation therapy in patients with spastic cerebral palsy. NeuroRehabilitation. 2014;35:123–9.
Brandenburg JE, Eby SF, Song P, et al. Quantifying effect of onabotulinum toxin A on passive muscle stiffness in children with cerebral palsy using ultrasound shear wave elastography. Am J Phys Med Rehab. 2018;97:500–6.
Wong V. Use of botulinum toxin injection in 17 children with spastic cerebral palsy. Pediatr Neurol. 1998;18:124–31.
Flett P, Stern L, Waddy H, et al. Botulinum toxin A versus fixed cast stretching for dynamic calf tightness in cerebral palsy. J Pediatr Child H. 1999;35:71–7.
Friedman A, Diamond M, Johnston MV, et al. Effects of botulinum toxin A on upper limb spasticity in children with cerebral palsy. Am J Phys Med Rehab. 2000;79:53–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
Protocol approval and written informed consent were obtained according to the standards of the ethics committee of the Keçiören Training and Research Hospital in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Dağ, N., Cerit, M.N., Şendur, H.N. et al. The utility of shear wave elastography in the evaluation of muscle stiffness in patients with cerebral palsy after botulinum toxin A injection. J Med Ultrasonics 47, 609–615 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-020-01042-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-020-01042-6