Abstract
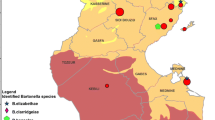
The host–parasite–vector relationship of Bartonella spp. system in wild carnivores and their fleas from northwestern Mexico was investigated. Sixty-six carnivores belonging to eight species were sampled, and 285 fleas belonging to three species were collected during spring (April–May) and fall (October–November) seasons. We detected Bartonella species in 7 carnivores (10.6%) and 27 fleas (9.5%) through either blood culture or PCR. Of the 27 Bartonella-positive fleas, twenty-two were Pulex simulans, three were Pulex irritans and one was Echidnophaga gallinacea. The gltA gene and ITS region sequences alignment revealed six and eight genetic variants of Bartonella spp., respectively. These variants were clustered into Bartonella rochalimae, Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii and another genotype, which likely represents a novel species of Bartonella spp. Although experimental infection studies are required to prove the vector role of P. simulans, our results suggest that this flea may play an important role in the Bartonella transmission. The results indicated possible host-specific relationships between Bartonella genotypes and the families of the carnivores, but further studies are needed to verify this finding. The presence of zoonotic species of Bartonella spp. in wild carnivores raises the issue of their potential risk for humans in fragmented ecosystems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbot P, Aviles AE, Eller L, Durden LA (2007) Mixed infections, cryptic diversity, and vector-borne pathogens: evidence from polygenis fleas and Bartonella species. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73:6045–6052.
Almuna MR (2016) Factores de riesgo asociados a tasas de infeccion de distemper canino en perro domestico (Canis familiaris) y carnivoros silvestres en la Reserva de la Biosfera de Janos, Chihuahua, Mexico. Bachelor Thesis submitted to the Universidad de Chile
Bai Y, Gilbert A, Fox K, Osikowicz L, Kosoy M (2016) Bartonella rochalimae and B. vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii in wild carnivores from Colorado, USA. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 52:844–849.
Bevins SN, Carver S, Boydston EE, Lyren LM, Alldredge M, Logan KA, et al. (2012) Three pathogens in sympatric populations of pumas, Bobcats, and domestic cats: implications for infectious disease transmission. PLoS One 7:e31403.
Brinkerhoff RJ, Kabeya H, Inoue K, Bai Y, Maruyama S (2010) Detection of multiple Bartonella species in digestive and reproductive tissues of fleas collected from sympatric mammals. International Society for Microbial Ecology Journal 4:955–8.
Billeter SA, Gundi VAKB, Rood MP, Kosoy MY (2011a) Molecular detection and identification of Bartonella species in Xenopsylla cheopis fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) collected from Rattus norvegicus rats in Los Angeles, California. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 77:7850–7852.
Billeter SA, Cáceres AG, Gonzales-Hidalgo J, Luna-Caypo D, Kosoy MY (2011b) Molecular detection of Bartonella species in ticks from Peru. Journal of Medical Entomology 48:1257–1260.
Birtles RJ, Hazel SM, Bennett M, Bown K, Raoult D, Begon M. (2001). Longitudinal monitoring of the dynamics of infections due to Bartonella species in UK woodland rodents. Epidemiology and Infection 126: 323–329.
Bouhsira E, Ferrandez Y, Liu M, Franc M, Boulouis HJ, Biville F (2013) Ctenocephalides felis an in vitro potential vector for five Bartonella species. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 36:105–111.
Boulouis HJ, Chang CC, Henn JB, Kasten RW, Chomel BB (2005). Factors associated with the rapid emergence of zoonotic Bartonella infections. Vet Res 36:383-410.
Breitschwerdt EB, Maggi RG, Chomel BB, Lappin MR (2010) Bartonellosis: an emerging infectious disease of zoonotic importance to animals and human beings. Journal of Veterinary Emergency and Critical Care 20:8-30.
Buffet JP, Pisanu B, Brisse S, Roussel S, Felix B, Halos L, Chapuis JL, Vayssier-Taussat M (2013) Deciphering Bartonella diversity, recombination, and host specificity in a rodent community. PLoS One 8: e68956.
Castle KT, Kosoy M, Lerdthusnee K, Phelan L, Bai Y, Gage KL, et al. (2004). Prevalence and diversity of Bartonella in rodents of northern Thailand: a comparison with Bartonella in rodents from southern China. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 70:429-433.
Ceballos G, Davidson A, List R, Pacheco J, Manzano-Fischer P, Santos-Barrera G, Cruzado J (2010) Rapid decline of a grassland system and its ecological and conservation implications. PLoS One 5:e8562.
Chang CC, Kasten RW, Chomel BB, Simpson DC, Hew CM, Kordick DL, et al. (2000). Coyotes (Canis latrans) as the reservoir for a human pathogenic Bartonella sp.: molecular epidemiology of Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii infection in coyotes from central coastal California. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 38:4193-4200.
Chomel BB, Boulouis HJ, Breitschwerdt EB, Kasten RW, Vayssier-Taussat M, Birtles RJ, et al. (2009). Ecological fitness and strategies of adaptation of Bartonella species to their hosts and vectors. Veterinary Research 40:29.
Chomel BB, Boulouis HJ, Maruyama S, and Breitschwerdt EB (2006). Bartonella spp. in pets and effect on human health. Emerging Infectious Diseases 12:389-394.
Chomel BB, and Kasten RW (2010). Bartonellosis, an increasingly recognized zoonosis. Journal of Applied Microbiology 109:743-750.
Chomel BB, Kikuchi Y, Martenson JS, Roelke-Parker ME, Chang CC, Kasten RW, et al. (2004). Seroprevalence of Bartonella infection in American free-ranging and captive pumas (Felis concolor) and bobcats (Lynx rufus). Veterinary Research 35:233-241.
Daszak P, Cunningham AA, Hyatt AD (2000) Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife—threats to biodiversity and human health. Science 287:443–449.
Diniz PPVDP, Maggi RG, Schwartz DS, Cadenas MB, Bradley JM, Hegarty B, Breutschwerdt EB (2007) Canine bartonellosis: Serological and molecular prevalence in Brazil and evidence of co-infection with Bartonella henselae and Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii. Veterinary Research 38:697–710.
Eads DA, Biggins DE, Antolin MF, Long DH, Huyvaert KP, Gage KL (2015) Prevalence of the generalist flea Pulex simulans on Black-tailed prairie fogs (Cynomys ludovicianus) in New Mexico, USA: The importance of considering imperfect detection. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 51:498–502.
Eremeeva ME, Gerns HL, Lydy SL, Goo JS, Ryan ET, Mathew SS, et al. (2007). Bacteremia, fever, and splenomegaly caused by a newly recognized Bartonella species. New England Journal of Medicine 356:2381-2387.
Fernández-González AM, Kosoy MY, Rubio A V., Graham CB, Montenieri JA, Osikowicz LM, Bai Y, Acosta-Gutierrez R, Avila-Flores R, Gage KL, Suzan G (2016) Molecular Survey of Bartonella Species and Yersinia pestis in Rodent Fleas (Siphonaptera) From Chihuahua, Mexico. Journal of Medical Entomology 53:1–7.
Fredrickson EL, Estell RE, Laliberte A, Anderson DM (2006) Mesquite recruitment in the Chihuahuan Desert: Historic and prehistoric patterns with long-term impacts. Journal of Arid Environments 65: 285–295.
Furman DP, Catts PE (1982) Manual of Medical Entomology, New York: Cambridge University Press
Gabriel MW, Henn J, Foley JE, Brown RN, Kasten RW, Foley P, et al. (2009). Zoonotic Bartonella species in fleas collected on gray foxes (Urocyon cinereoargenteus). Vector Borne Zoonotic Diseases 9:597-602.
Gerrikagoitia X, Gil H, Garcia-Esteban C, Anda P, Juste RA, and Barral M (2012). Presence of Bartonella species in wild carnivores of northern Spain. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 78:885-888.
Gutiérrez R, Nachum-Biala Y, Harrus S (2015) The relations between the presence and bacterial loads of Bartonella species in the cat and cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), under natural conditions. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 81:5613–5621.
Gutiérrez R, Morick D, Cohen C, Hawlena H, Harrus S (2014) The effect of ecological and temporal factors on the composition of Bartonella infection in rodents and their fleas. International Society for Microbial Ecology Journal 8:1598–1608.
Guy L, Nystedt B, Toft C, Zaremba-Niedzwiedzka K, Berglund EC, Granberg F, et al. (2013). A gene transfer agent and a dynamic repertoire of secretion systems hold the keys to the explosive radiation of the emerging pathogen Bartonella. PLoS Genetics 9:e1003393.
Henn JB, Chomel BB, Boulouis HJ, Kasten RW, Murray WJ, Bar-Gal GK, et al. (2009a). Bartonella rochalimae in raccoons, coyotes, and red foxes. Emerging Infectiuos Diseases 15:1984-1987.
Henn JB, Gabriel MW, Kasten RW, Brown RN, Koehler JE, MacDonald KA, et al. (2009b). Infective endocarditis in a dog and the phylogenetic relationship of the associated “Bartonella rochalimae” strain with isolates from dogs, gray foxes, and a human. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 47:787-790.
Henn JB, Gabriel MW, Kasten RW, Brown RN, Theis JH, Foley JE, et al. (2007). Gray foxes (Urocyon cinereoargenteus) as a potential reservoir of a Bartonella clarridgeiae-like bacterium and domestic dogs as part of a sentinel system for surveillance of zoonotic arthropod-borne pathogens in northern California. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 45:2411-2418.
Higgins JA, Radulovic S, Jaworski DC, and Azad AF (1996). Acquisition of the Cat Scratch Disease Agent Bartonella henselae by Cat Fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). Journal of Medical Entomology 33:490-495.
Hubbard CA (1968). Fleas of Western North America. New York: Hafner Publishing Co.
Hwang J, and Gottdenker NL (2013). Bartonella species in raccoons and feral cats, Georgia, USA. Emerging Infectious Diseases 19:1167-1168.
Kaewmongkol G, Kaewmongkol S, Fleming PA, Adams PJ, Ryan U, Irwin PJ, et al. (2011a). Zoonotic Bartonella species in fleas and blood from red foxes in Australia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Diseases 11:1549-1553.
Kaewmongkol G, Kaewmongkol S, McInnes LM, Burmej H, Bennett MD, Adams PJ, et al. (2011b). Genetic characterization of flea-derived Bartonella species from native animals in Australia suggests host-parasite co-evolution. Infections, Genetics and Evolution 11:1868-1872.
Keesing F, Belden LK, Daszak P, Dobson A, Harvell CD, Holt RD, Hudson P, Jolles A, Jones KE, Mitchell CE, Myers SS, Bogich T, Ostfeld RS (2010). Impacts of biodiversity on the emergence and transmission of infectious diseases. Nature 468:647–652.
Kordick DL, and Breitschwerdt EB (1998). Persistent infection of pets within a household with three Bartonella species. Emerging Infectious Diseases 4:325-328.
Kosoy M, Hayman DT, and Chan KS (2012). Bartonella bacteria in nature: where does population variability end and a species start? Infection, Genetics and Evolution 12:894-904.
Kosoy M, Mandel E, Green D, Marston E, Jones D, Childs J (2004). Prospective studies of Bartonella of rodents. Part II. Diverse infections in a single rodent community. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases 4: 296–305
Kosoy M, Murray M, Gilmore RD, Jr., Bai Y, and Gage KL (2003). Bartonella strains from ground squirrels are identical to Bartonella washoensis isolated from a human patient. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 41:645-650.
Kosoy MY, Regnery RL, Tzianabos T, Marston EL, Jones DC, Green D, et al. (1997). Distribution, diversity, and host specificity of Bartonella in rodents from the Southeastern United States. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 57:578-588.
Kreeger T, Aremo J, and Raath J (2002). Handbook of wildlife chemical immobilization. Colorado, USA: Wildlife Pharmaceuticals.
Lantos PM, Maggi RG, Ferguson B, Varkey J, Park LP, Breitschwerdt EB, et al. (2014). Detection of Bartonella species in the blood of veterinarians and veterinary technicians: a newly recognized occupational hazard? Vector Borne Zoonotic Diseases 14:563-570.
La Scola B, Zeaiter Z, Khamis A, Raoult D (2003) Gene-sequencebased criteria for species definition in bacteriology: the Bartonella paradigm. Trends in Microbiology 11:318–321.
Lei BR, and Olival KJ (2014). Contrasting Patterns in Mammal–Bacteria Coevolution: Bartonella and Leptospira in Bats and Rodents. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 8:e2738.
Leulmi H, Socolovschi C, Laudisoit A, Houemenou G, Davoust B, Bitam I, et al. (2014). Detection of Rickettsia felis, Rickettsia typhi, Bartonella Species and Yersinia pestis in Fleas (Siphonaptera) from Africa. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases 8:e3152.
Loftis AD, Reeves WK, Szumlas DE, Abbassy MM, Helmy IM, Moriarity JR, et al. (2006). Surveillance of Egyptian fleas for agents of public health significance: Anaplasma, Bartonella, Coxiella, Ehrlichia, Rickettsia, and Yersinia pestis. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 75:41-48.
López-Pérez AM, Rubio A, Suzan G, List R (in preparation) Carnivore diversity and habitat selection in Janos Biosphere Reserve, Mexico
Marquez FJ, Millan J, Rodriguez-Liebana JJ, Garcia-Egea I, and Muniain MA (2009). Detection and identification of Bartonella sp. in fleas from carnivorous mammals in Andalusia, Spain. Medical and Veterinary Entomology 23:393-398.
Martinez-Estevez L, Balvanera P, Pacheco J, Ceballos G (2013) Prairie Dog Decline Reduces the Supply of Ecosystem Services and Leads to Desertification of Semiarid Grasslands. PLoS One 8: e75229
McKee CD, Hayman DTS, Kosoy MY, Webb CT (2016) Phylogenetic and geographic patterns of Bartonella host shifts among bat species. Infections, Genetics and Evolution 44:382–394.
Millán J, Proboste T, Fernández de Mera IG, Chirife AD, de la Fuente J, Altet L (2016) Molecular detection of vector-borne pathogens in wild and domestic carnivores and their ticks at the human–wildlife interface. Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases 7:284–290.
Mogollon-Pasapera E, Otvos L, Jr., Giordano A, and Cassone M (2009). Bartonella: emerging pathogen or emerging awareness? International Journal of Infectious Diseases 13:3-8.
Molia S, Chomel BB, Kasten RW, Leutenegger CM, Steele BR, Marker L, et al. (2004). Prevalence of Bartonella infection in wild African lions (Panthera leo) and cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus). Veterinary Microbiology 100:31-41.
Montiel-arteaga A, Atilano D, Ayanegui A, Ceballos G (2015) Risk Factors Associated With Prevalence of Antibodies To Leptospira Interrogans in a Metapopulation of Black-Tailed Prairie Dogs in Mexico. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 51:28–35.
Moreno-Torres K, Gual-Sill F, Morales-Jimenez R, Rubio A V, Ceballos G, Suzán G (2014) Serological Survey of Hantavirus in Rodents From Prairie Dog Ecosystems in Chihuahua, Mexico. Southwest Naturalist 59:590–594.
Norman AF, Regnery R, Jameson P, Greene C, Krause DC (1995) Differentiation of Bartonella-like isolates at the species level by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism in the citrate synthase gene. The Journal of Clinical Microbiology 33:1797–1803.
Nyakatura K, and Bininda-Emonds OR (2012). Updating the evolutionary history of Carnivora (Mammalia): a new species-level supertree complete with divergence time estimates. BMC Biology 10:12.
Quinn JH, Girard YA, Gilardi K, Hernandez Y, Poppenga R, Chomel BB, et al. (2012). Pathogen and rodenticide exposure in American badgers (Taxidea taxus) in California. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 48:467-472.
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
Roux V, Eykyn SJ, Wyllie S, and Raoult D (2000). Bartonella vinsonii subsp. berkhoffii as an agent of afebrile blood culture-negative endocarditis in a human. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 38:1698-1700.
Roy AF, Corstvet RE, Tapp RA, O’Reilly KL, Cox HU (2001) Evaluation and Use of a Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay in Cats Experimentally Infected with Bartonella henselae Genotype I and Bartonella henselae Genotype II. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 13:312–322.
Rubio AV, Avila-Flores R, Osikowicz LM, Bai Y, Suzán G, Kosoy MY (2014) Prevalence and genetic diversity of Bartonella strains in rodents from northwestern Mexico. Vector Borne Zoonotic Diseases 14:838–45.
Rubio A V, Vigueras-Galván AL, Schountz T, Moreno-Torres K, List R, Sarmiento-Silva RE, Ávila-Flores R, Suzán G (2015) Abundance of hantavirus hosts in a landscape with black-tailed prairie dog colonies in northwestern Mexico. Mammalian Biology 80:491–495.
Sackal C, Laudisoit A, Kosoy M, Massung R, Eremeeva ME, Karpathy SE, et al. (2008). Bartonella spp. and Rickettsia felis in fleas, Democratic Republic of Congo. Emerging Infectious Diseases 14:1972-1974.
Sato S, Kabeya H, Miura T, Suzuki K, Bai Y, Kosoy M, et al. (2012). Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of Bartonella species from wild carnivores of the suborder Caniformia in Japan. Veterinary Microbiology 161:130-136.
Schaefer JD, Kasten RW, Coonan TJ, Clifford DL, and Chomel BB (2011). Isolation or detection of Bartonella vinsonii subspecies berkhoffii and Bartonella rochalimae in the endangered island foxes (Urocyon littoralis). Veterinary Microbiology 154:135-139.
Schaefer JD, Moore GM, Namekata MS, Kasten RW, and Chomel BB (2012). Seroepidemiology of Bartonella infection in gray foxes from Texas. Vector Borne Zoonotic Diseases 12:428-430.
Sikes RS, and Gannon WL (2011). Guidelines of the American Society of Mammalogists for the use of wild mammals in research. Journal of Mammalogy 92:235-253.
Sreter-Lancz Z, Tornyai K, Szell Z, Sreter T, Marialigeti K (2006) Bartonella infections in fleas (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) and lack of bartonellae in ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) from Hungary. Folia Parasitologica (Praha) 53:313–316.
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30:2725–2729.
Telfer S, Begon M, Bennett M, Bown KJ, Burthe S, Lambin X et al. (2007). Contrasting dynamics of Bartonella spp. in cyclic field vole populations: the impact of vector and host dynamics. Parasitology 134: 413–425.
Tsai YL, Chang CC, Chuang ST, Chomel BB (2011) Bartonella species and their ectoparasites: selective host adaptation or strain selection between the vector and the mammalian host? Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases 34:299–314.
Traub R (1985) Coevolution of fleas and mammals. In: Kim KC (ed) Coevolution of parasitic arthropods and mammals. Wiley-Inter-Science, New York, pp 295–437.
Vayssier-Taussat M, Le Rhun D, Bonnet S, and Cotte V (2009). Insights in Bartonella host specificity. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1166:127-132.
Yamamoto K, Chomel BB, Lowenstine LJ, Kikuchi Y, Phillips LG, Barr BC, et al. (1998). Bartonella henselae antibody prevalence in free-ranging and captive wild felids from California. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 34:56-63.
Ying B, Kosoy MY, Maupin GO, Tsuchiya KR, and Gage KL (2002). Genetic and ecologic characteristics of Bartonella communities in rodents in southern China. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 66:622-627.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by CONACyT Project No. 179482, Graduate student Support program (PAEP-UNAM) and CDC Global Diseases Detection program. We would like to thank A.Vigueras, H.Mendoza, J.Lopez, L.Aguilar, L.Orozco and M.Moguel for helping us during field sampling. We thank J. Diaz, E. Ponce and R. Sierra (Janos Grassland Biological Station, IE-UNAM) and A.Esquer and L.Garcia (Rancho El Uno TNC) for logistical support in the field. We are grateful to L.Lecuona (APHIS-USDA) for logistical support. A.M. López-Pérez is student in the Ph.D. program: Programa de Doctorado en Ciencias de la Producción y la Salud Animal (FMVZ-UNAM) and supported by CONACYT Grant Scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-Pérez, A.M., Osikowicz, L., Bai, Y. et al. Prevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Bartonella Species of Wild Carnivores and Their Fleas in Northwestern Mexico. EcoHealth 14, 116–129 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-017-1216-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-017-1216-2