Abstract
Aim
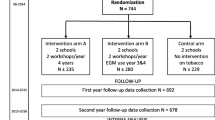
A randomised field trial was conducted to evaluate a school-based programme to prevent tobacco use in children and adolescents.
Subject and methods
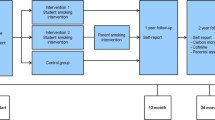
The trial included 534 children and 308 adolescents who were randomly selected to receive or not to receive the prevention programme. The prevention programme included: (a) health facts and the effect of smoking, (b) analysis of the mechanisms underlying intiation of smoking and (c) refusal skills training to deal with the social pressures to smoke. A questionnaire was administered before the intervention programme and 2 years later.
Results
The prevalence rates of smoking in both groups of children and adolescents were increased at the end of the study. Anyway, the difference of smoking prevalence between the intervention and control groups was statistically significant only for the children’s group (from 18.3 to 18.8% for the intervention group and from 17.8 to 26.9% in the control group) (p = 0.035). As regards reasons that induced the start of smoking, there was a significant increase of the issue “because smokers are fools” (p = 0.004 for children; p < 0.001 for adolescents) and “because smokers are irresponsible” (p ≤ 0.001 for both children and adolescents) in the experimental groups.
Conclusion
The results suggest that a school-based intervention programme addressing tobacco use among children and adolescents, based on the development of cognitive and behavioural aspects, can be effective. After 1 year of intervention, smoking prevalence was significantly lower in children belonging to the intervention group than in children not randomised to intervention. Targeting young children before they begin to smoke can be a successful way of prevention.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adelman WP, Duggan AK, Hauptman P, Joffe A (2001) Effectiveness of a high school smoking cessation program. Pediatrics 107:E50–E56
Ajzen I, Fishbein M (1980) Understanding attitudes and predicting social behavior. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Best JA, Thomson SJ, Santi SM, Smith E, Brown KS (1988) Preventing cigarette smoking among school children. Annu Rev Public Health 9:161–201
Botvin GJ, Griffin KW (2007) School-based programmes to prevent alcohol, tobacco and other drug use. Int Rev Psychiatry 19:607–615
Bruvold WH (1993) A meta-analysis of adolescent smoking prevention programs. Am J Public Health 83:872–880
Campbell R, Starkey F, Holliday J, Audrey S, Bloor M, Parry-Langdon N, Hughes R, Moore L (2008) An informal school-based peer-led intervention for smoking prevention in adolescence (ASSIST): a cluster randomised trial. Lancet 371:1595–1602
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (1994) Guidelines for school health programs to prevent tobacco use and addiction. MMWR Recomm Rep 43:1–18
Clarke JH, MacPherson B, Holmes DR, Jones R (1986) Reducing adolescent smoking: a comparison of peer-led, teacher-led, and expert interventions. J Sch Health 56:102–106
Donner A, Klar N (2000) Design and analysis of cluster randomization trials in health research. Arnold, London
Errecart MT, Walberg HJ, Ross JG, Gold RS, Fiedler JL, Kolbe LJ (1991) Effectiveness of teenage health teaching modules. J Sch Health 61:26–30
Evans RI (1976) Smoking in children: developing a social psychological strategy of deterrence. Prev Med 5:122–127
Faggiano F, Galanti MR, Bohrn K et al (2008) The effectiveness of a school-based substance abuse prevention program: EU-Dap cluster randomised controlled trial. Prev Med 47:537–543
Farrelly MC (2009) Monitoring the tobacco use epidemic V. The environment: factors that influence tobacco use. Prev Med 48:S35–S43
Ferketich AK, Gallus S, Iacobelli N, Zuccaro P, Colombo P, La Vecchia C (2008) Smoking in Italy 2007, with a focus on the young. Tumori 94:793–797
Garrison MM, Christakis DA, Ebel BE, Wiehe SE, Rivara FP (2003) Smoking cessation interventions for adolescents: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med 25(4):363–367
Gianti A, Vianello S, Casinghini C, Roncarolo F, Ramella F, Maccagni M, Tenconi MT (2007) The “Quit and Win” campaign to promote smoking cessation in Italy: results and one year follow-up across three Italian editions (2000–2004). Ital J Public Health 5:59–64
Hatsukami DK, Stead LF, Gupta PC (2008) Tobacco addiction. Lancet 371:2027–2038
Hiemstra M, Ringlever L, Otten R, Jackson C, van Schayck OC, Engels RC (2009) Efficacy of smoking prevention program ‘Smoke-free Kids’: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health 9:477
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (1989) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, New York
Hwang MS, Yeagley KL, Petosa R (2004) A meta-analysis of adolescent psychosocial smoking prevention programs published between 1978 and 1997 in the United States. Health Educ Behav 31:702–719
Istat (2000) I cittadini e l’ambiente. Indagine multiscopo sulle famiglie. Aspetti della vita quotidiana [The citizens and the environment. A multiscope survey on families, daily aspects]. Istat, Roma
Johnson CC, Myers L, Webber LS, Boris NW, He H, Brewer D (2009) A school-based environmental intervention to reduce smoking among high school students: the Acadiana Coalition of Teens against Tobacco (ACTT). Int J Environ Res Public Health 6:1298–1316
La Torre G, Langiano E, De Vito E, Soave G, Ricciardi G (1998) Abitudine al fumo di tabacco negli studenti universitari: risultati di un'indagine campionaria sugli studenti di Cassino. [Tobacco smoking habits among university students: results of a sample survey in Cassino]. Ig Mod 110:377–387
La Torre G, Moretti C, Capitano D, Alonzi MT, Ferrara M, Gentile A, Mannocci A, Capelli G (2004) La prevenzione del tabagismo: risultati di uno studio controllato randomizzato in adolescenti scolarizzati in Cassino. [Tobacco prevention: results of a randomised controlled trial among adolescents in Cassino]. Riv Ital Med Adolesc 2:36–40
La Torre G, Chiaradia G, Ricciardi G (2005) School-based smoking prevention in children and adolescents: review of the scientific literature. J Public Health 13:285–290
Pampel FC, Aguilar J (2008) Changes in youth smoking, 1976–2002: a time-series analysis. Youth Soc 39:453–479
Perry CL, Kelder SH, Murray DM et al (1992) Communitywide smoking prevention: long-term outcomes of the Minnesota Heart Health Program and the Class of 1989 Study. Am J Public Health 82:1210–1216
Perry CL, Stigler MH, Arora M, Reddy KS (2009) Preventing tobacco use among young people in India: Project MYTRI. Am J Public Health 99:899–906
Peters LW, Wiefferink CH, Hoekstra F, Buijs GJ, Ten Dam GT, Paulussen TG (2009) A review of similarities between domain-specific determinants of four health behaviors among adolescents. Health Educ Res 24:198–223
Puska P, Vartiainen E, Pallonen U et al (1981) The North Karelia Youth Project. A community-based intervention study on CVD risk factors among 13- to 15-year-old children: study design and preliminary findings. Prev Med 10:133–148
Rasmussen M, Damsgaard MT, Due P, Holstein BE (2002) Boys and girls smoking within the Danish elementary school classes: a group-level analysis. Scand J Public Health 30:62–69
Resnicow K, Reddy SP, James S et al (2008) Comparison of two school-based smoking prevention programs among South African high school students: results of a randomized trial. Ann Behav Med 36:231–243
Richardson L, Hemsing N, Greaves L, Assanand S, Allen P, McCullough L, Bauld L, Humphries K, Amos A (2009) Preventing smoking in young people: a systematic review of the impact of access interventions. Int J Environ Res Public Health 6:1485–1514
Rooney BL, Murray DM (1996) A meta-analysis of smoking prevention programs after adjustment for errors in the unit of analysis. Health Educ Q 23:48–64
Rundall TG, Bruvold WH (1988) Meta-analysis of school-based smoking and alcohol use prevention programs. Health Educ Q 15:317–334
Sherman E, Primack BA (2009) What works to prevent adolescent smoking? A systematic review of the National Cancer Institute’s research-tested intervention programs. J Sch Health 79:391–399
Sowden A, Arblaster L, Stead L (2003) Community interventions for preventing smoking in young people. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1:CD001291
Thomas R (2002) School-based programmes for preventing smoking. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD001293
Thomas RE, Perera R (2006) School-based programmes for preventing smoking. Cochrane Database of Syst Rev 3:CD001293
Wold B, Torsheim T, Currie C, Roberts C (2004) National and school policies on restrictions of teacher smoking: a multilevel analysis of student exposure to teacher smoking in seven European countries. Health Educ Res 19:217–226
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the Heads and the teachers of the schools involved, particularly for their valuable contribution Prof. Lea Monte of “Comprensivo di Capodrise” (CE) and Prof. Claudia Moretti of Liceo Scientifico “Pellecchia”, Cassino (FR).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
La Torre, G., Chiaradia, G., Monte, L. et al. A randomised controlled trial of a school-based intervention to prevent tobacco use among children and adolescents in Italy. J Public Health 18, 533–542 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-010-0328-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-010-0328-8