Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to assess the clinical outcomes of palliative interventions for patients with incurable locally advanced or metastatic esophageal carcinoma.
Methods
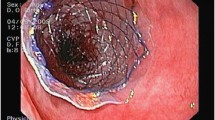
A total of 131 patients with thoracic esophageal carcinoma who underwent palliative interventions were enrolled. Insertion of a self-expandable metallic stent (SEMS), tube enterostomy for enteral nutrition (EN), and palliative esophagectomy (PE) were performed in 38, 65, and 28 patients, respectively. The clinicopathological characteristics and clinical outcomes of each group were retrospectively reviewed.
Results
Patients in the EN group frequently received chemoradiotherapy (P < 0.01). SEMS insertion, but not PE or EN, improved the mean dysphagia score after the intervention (P < 0.01). For the SEMS, EN, and PE groups, the occurrence of intervention-related complications was 31.6, 10.8, and 96.4%, respectively, the median survival time was 88, 208, and 226 days (P < 0.01), and the mean ratio of duration of home care to survival time was 28.9, 38.5, and 39.6% (P = 0.95).
Conclusions
SEMS insertion effectively relieved obstructive symptoms, but had no survival benefit. Tube enterostomy showed a low complication rate and has the potential to improve survival in combination with additional treatment, with no palliation of obstructive symptoms.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frenken M. Best palliation in esophageal cancer: surgery, stenting, radiation, or what? Dis Esophagus. 2001;14:120–3.
Homs MYV, Steyerberg EW, Eijkenboom WMH, et al. Single-dose brachytherapy versus metal stent placement for the palliation of dysphagia from oesophageal cancer: multicenter randomized trial. Lancet. 2004;364:1497–504.
Burstow M, Kelly T, Panchani S, et al. Outcome of palliative esophageal stenting for malignant dysphagia: a retrospective analysis. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:519–25.
Besharat S, Jabbari A, Semnami S, et al. Inoperable esophageal cancer and outcome of palliative care. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14:3725–8.
Yajima K, Kanda T, Nakagawa S, et al. Self-expandable metallic stents for palliation of malignant esophageal obstruction: special reference to quality of life and survival patients. Dis Esophagus. 2004;17:71–5.
Neil AC, Percival OB, Hiran CF, et al. Results of expandable metal stents for malignant esophageal obstruction in 100 patients: short-term and long-term follow-up. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71:1797–802.
Aoki T, Osaka Y, Takagi Y, et al. Comparative study of self-expandable metallic stent and bypass surgery for inoperable esophageal cancer. Dis Esophagus. 2001;14:208–11.
Tanaka T, Fujita H, Matono S, et al. Outcomes of multimodality therapy for stage IVB esophageal cancer with distant organ metastasis (M1-Org). Dis Esophagus. 2010;23:646–51.
George S, Ines G, Constantine K, et al. Survival after chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy versus self-expanding metal stent insertion in the setting of inoperable esophageal cancer: a case control study. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:70.
Battersby NJ, Bonney GK, Subar D, et al. Outcomes following oesophageal stent insertion for palliation of malignant strictures: a large single centre series. J Surg Oncol. 2012;105:60–5.
Siddiqui AA, Glynn C, Loren D, et al. Self-expanding plastic esophageal stents versus jejunostomy tubes for the maintenance of nutrition during neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in patients with esophageal cancer: a retrospective study. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:216–22.
Grilo A, Santos CA, Fonseca J. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy for nutritional palliation of upper esophageal cancer unsuitable for esophageal stenting. Arq Gastroenterol. 2012;49:227–31.
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C. TNM classification of malignant tumors. 7th ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010.
Neuhaus H, Hoffmann W, Dittler HJ, et al. Implantation of self-expanding esophageal metal stents for palliation of malignant dysphagia. Endoscopy. 1992;24:405–10.
Clavien PA, Barkun J, de Oliveira ML, et al. The Clavien–Dindo classification of surgical complications: five-year experience. Ann Surg. 2009;250:187–96.
Madhusudhan C, Saluja SS, Pal S, et al. Palliative stenting for relief of dysphagia in patients with inoperable esophageal cancer: impact on quality of life. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:331–6.
Diamantis G, Scarpa M, Bocus P, et al. Quality of life in patients with esophageal stenting for the palliation of malignant dysphagia. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:144–50.
Schoppmann SF, Langer FB, Prager G, et al. Outcome and complications of long-term self-expanding esophageal stenting. Dis Esophagus. 2013;26:154–8.
Stewart DJ, Balamurugan R, Everitt NJ, et al. Ten-year experience of esophageal self-expanding metal stent insertion at a single institution. Dis Esophagus. 2013;26:276–81.
Yokota T, Kato K, Hamamoto Y, et al. Phase II study of chemo-selection with docetaxel plus cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil induction chemotherapy and subsequent conversion surgery for locally advanced unresectable oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2016;115:1328–34.
Penniment MG, Deleso PB, Harvey JA, et al. Palliative chemoradiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for dysphagia in advanced oesophageal cancer: a multicentre randomised controlled trial (TROG 03.01). Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;3:114–24.
Murray LJ, Din OS, Kumar VS, et al. Palliative radiotherapy in patients with esophageal carcinoma: a retrospective review. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2012;2:257–64.
Welsch J, Kup PG, Nieder C, et al. Survival and symptom relief after palliative radiotherapy or esophageal cancer. J Cancer. 2016;7:125–30.
Nishimura Y, Nagata K, Katano S, et al. Severe complications in advanced esophageal cancer treated with radiotherapy after intubation of esophageal stents: a questionnaire survey of the Japanese Society for Esophageal Diseases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;56:1327–32.
Adamson D, Blazeby J, Nelson A, et al. Palliative radiotherapy in addition to self-expanding metal stent for improving dysphagia and survival in advanced oesophageal cancer (ROCS: Radiotherapy after Oesophageal Cancer Stenting): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. 2014;15:402.
Adler DG, Fang J, Wong R, et al. Placement of Polyflex stents in patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer is safe and improves dysphagia during neoadjuvant therapy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70:614–9.
Bower M, Jones W, Vessels B, et al. Nutritional support with endoluminal stenting during neoadjuvant therapy for esophageal malignancy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16:3161–8.
Fayers PM, Aaronson NK, Bjordal K, on behalf of the EORTC Quality of Life Group, et al. The EORTC QLQ-C30 scoring manual. 3rd ed. Brussels: EORTC; 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kakuta, T., Kosugi, Si., Ichikawa, H. et al. Palliative interventions for patients with incurable locally advanced or metastatic thoracic esophageal carcinoma. Esophagus 16, 278–284 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-019-00665-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-019-00665-0