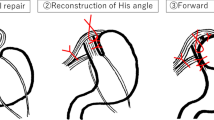
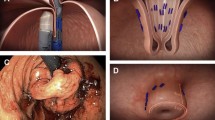
Abstract
Background
Surgical results of GERD have mainly been reported from the Western countries, with a few reports found in Japan. We examined the surgical results of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication and clarify the characteristics of recurrent cases.
Methods
The subjects included 375 patients who underwent laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication from June 1997 to December 2016 as the initial surgery. Patient characteristics, pathophysiology, and surgical results were examined. In addition, we compared the patient characteristics and pathophysiology of recurrent cases in comparison with non-recurrent cases.
Results
Age 59 (43–70) and male 211 (56.3%). The operation time was 141 min (113–180) and intraoperative complications were found to have onset in 13 subjects (3.5%). Dysphagia after surgery was found in 18 cases (4.8%). The A factor (the degree of hiatal hernia), P factor (the degree of esophagitis), and pH < 4 holding time significantly improved after surgery compared with prior to surgery (p < 0.001 for all), while the LES lengths and abdominal LES lengths were extended (p < 0.001 for each). Recurrence was found in 48 patients (15.1%) among the 318 patients for whom we could confirm the presence or absence of recurrence. The A factor, P factor, and pH < 4 holding time prior to surgery were, respectively, higher in the recurrence group (p = 0.031, p < 0.001, p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication for GERD could be performed safely, with a response rate as good as 85%. Compared with non-recurrent cases, preoperative clinical conditions such as esophageal hiatal hernia, reflux esophagitis, and acid reflux time were all advanced in recurrent cases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chrysos E, Tsiaoussis J, Athanasakis E, et al. Laparoscopic vs open approach for Nissen fundoplication: a comparative study. Laparoscopic Surg Endosc. 2002;16:1679–84.
Gee DW, Andreoli MT, Rattner DW. Measuring the effectiveness of laparoscopic antireflux surgery: long-term results. Arch Surg. 2008;143:482–7.
Roks DJ, Broeders JA, Baigrie RJ. Long-term symptom control of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease 12 years after laparoscopicNissen or 180° anterior partial fundoplication in a randomized clinical trial. Br J Surg. 2017;104:852–6.
Koetje JH, Nieuwenhuijs VB, Irvine T, et al. Measuring outcomes of laparoscopic anti-reflux surgery: quality of life versus symptom scores? World J Surg. 2016;40:1137–44.
Koch OO, Kaindlstorfer A, Antoniou SA. et al. Comparison of results from a randomized trial 1 year after laparoscopic Nissen and Toupet fundoplications. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:2383–90.
Broeders JA, Mauritz FA, Ahmed Ali U, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of laparoscopic Nissen (posterior total) versus Toupet (posterior partial) fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg. 2010;97:1318–30.
Tian ZC, Wang B, Shan CX, et al. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to compare long-term outcomes of Nissen and Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0127627. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127627. eCollection 2015.
Feussner H, Petri A, Walker S, et al. The modified AFP score: an attempt to make the results of anti-reflux surgery comparable. Br J Surg. 1991;78:942–6.
Matthews HR. A proposed classification for hiatal hernia and gastroesophageal reflux. Dis Esophagus. 1996;9:1–3.
Ismail T, Bancewicz J, Barlow J. Yield pressure, anatomy of the cardia and gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg. 1995;82:943–7.
Dallemagne B, Weerts JM, Jehaes C, et al. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1991;1:138–43.
Omura N, Kashiwagi H, Yano F, et al. Postoperative recurrence factors of GERD in the elderly after laparoscopic fundoplication. Esophagus. 2010;7:31–5.
Katada N, Moriya H, Yamashita K, et al. Laparoscopic antireflux surgery improves esophageal body motility in patients with severe reflux esophagitis. Surg Today. 2014;44:740–7.
Schwameis K, Zehetner J, Rona K, et al. Post-Nissen dysphagia and bloating syndrome: outcomes after conversion to Toupet fundoplication. J Gastrointest Surg. 2017;21:441–5.
Frazzoni M, Piccoli M, Conigliaro R, et al. Laparoscopic fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:14272–9.
Simorov A, Ranade A, Jones R, et al. Long-term patient outcomes after laparoscopic anti-reflux procedures. J Gastrointest Surg. 2014;18:157–62 (discussion 162–3).
Hoshino M, Omura N, Yano F, et al. Backflow prevention mechanism of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication using high-resolution manometry. Surg Endosc. 2016;30:2703–10.
Tekin K, Toydemir T, Yerdel MA. Is laparoscopic antireflux surgery safe and effective in obese patients? Surg Endosc. 2012;26:86–95.
Hoshino M, Omura N, Yano F, et al. Effects of the body mass index (BMI) on the surgical outcomes of laparoscopic fundoplication for gastro-esophageal reflux disease: a propensity score-matched analysis. Surg Today. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-017-1579-6 (Epub ahead of print).
Morgenthal CB, Lin E, Shane MD, et al. Who will fail laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication? Preoperative prediction of long-term outcomes. Surg Endosc. 2007;21:1978–84.
Staehelin A, Zingg U, Devitt PG, et al. Preoperative factors predicting clinical outcome following laparoscopic fundoplication. World J Surg. 2014;38:1431–43.
Power C, Maguire D, McAnena O. Factors contributing to failure of laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication and the predictive value of preoperative assessment. Am J Surg. 2004;187:457–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NO analyzed data and wrote the manuscript. FY, KT, MH, S-RY, SA, TM, and HK collected data. KY critically revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
The protocol of this study has been approved by the Jikei University School of Medicine Institutional Review Board (#28–047). All informed consent was obtained from the subjects and guardians.
Conflict of interest
Drs. Omura, Yano, Tsuboi, Hoshino, Yamamoto, Akimoto, Masuda, Kashiwagi, and Yanaga have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Omura, N., Yano, F., Tsuboi, K. et al. Surgical results of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease with special reference to recurrence. Esophagus 15, 217–223 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-018-0616-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-018-0616-x