Abstract
Background
The purpose of this research is to determine the correlation between IGFBP-4/IGF-I expression and the clinical status of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Materials and methods
Immunohistochemical staining for IGFBP-4 and IGF-I was performed in 61 clinical samples. The correlation between IGFBP-4/IGF-I staining and clinicopathological features was examined statistically. In addition, we compared the mRNA expression levels of IGFBP-4 and IGF-I between ESCC cancer tissues and the normal esophageal epithelium using a quantitative real-time RT-PCR.
Results
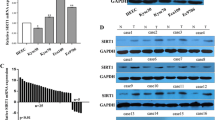
According to the results of immunohistochemical staining, IGFBP-4 expression in the region of normal epithelial cells showed an increase of 52.5 % compared to expression in the tumor cells. There was no statistically significant correlation between IGFBP-4/IGF-I and clinicopathological features. The correlation between IGF-I and IGFBP-4 was not significant either. RT-PCR assay showed IGF-I expression in ESCC tissue has a tendency to be higher than that of normal esophageal epithelium. On the other hand, IGFBP-4 expression levels in cancer tissue were lower in comparison with normal epithelium. These results were not significant.
Conclusions
There were the differences of IGFBP-4 expression between the region of ESCC and the region of normal epithelium cells. One suggested possibility is that IGF-independent action of IGFBP-4 might have taken part in these results. We need further exploratory experiments to elucidate the details of the actual function of IGFBP-4 expression in ESCC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohick WS, Clemmons DR. The insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1993;55:131–53.
Stewart CE, Rotwein P. Growth, differentiation, and survival: multiple physiological functions for insulin-like growth factors. Physiol Rev. 1996;76:1005–26.
Mohan S, Baylink DJ. IGF-binding proteins are multifunctional and act via IGF-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Endocrinol. 2002;175:19–31.
Butler AA, LeRoith D. Minireview: tissue-specific versus generalized gene targeting of the IGF1 and IGF1R genes and their roles in insulin-like growth factor physiology. Endocrinology. 2001;142:1685–8.
Bach LA, Hsieh S, Sakano K, Fujiwara H, Perdue JF, Rechler MM. Binding of mutants of human insulin-like growth factor II to insulin-like growth factor binding proteins 1–6. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:9246–54.
Kelley KM, Oh Y, Gargosky SE, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBPs) and their regulatory dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1996;28:619–37.
Clemmons DR. Use of mutagenesis to probe IGF-binding protein structure/function relationships. Endocr Rev. 2001;22:800–17.
Durai R, Davies M, Yang W, et al. Biology of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 and its role in cancer (review). Int J Oncol. 2006;28:1317–25.
Cheung PT, Smith EP, Shimasaki S, Ling N, Chernausek SD. Characterization of an insulin-like growth factor binding protein (IGFBP-4) produced by the B104 rat neuronal cell line: chemical and biological properties and differential synthesis by sublines. Endocrinology. 1991;129:1006–15.
Ceda GP, Fielder PJ, Henzel WJ, et al. Differential effects of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-II on the expression of IGF binding proteins (IGFBPs) in a rat neuroblastoma cell line: isolation and characterization of two forms of IGFBP-4. Endocrinology. 1991;128:2815–24.
Mohan S, Nakao Y, Honda Y, et al. Studies on the mechanisms by which insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein-4 (IGFBP-4) and IGFBP-5 modulate IGF actions in bone cells. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:20424–31.
Zhu W, Shiojima I, Ito Y, et al. IGFBP-4 is an inhibitor of canonical Wnt signalling required for cardiogenesis. Nature. 2008;454:345–9.
Bostedt KT, Schmid C, Ghirlanda-Keller C, Olie R, Winterhalter KH, Zapf J. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I down-regulates type 1 IGF receptor (IGF 1R) and reduces the IGF I response in A549 non-small-cell lung cancer and Saos-2/B-10 osteoblastic osteosarcoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 2001;271:368–77.
Dai B, Widen SG, Mifflin R, Singh P. Cloning of the functional promoter for human insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 gene: endogenous regulation. Endocrinology. 1997;138:332–43.
Ng EH, Ji CY, Tan PH, Lin V, Soo KC, Lee KO. Altered serum levels of insulin-like growth-factor binding proteins in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 1998;5:194–201.
Diehl D, Hoeflich A, Wolf E, Lahm H. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-4 inhibits colony formation of colorectal cancer cells by IGF-independent mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1600–3.
Park JH, Corkins MR, Vanderhoof JA, et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor-II and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins during Caco-2 cell proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1996;166:396–406.
Hoeflich A, Yang Y, Huber S, et al. Expression of IGFBP-2, -3, and -4 mRNA during differentiation of Caco-2 colon epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:E922–31.
Corkins MR, McQuade J, Schaffer BS, MacDonald RG. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-4 expression is dependent on the carbohydrate in the media in HT-29 cells. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2002;12:184–92.
Remacle-Bonnet MM, Garrouste FL, Pommier GJ. Surface-bound plasmin induces selective proteolysis of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-4 (IGFBP-4) and promotes autocrine IGF-II bio-availability in human colon-carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1997;72:835–43.
Guo YS, Beauchamp RD, Jin GF, Townsend CM Jr, Thompson JC. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein modulates the growth response to insulin-like growth factor 1 by human gastric cancer cells. Gastroenterology. 1993;104:1595–604.
Yi HK, Hwang PH, Yang DH, Kang CW, Lee DY. Expression of the insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and the IGF-binding proteins (IGFBPs) in human gastric cancer cells. Eur J Cancer. 2001;37:2257–63.
Takaoka M, Kim SH, Okawa T, et al. IGFBP-3 regulates esophageal tumor growth through IGF-dependent and independent mechanisms. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6:534–40.
Salahshor S, Naidoo R, Serra S, et al. Frequent accumulation of nuclear E-cadherin and alterations in the Wnt signaling pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:271–81.
Peng H, Zhong XY, Liu KP, Li SM. Expression and significance of adenomatous polyposis coli, beta-catenin, E-cadherin and cyclin D1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma assessed by tissue microarray. Ai Zheng. 2009;28:38–41.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isozaki, Y., Hoshino, I., Akutsu, Y. et al. Role of IGFBP4 and IGF-I expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus 10, 79–85 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-013-0368-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-013-0368-6