Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the frequency of infraorbital nerve enlargement (IONE) in orbital lymphoproliferative disorders, and to show that IONE can contribute to the clinical diagnosis of IgG4-related orbital diseases (IgG4-ROD).
Subjects and methods
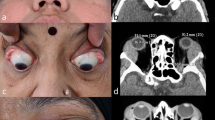
71 cases in which orbital lymphoproliferative disorders were diagnosed at Okayama Medical Center and Mitoyo General Hospital from April, 2004 to March, 2011 were investigated. The male-to-female ratio was 39:32, and the age range 27–87 years old (average age 64.1 years). Whenever the coronal section of the infraorbital nerve was larger than that of the optic nerve on MRI, it was defined as IONE.
Results
The breakdown of the 71 cases was: 45 cases of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, 16 cases of IgG4-ROD, 5 cases of reactive lymphoid hyperplasia, and 5 cases of idiopathic orbital inflammation. Of these, a total of 9 cases had IONE. The incidence of IONE was compared between the IgG4-ROD patient group and the non-IgG4-ROD patient group and was significantly higher in the IgG4-ROD patient group (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion
If IONE is observed in a case of orbital lymphoproliferative disorders on MRI, then it is highly possible that such a case is IgG4-ROD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sato Y, Ohshima K, Ichimura K, Sato M, Yamadori I, Tanaka T, et al. Ocular adnexal IgG4-related disease has uniform clinicopathology. Pathol Int. 2008;58:465–70.
Sato Y, Notohara K, Kojima M, Takata K, Masaki Y, Yoshino T, et al. IgG4-related disease: historical overview and pathology of hematological disorders. Pathol Int. 2010;60:247–58.
Oyama T, Takizawa J, Nakamura N, Aoki S, Aizawa Y. Abe H Multifocal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma associated with IgG4-related disease: a case report. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2011;55:304–6.
De Potter P, Dolinskas C, Shields CL, Shields JA. Lymphoproliferative and histiocytic disorders. In: De Potter P, Shields CL, Shields JA, editors. MRI of the eye and orbit. Philadelphia: J. B. Lippincott Company; 1995. p. 245–53.
Sato Y, Kojima M, Takata K, Morito T, Asaoku H, Takeuchi T, et al. Systemic IgG4-related lymphadenopathy: a clinical and pathologic comparison to multicentric Castleman’s disease. Mod Pathol. 2009;22:589–99.
Cheuk W. IgG4-related sclerosing disease. A critical appraisal of an evolving clinicopathologic entity. Adv Anat Pathol. 2010;17:303–32.
Watanabe T, Fujinaga Y, Kawakami S, Hatta T, Hamano H, Kawa S, et al. Infraorbital nerve swelling associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Jpn J Radiol. 2011;29:194–201.
Katsura M, Morita A, Horiuchi H, Ohtomo K, Machida T. IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the trigeminal nerve: another component of IgG4-related sclerosing disease? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2256.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ohshima, Ki., Sogabe, Y. & Sato, Y. The usefulness of infraorbital nerve enlargement on MRI imaging in clinical diagnosis of IgG4-related orbital disease. Jpn J Ophthalmol 56, 380–382 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-012-0151-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-012-0151-6