Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the clinical characteristics of patients with idiopathic optic neuritis (ON) in Taiwan and to assess the conversion rate to multiple sclerosis (MS) in these patients.
Methods
We studied the medical records of a total of 109 patients with a clinical diagnosis of idiopathic ON treated in the Taipei Veterans General Hospital during the period from January 1986 to May 2003. Clinical characteristics, management, and disease courses were retrospectively reviewed. Our main focus was on the development of multiple sclerosis after an ON attack. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to evaluate the risk indicators for MS conversion.
Results
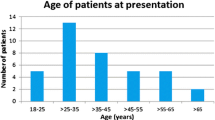
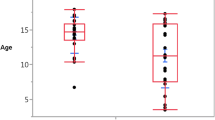
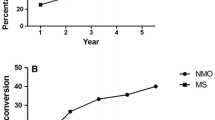
The patients (58 women, 51 men) had a mean age of 41.2 years at onset. ON was retrobulbar in 46.8% of the patients. Management with or without pulse therapy did not affect the final visual outcome. Female sex, retrobulbar type ON, recurrent cases, elevated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) IgG index, and central nervous system (CNS) imaging abnormalities were identified as risk indicators for the development of MS (P < 0.05). The 2-year cumulative probability of developing MS was 5.92%, and the 5-year cumulative probability was 14.28%. The conversion rate to MS did not differ among treatment groups.
Conclusions
Idiopathic ON patients in Taiwan have an older age at onset and a higher percentage of optic disc edema than reported in previous literature. The characteristic features of ON patients associated with a high risk of developing MS are female sex, retrobulbar type ON, CNS imaging abnormalities, elevated CSF IgG index, and recurrence. Idiopathic ON patients in Taiwan display a significantly lower conversion rate to MS. Jpn J Ophthalmol 2006;50:170–175 © Japanese Ophthalmological Society 2006
Similar content being viewed by others
References
GD Perkin CF Rose (1979) Optic neuritis and its differential diagnosis Oxford Medical Publications Oxford
WB Roy (1998) Optic neuritis. Walsh and Hoyt's clinical neuro-ophthalmology EditionNumber5th ed, Vol. 1. Williams & Wilkins Baltimore 599–639
M Söderström (2001) ArticleTitleReview article: optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis Acta Ophthalmol Scand 79 223–227 Occurrence Handle11401627
M Sandberg-Wollheim H Bynke S Cronqvist et al. (1990) ArticleTitleA long-term prospective study of optic neuritis: evaluation of risk factors Ann Neurol 27 386–393 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ana.410270406 Occurrence Handle2353793 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BB1c3ktlA%3D
M Rodriquez A Siva SA Cross et al. (1995) ArticleTitleOptic neuritis: a population-based study in Olmsted County, Minnesota Neurology 45 244–245
JI O'Riordan AJ Thompson DP Kingsley et al. (1998) ArticleTitleThe prognostic value of brain MRI in clinically isolated syndromes of the CNS. A 10-year follow-up Brain 121 495–503 Occurrence Handle10.1093/brain/121.3.495 Occurrence Handle9549525
M Söderström J Ya-Ping J Hillert et al. (1998) ArticleTitleOptic neuritis. Prognosis for multiple sclerosis from MRI, CSF and HLA findings Neurology 50 708–714 Occurrence Handle9521261
Y Isayama T Takahashi T Shimoyoma et al. (1982) ArticleTitleAcute optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis Neurology 32 73–76 Occurrence Handle7198735 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi2C3cvjsFA%3D
T Corona-Vazquez J Ruiz-Scadoval N Arriada-Mendicoa (1997) ArticleTitleOptic neuritis progression to multiple sclerosis Acta Neurol Scand 95 85–89 Occurrence Handle9059726 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB3M3ptVw%3D
SM Leary DH Miller VL Stevenson et al. (2003) ArticleTitleInterferon beta-1a in primary progressive MS: an exploratory, randomized, controlled trial Neurology 60 44–51 Occurrence Handle12525716 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xps1aiu74%3D
DM Wingerchuk JH Noseworthy (2002) ArticleTitleRandomized controlled trials to assess therapies for multiple sclerosis Neurology 58 S40–S48 Occurrence Handle11971125 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjslSqsrk%3D
RW Beck FR Arrington J Murtagh et al. (1993) ArticleTitleBrain magnetic resonance imaging in acute optic neuritis. Experience of the Optic Neuritis Study Group Arch Neurol 50 841–846 Occurrence Handle8352671 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyA2MnmsFI%3D
RW Beck PA Cleary (1993) ArticleTitleOptic Neuritis Treatment Trial: one-year follow-up results Arch Ophthalmol 111 773–775 Occurrence Handle8512477 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB1M%2FlsVE%3D
CM Poser DW Paty L Scheinberg et al. (1983) ArticleTitleNew diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols Ann Neurol 13 227–231 Occurrence Handle6847134 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiyB3c3ntlM%3D
M Alter J Good M Okihiro (1973) ArticleTitleOptic neuritis in Orientals and Caucasians Neurology 23 631–639 Occurrence Handle4736309 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSyC1Mzot1Y%3D
RW Beck PA Cleary JD Trobe InstitutionalAuthorNameand the Optic Neuritis Study Group et al. (1993) ArticleTitleThe effect of corticosteroids for acute optic neuritis on the subsequent development of multiple sclerosis N Engl J Med 329 1764–1769 Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM199312093292403 Occurrence Handle8232485 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD2M%2FgsF0%3D
InstitutionalAuthorNameOptic Neuritis Study Group (1991) ArticleTitleThe clinical profile of acute optic neuritis: experience of the Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial Arch Ophthalmol 109 1673–1678
MA Hely PG McManis TJ Doran et al. (1986) ArticleTitleAcute optic neuritis: a prospective study of risk factors for multiple sclerosis J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 49 1125–1130 Occurrence Handle3783173 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiD2MbovFc%3D
InstitutionalAuthorNameThe Optic Neuritis Study Group (1997) ArticleTitleThe 5-year risk of MS after optic neuritis: experience of the Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial Neurology 49 1404–1413
LD Jacobs SE Kaba CM Miller et al. (1997) ArticleTitleCorrelation of clinical, magnetic resonance imaging, and cerebrospinal fluid findings in optic neuritis Ann Neurol 41 392–398 Occurrence Handle9066361 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByiB3Mbgs1U%3D
JL Frederiksen J Petrera (1999) ArticleTitleSerial visual evoked potentials in 90 untreated patients with acute optic neuritis Surv Ophthalmol 44 IssueIDSuppl 1 S54–S62 Occurrence Handle10548117
SP Morrissey DH Miller BE Kendall et al. (1993) ArticleTitleThe significance of brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities at presentation with clinical isolated syndromes suggestive of multiple sclerosis Brain 116 135–146 Occurrence Handle8453454
PH Phillips NJ Newman MJ Lynn (1998) ArticleTitleOptic neuritis in African-Americans Arch Neurol 55 186–192 Occurrence Handle10.1001/archneur.55.2.186 Occurrence Handle9482360 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7ktFCltg%3D%3D
I Nakashima K Fujihara T Mitsu et al. (2001) ArticleTitleEpidemiology and clinical features of optico-spinal form multiple sclerosis in Japan (in Japanese) No To Shinkei (Brain and Nerve) 53 911–917 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MnnvFCitw%3D%3D
JL Frederiksen HBW Larsson J Oleson (1992) ArticleTitleCorrelation of magnetic resonance imaging and CSF findings in patients with acute monosymptomatic optic neuritis Acta Neurol Scand 86 317–322 Occurrence Handle1414254 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyD3svhsVI%3D
LA Rolak RW Beck DW Paty InstitutionalAuthorNameand the Optic Neuritis Study Group et al. (1996) ArticleTitleCerebrospinal fluid in acute optic neuritis: experience of the Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial Neurology 46 368–372 Occurrence Handle8614496 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymC1c7psFw%3D
RW Beck PA Cleary MM Anderson SuffixJr et al. (1992) ArticleTitleA randomized, controlled trial of corticosteroids in the treatment of acute optic neuritis N Engl J Med 326 581–588 Occurrence Handle1734247 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2C3s7gslA%3D
M Wakakura K Mashimo S Oono et al. (1999) ArticleTitleMulticenter clinical trial for evaluating methylprednisolone pulse treatment of idiopathic optic neuritis in Japan Jpn J Ophthalmol 43 133–138 Occurrence Handle10340796 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXit1Wltbg%3D
InstitutionalAuthorNameThe Optic Neuritis Study Group (1997) ArticleTitleVisual function 5 years after optic neuritis: experience of the Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial Arch Ophthalmol 115 1545–1552
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YC., Yen, MY., Hsu, WM. et al. Low Conversion Rate to Multiple Sclerosis in Idiopathic Optic Neuritis Patients in Taiwan. Jpn J Ophthalmol 50, 170–175 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-005-0281-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-005-0281-1