Summary
Background
There is a considerable clinical need for a sufficient prosthetic small-diameter substitute which can compete with autologous vessels. Currently used synthetic materials have a poor performance due to high thrombogeneicity and development of intimal hyperplasia. Tissue engineering is an interesting alternative approach for vascular graft fabrication.
Methods
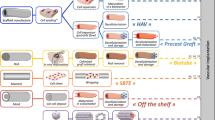
We briefly overviewed the development of tissue-engineered vascular substitutes including endothelialized biohybrid grafts, collagen and fibrin-based scaffolds, decellularized scaffolds, cell self-assembly approaches, and biodegradable constructs based on synthetic polymers.
Results
Significant advances have been made over the past decades in the development of tissue-engineered conduits. Biomechanical weakness, one of the major limitations of biologically based grafts has been resolved and two tissue-engineered grafts are currently under further investigation for clinical application.
Conclusions
Vascular tissue engineering is a promising approach to overcome the limitations of current therapies in small-diameter vascular replacement.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xue L, Greisler HP. Biomaterials in the development and future of vascular grafts. J Vas Surg. 2003;37:472–80.
Kakisis JD, Liapis CD, Breuer C, Sumpio BE. Artificial blood vessel: the holy grail of peripheral vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg. 2005;41:349–54.
Wang X, Lin P, Yao Q, Chen C. Development of small-diameter vascular grafts. World J Surg. 2007;31:682–9.
Venkatraman S, Boey F, Lao LL. Implanted cardiovascular polymers: natural, synthetic and bio-inspired. Prog Polym Sci. 2008;33:853–74.
Brewster DC. Prosthetic grafts. In: Rutherford RB, editor. Vascular surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 2000. pp 559–84.
Klinkert P, Post PN, Breslau PJ, van Bockel JH. Saphenous vein versus PTFE for above-knee femoropopliteal bypass. A review of the literature. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004;27:357–62.
Weitz JI, Byrne J, Clagett P, Farkouh ME, Porter JM, Sackett DL, Strandness DE, Taylor LM. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic arterial insufficiency of the lower extremities: a critical review. Circulation. 1996;94:3026–49.
Loh SA, Howell BS, Rockman CB, Cayne NS, Adelman MA, Gulkarov I, Veith FJ, Maldonado TS. Ann Mid- and long-term results of the treatment of infrainguinal arterial occlusive disease with precuffed expanded polytetrafluoroethylene grafts compared with vein grafts. Vasc Surg. 2013;27:208–17.
Pereira CE, Albers M, Romiti M, Brochado-Neto FC, Pereira CA. Meta-analysis of femoropopliteal bypass grafts for lower extremity arterial insufficiency. J Vasc Surg. 2006;44:510–7.
de Mel A, Jell G, Stevens MM, Seifalian AM. Biofunctionalization of biomaterials for accelerated in situ endothelialization: a review. Biomacromolecules. 2008;9:2969–79.
Jordan SW, Chaikof EL. Novel thromboresistant materials. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45:104A–15A.
Zilla P, Bezuidenhout D, Human P. Prostheic vascular grafts: wrong models, wrong questions and no healing. Biomaterials. 2007;28:5009–27.
Kapadia MR, Popwich DA, Kibbe MR. Modified prosthetic vascular conduits. Circulation. 2008;117:1873–82.
Nerem RM, Seliktar D. Vascular tissue engineering. Annu Rev Eng. 2001;3:225–43.
Isenberg BC, Chrysanthi W, Tranquillo RT. Small-diameter artificial arteries engineered in vitro. Circ Res. 2006;98:25–35.
Ratcliffe A. Tissue engineering of vascular grafts. Matrix Biol. 2000;19:353–7.
L’Heraux N, Dusserre N, Garrido S, de la Fuente L, McAllister T. Technology insight: the evolution of tissue-engineered vascular grafts-from research to clinical practice. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007;4:389–95.
Herring MB. Endothelial cell seeding. J Vasc Surg. 1991;13:731–2.
Herring M, Smith J, Dalsing M, Glover J, Compton R, Etchberger K, Zollinger T. Endothelial seeding of polytetrafluoroethylene femoral popliteal bypasses: the failure of low-density seeding to improve patency. J Vasc Surg. 1994;20:650–5.
Pasic M, Müller-Glauser W, von Segesser LK, Lachat M, Mihaljevic T, Turina MI. Superior late patency of small-diamter dDacron grafts seeded with omental microvascular cells: an experimental study. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58:677–83.
Zilla P, Deutsch M, Meinhart J. Endothelial cell transplantation. Semin Vasc Surg. 1999;12:52–63.
Zilla P, Fasol R, Deutsch M, Fischlein T, Minar E, Hammerle A, Krupicka O, Kadletz M, Meinhart J. Endothelial cell seeding of polytetrafluoroethylene vascular grafts in humans: a preliminary report. J Vasc Surg. 1987;6:535–22.
Feugier P, Black RA, Hunt JA, How TV. Attachment, morphology and adherence of human endothelial cells to vascular prosthesis materials under the action of shear stress. Biomaterials. 2005;26:1457–66.
Baguneid M, Murray D, Salacinski HJ, Fuller B, Hamilton G, Walker M, Seifalian AM. Shear stress preconditioning and tissue-engineering-based paradigms for generating arterial substitutes. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2004;39:151–7.
Deutsch M, Meinhart J, Zilla P, Howanitz N, Gorlitzer M, Froeschl A, Stuempflen A, Bezidenhout D, Grabenwoeger M. Long-term experience in autologous in vitro endothelialisation of infrainguinal ePTFE grafts. J Vasc Surg. 2009;49:352–62.
Parikh SA, Edelman ER. Endothelial cell delivery for cardiovascular therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2000;42:139–61.
Meinhart JG, Schense JC, Schima H, Gorlitzer M, Hubbel JA, Deutsch M, Zilla P. Enhanced endothelial cell retention on shear-stressed synthetic vascular grafts precoated with RGD-cross-linked fibrin. Tissue Eng. 2005;11:887–95.
Weinberg CB, Bell E. A blood vessel model constructed from collagen and cultured vascular cells. Science. 1986;231:397–400.
L’Heraux N, German L, Labbe R, Auger FA. In vitro construction of a human blood vessel from cultured vascular cells: a morphologic study. J Vasc Surg. 1993;17:499–509.
Girton TS, Oegama TR, Grassl ED, Isenberg BC, Tranquillo RT. Mechanisms of stiffening and strengthening in media-equivalents fabricated using glycation. J Biomech Eng. 2000;122:216–23.
Swartz DD, Russel JA, Andreadis ST. Engineering of fibrin-based functional and implantable small-diameter blood vessels. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:1451–60.
Barocas VH, Girton TS, Tranquillo RT. Enginered alignment in media equivalents: magnetic prealignment and mandrel compaction. J Biomech Eng. 1998;120:660–6.
Syedain ZH, Meier LA, Bjork JW, Lee A, Tranquillo RT. Implantable arterial grafts from human fibroblasts and fibrin using a multi-graft pulsed flow-stretch bioreactor with noninvasive strength monitoring. Biomaterials. 2011;32:714–22.
Schmidt CE, Baier JM. Acellular vascular tissues: natural biomaterials for tissue repair and tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2000;21:2215–31.
Wilson GJ, Courtman DW, Klement P, Lee JM, Yeger H. Acellular matrix: a biomaterials approach for coronary artery bypass and heart valve replacement. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995;60:353–8.
Ketchedjian A, Jones AL, Krueger P, Robinson E, Crouch K, Wolfinbarger L, Hopkins R. Recellularization of decellularized allograft scaffolds in ovine great vessel reconstructions. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79:888–96.
Mc Fetridge PS, Daniel JW, Bodamyali T, Horrocks M, Chaudhuri JB. Preparation of porcine carotid arteries for vascular tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2004;70:224–34.
Conklin BS, Wu H, Lin PH, Lumsden AB, Chen C. Basic fibroblast growth factor coating and endothelial cell seeding of a decellularized heparin-coated vascular graft. Artif Organs. 2004;28:668–75.
Kaushal S, Amiel GE, Guleserian KJ, Shapira OM, Perry T, Sutherland FW, Rabkin E, Moran AM, Schoen FJ, Atala A, Soker S, Bischoff J, Mayer JE. Functional small diameter neovessels created using endothelial progenitor cells expanded ex vivo. Nat Med. 2001;7:1035–40.
Andree B, Bär A, Haverich A, Hilfiker A. Small intestinal submucosa segments as matrix for tissue engineering: review. Tiss Eng Part B Rev. 2013 Jan 14;19(4):279–91.
Bergmeister H, Boeck P, Kasimir M, Fleck T, Fitzal F, Husinsky W, Mittlboeck M, Stoehr H, Losert U, Wolner E, Grabenwoeger M. Effect of laser perforation on the remodeling of acellular matrix grafts. J Biomed Mater Res B: Appl Biomater. 2005;74:495–503.
Bergmeister H, Plasenzotti R, Walter I, Plass C, Bastian F, Rieder E, Sipos W, Kaider A, Losert U, Weigel G. Decellularized xenogeneic small-diameter arteries: transition from a muscular to an elastic phenotype in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2008;87:95–104.
L’Heraeux N, Paquet S, Lacoe R, Germain L, Auger FA. A completely biological tissue engineered human blood vessel. FASEB J. 1998;12:47–56.
Peck M, Gebhart D, Dusserre N, McAllister T, L’Heraeux N. The evolution of vascular tissue engineering and current state of the art. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;195:144–58.
Niklason LE, Gao J, Abbott WM, Hirschi KK, Houser S, Marini R, Langer R. Functional arteries grown in vitro. Science. 1999;284:489–93.
Shin’oka T, Imai Y, Ikada Y. Transplantation of tissue-engineered pulmonary artery. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:532–3.
Qint C, Arief M, Muto A, Dradik A, Niklason LE. Allogeneic human tissue-engineered blood vessel. J Vasc Surg. 2012;55:790–8.
Dahl SL, Blum JL, Niklason LE. Bioengineered vascular grafts: can we make them of off-the-shelf? Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2011;21:83–9.
Vasita R, Katti DS. Nanofibers and their applications in tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2006;1:15–30.
Wu W, Allen RA, Wang Y. Fast-degrading elastomer enables rapid remodeling of a cell-free synthetic graft into a neoartery. Nat Med. 2012;18:1148–53.
De Valence S, Tille JC, Mugnal D, Mrowczynski W, Gurny R, Möller M, Walpoth BH. Long term performance of polycaprolactone vascular grafts in a rat abdominal aorta replacement model. Biomaterials. 2012;33:38–47.
Pham QP, Sharma U, Mikos AG. Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for tissue engineering applications: a review. Tissue Eng. 2006;12:1197–211.
Prabhakaran MP, Ghasemi-Mobarakeh L, Ramakrishna S. Electrospun composite nanofibers for tissue engineering regeneration. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11:3039–57.
Kong X, Han B, Li H, Liang Y, Shao K, Liu W. New biodegradable small-diameter artificial vascular prosthesis: a feasibility study. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2012;100A:1494–1504.
Szentivanyi A, Chakradeo T, Zernetsch H, Glasmacher B. Electrospun cellular microenvironments: understanding controlled release and scaffold structure. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2011;63:209–20.
Sill TJ, von Recum HA. Electrospinning: applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2008;29:1989–2006.
Sell SA, McClure MJ, Barnes CP, Knapp DC, Walpoth BH, Simpson DG, Bowlin GL. Electrospun polydioxanone-elastin blends: potential for bioresorbable vascular grafts. Biomed Mater. 2006;1:72–80.
Grasl C, Bergmeister H, Stoiber M, Schima H, Weigel G. Electrospun polyurethane vascular grafts: in vitro mechanical behaviour and endothelial adhesion molecule expression. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93:716–23.
Bergmeister H, Schreiber C, Grasl C, Walter I, Plasenzotti R, Stoiber M, Bernhard D, Schima H. Healing characteristics of electrospun polyurethane grafts with various porosities. Acta Biomater. 2013;9:6032–40.
Bergmeister H, Grasl C, Walter I, Plasenzotti R, Stoiber M, Losert U, Weigel G, Schima H. Electrospun small-diameter polyurethane vascular grafts: ingrowth and differentiation of vascular specific host cells. Artif Organs. 2012;36:54–61.
Baudis S, Ligon SC, Seidler K, Weigel G, Grasl C, Bergmeister H, Schima H, Liska R. Hard-block degradable thermoplastic urethane-elastomers for electrospun vascular prostheses. J Polym Sci Part A: Polym Chem. 2012;50:1272–80.
Bergmeister H, Baudis S, Grasl C, Stoiber M, Schreiber C, Walter I, Plasenzotti R, Liska R, Schima H. In vivo evaluation of electrospun, biodegradable and non-degradable elastomeric vascular grafts. Int J Art Organs. 2011;34:641.
Conflict of interest
Helga Bergmeister, Magdalena Strobl, Christian Grasl, Robert Liska, and Heinrich Schima declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergmeister, H., Strobl, M., Grasl, C. et al. Tissue engineering of vascular grafts. Eur Surg 45, 187–193 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-013-0224-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-013-0224-x