Abstract
Purpose
We report the results of the cleft lift procedure in the management of nonacute pilonidal sinus disorders.
Methods
Seventy consecutive patients who underwent a cleft lift for nonacute pilonidal sinus were evaluated prospectively. Responses to a postal questionnaire were analyzed for long-term outcome.
Results
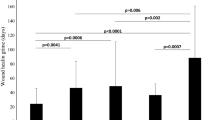
All patients who fulfilled the criteria for day-case were operated on as such. Sixty-six patients achieved complete wound healing within six weeks. Delayed wound healing occurred in three patients and nonhealing occurred in one. Fourteen patients had one or more complications: wound breakdown, superficial (n = 7) and deep (n = 1); wound infection (n = 5); wound seroma (n = 4); and early recurrence (n = 1). The median time off work and to return to normal activities was two and four weeks, respectively (range, 0.5–12). Forty-seven patients completed the questionnaire at a median follow-up of 24 months: five patients reported minimal tenderness in the sacral region; none reported recurrence of pilonidal symptoms; and all were satisfied.
Conclusions
The cleft lift procedure is easy to perform as a day-case procedure. It is associated with high rates of primary healing, durable low recurrence rates, and early functional recovery. This technique may be the procedure of choice in the surgical management of nonacute pilonidal disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sondenaa K, Andersen E, Nesvik I, Soreide JA. Patient characteristics and symptoms in chronic pilonidal sinus disease. Int J Colorectal Dis 1995;10:39–42.
Davage ON. The origin of sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinuses: based on an analysis of four hundred sixty-three cases. Am J Pathol 1954;30:1191–205.
Allen-Mersh TG. Pilonidal sinus: finding the right track for treatment. Br J Surg 1990;77:123–32.
Chintapatla S, Safarani N, Kumar S, Haboubi N. Sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus: historical review, pathological insight and surgical options. Tech Coloproctol 2003;7:3–8.
Karydakis GE. Easy and successful treatment of pilonidal sinus after explanation of its causative process. ANZ J Surg 1992;62:385–9.
Bascom J, Bascom T. Failed pilonidal surgery: new paradigm and new operation leading to cures. Arch Surg 2002;137:1146–50.
Bascom J. Pilonidal sinus: origin from follicles of hairs and results of follicle removal as treatment. Surgery 1980;87:567–72.
Bascom J. Pilonidal sinus. In: Fazio VW. Current therapy in colon and rectal surgery. Toronto: B.C. Decker, 1990:32–9.
Karydakis GE. New approach to the problem of pilonidal sinus. Lancet 1973;2:1414–5.
Kitchen PR. Pilonidal sinus: experience with the Karydakis flap. Br J Surg 1996;83:1452–5.
Bascom J. Pilonidal disease: long-term results of follicle removal. Dis Colon Rectum 1983;26:800–7.
Senapati A, Cripps N, Thompson M. Bascom’s operation in the day-surgical management of symptomatic pilonidal sinus. Br J Surg 2000;87:1067–70.
Parvaiz A, Kennedy R. Bascom’s procedure in the day-surgical management of symptomatic pilonidal sinus. Br J Surg 2001;88:155–6.
Bascom J, Bascom T. Utility of the cleft lift procedure in refractory pilonidal disease. Am J Surg 2007;193:606–9.
Dewigt R, Maloy J. Pilonidal sinus, experience with 449 cases. N Engl J Med 1953;249:926–30.
Akinci OF, Bozer M, Uzunkoy A, Duzgun SA, Cokun A. Incidence and aetiological factors in pilonidal sinus among Turkish soldiers. Eur J Surg 1999;165:339–42.
Hospital Episode Statistics. Available at: http://www.doh.gov.uk/hes/standard_data/available_tables/main_operations/tb02100e.xls. January 2000.
Akinci OF, Coskun A, Ozgonul A, Terzi A. Surgical treatment of complicated pilonidal disease: limited separate elliptical excision with primary closure. Colorectal Dis 2006;8:704–9.
Erdem E, Sungurtekin U, Near M. Are postoperative drains necessary with the Limberg flap for treatment of pilonidal sinus? Dis Colon Rectum 1998;41:1427–31.
Notaras MJ. A review of three popular methods of treatment of postanal (pilonidal) sinus disease. Br J Surg 1970;57:886–90.
Petersen S, Koch R, Stelzner S, Wendlandt TP, Ludwig K. Primary closure techniques in chronic pilonidal sinus: a survey of the results of different surgical approaches. Dis Colon Rectum 2002;45:1458–67.
Acknowledgment
The authors thank all the consultants in the Department of General Surgery at York Hospital for their generous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelrazeq, A.S., Rahman, M., Botterill, I.D. et al. Short-Term and Long-Term Outcomes of the Cleft Lift Procedure in the Management of Nonacute Pilonidal Disorders. Dis Colon Rectum 51, 1100–1106 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-008-9262-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-008-9262-z