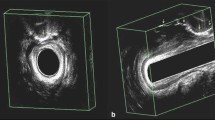
Purpose
In our center since 2001, follow-up examination has included three-dimensional endosonography in all patients with suspicion of local recurrence of anal cancer. This study was designed to investigate whether three-dimensional endosonography surpassed two-dimensional endosonography as a diagnostic tool for patients with suspected local recurrence.
Methods
This prospective study included 38 consecutive patients who have had anal carcinoma and were investigated using three-dimensional endosonography in combination with anoscopy and digital rectal examination at Rigshospitalet from July 2001 to January 2005 under suspicion of local recurrence. All endosonographic examinations—two-dimensional, three-dimensional, and three-dimensional in combination with anoscopy and digital rectal examination—were evaluated by blinded observers. The observers scored each examination according to a five-point scale in which a score from 1 to 3 was regarded as benign endosonographic findings and a score from 4 to 5 was regarded as malignant endosonographic findings. The endosonographic diagnosis for each examination was compared with histologic evaluation or when no biopsy had been taken with a follow-up period of at least six months. If a patient showed no signs of local recurrence in the follow-up period, no local recurrence was considered to be present at the time of the investigation.
Results
The sensitivity was 1.0 for three-dimensional endosonography in combination with palpation, 0.86 for three-dimensional endosonography alone, and 0.57 for two-dimensional endosonography. The differences between two-dimensional endosonography and three-dimensional endosonography alone as well as two-dimensional endosonography and three-dimensional endosonography + anoscopy and digital rectal examination both reached significance with P values <0.05.
Conclusions
This study indicates that three-dimensional endosonography surpasses two-dimensional endosonography in the evaluation of patients with suspicion of local recurrence of anal cancer especially in combination with anoscopy and digital rectal examination.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
U Herzog M Boss H Spichtin (1998) ArticleTitleEndoanal ultrasonography in the follow-up of anal carcinoma Surg Endosc 8 1186–1189 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00591047
D Tarantino M Bernstein (2002) ArticleTitleEndoanal ultrasound in the staging and management of squamous-cell carcinoma of the anal canal: potential implications of a new ultrasound staging system Dis Colon Rectum 45 16–22 Occurrence Handle11786758 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10350-004-6108-1
M Giovanni V Bardou R Barclay (2001) ArticleTitleAnal carcinoma: prognostic value of endorectal ultrasound (ERUS). Results of a prospective multi center study Endoscopy 33 231–236 Occurrence Handle10.1055/s-2001-12860
B Magdeburg M Fried C Meyenberger (1999) ArticleTitleEndoscopic ultrasonography in the diagnosis, staging and follow up of anal carcinomas Endoscopy 31 359–364 Occurrence Handle10433044 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1MzmtVChtA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1055/s-1999-35
M Indinnimeo C Chicchini A Stazi C Ghini P Mingazzini A Laghi (2001) ArticleTitleAnalysis of a follow-up program for anal canal carcinoma J Exp Clin Cancer Res 20 199–203 Occurrence Handle11484975 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FislCmtg%3D%3D
A Christensen M Nielsen S Engelholm H Roed L Svendsen H Christensen (2004) ArticleTitleThree-dimensional anal endosonography may improve staging of anal cancer compared with two-dimensional endosonography Dis Colon Rectum 47 340–347
M Nielsen (1998) ArticleTitleEndosonography of the anal sphincter muscles in healthy volunteers and in patients with defecation disorders Acta Radiol 39 1–21 Occurrence Handle10.3109/02841859809172140
G Akbari P Paty J Guillem et al. (2004) ArticleTitleOncologic outcomes of salvage surgery for epidermoid carcinoma of the anus initially managed with combined modality therapy Dis Colon Rectum 47 1136–1144 Occurrence Handle15164245 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10350-004-0548-5
A Clark A Hartley J Geh (2005) ArticleTitleCancer of the anal canal Lancet Oncol 5 149–157 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1470-2045(04)01410-X
P Nilsson C Svensson B Goldman et al. (2005) ArticleTitleEpidermoid anal cancer: a review of a population-based series of 308 consecutive patients treated according to prospective protocols Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 61 92–102 Occurrence Handle15629599 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.03.034
R Beets-Tan G Beets A Hoop Particlevan der (1999) ArticleTitleHigh-resolution magnetic resonance imaging of the anorectal region without an endocoil Abdom Imaging 24 576–584 Occurrence Handle10525811 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1Mvls1Kmtg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002619900567
E Rociu J Stoker J Marinus M Eiijkemanns J Lameris A Stazi (2000) ArticleTitleNormal anal spincter anatomy and age- sex-related variations at high-spatial-resolution MR imaging Radiology 217 395–401 Occurrence Handle11058634 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3crhtFeqsQ%3D%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Christensen, A.F., Nielsen, M.B., Svendsen, L.B. et al. Three-Dimensional Anal Endosonography May Improve Detection of Recurrent Anal Cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 49, 1527–1532 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-006-0661-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-006-0661-8