Abstract
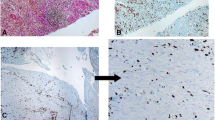
PURPOSE: Because increased enterocyte apoptosis has been associated with the pathogenesis of several chronic inflammatory diseases, the aim of our study was to investigate epithelial cell death in Crohn’s disease and the possible role of the Fas-Fas ligand system, E-cadherin, and matrix metalloproteinase-1 in modulating enterocyte apoptosis in this condition. METHODS: Endoscopic ileal and colonic biopsy specimens were collected from macroscopically involved and uninvolved areas of 20 patients with Crohn’s disease and 20 subjects who proved to have functional diarrhea. Diagnosis was established by clinical and pathologic criteria. Biopsy specimens were processed for traditional histology and for the immunohistochemical evaluation of Fas, Fas ligand, E-cadherin, Ki67 antigen, and matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression. For the in situ detection of apoptotic cells, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase–mediated digoxigenin-deoxyuridine triphosphate nick end labeling was used. RESULTS: The percentages of apoptotic enterocytes were higher in involved than in uninvolved areas of Crohn’s disease patients and normal intestine. No significant difference was found between Crohn’s disease uninvolved areas and normal intestine. In Crohn’s disease, both enterocyte Fas and lamina propria mononuclear cell Fas ligand expression did not differ from controls. E-cadherin was strongly expressed by epithelium in both normal and inflamed intestine, except for the regenerative epithelium over the base of the ulcers, where a reduced E-cadherin expression was observed. The number of Ki67-positive proliferating epithelial cells did not differ either in involved or uninvolved areas of Crohn’s disease patients compared with controls. A lamina propria overexpression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 was found in involved compared with uninvolved Crohn’s disease areas and normal tissue, and a significant positive correlation between matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression and enterocyte apoptosis was found in Crohn’s disease inflamed areas. CONCLUSIONS: Enterocyte apoptosis is increased in involved areas of Crohn’s disease. This increase is not mediated by a Fas-Fas ligand mechanism or by an abnormal E-cadherin distribution. Increased matrix metalloproteinase-1 release from lamina propria mononuclear cells might be one of the possible mechanisms responsible for the increased enterocyte apoptosis in Crohn’s disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CS Potten (1997) ArticleTitleEpithelial cell growth and differentiation II. Intestinal apoptosis Am J Physiol 273 253–257
AJ Watson (1995) ArticleTitleNecrosis and apoptosis in the gastrointestinal tract Gut 37 165–167
CB Thompson (1995) ArticleTitleApoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease Science 267 1456–1462
S Nagata P Golstein (1995) ArticleTitleThe Fas death factor Science 267 1449–1456
F Leithauser J Dhein G Mechtersheimer et al. (1993) ArticleTitleConstitutive and induced expression of APO-1, a new member of the nerve growth factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, in normal and neoplastic cells Lab Invest 69 415–429
DH Lynch F Ramsdell MR Alderson (1995) ArticleTitleFas and FasL in the homeostatic regulation of immune responses Immunol Today 16 569–574
LE French J Tschopp (1997) ArticleTitleThyroiditis and hepatitis Nat Med 3 387–388
R Ciccocioppo A Di Sabatino R Parroni et al. (2000) ArticleTitleCytolytic mechanisms of intraepithelial lymphocytes in coeliac disease Clin Exp Immunol 120 235–240
R Ciccocioppo A Di Sabatino R Parroni et al. (2001) ArticleTitleIncreased enterocyte apoptosis and Fas/FasL system in celiac disease Am J Clin Pathol 115 494–503
A Di Sabatino R Ciccocioppo S D’Alò et al. (2001) ArticleTitleIntraepithelial and lamina propria lymphocytes show distinct patterns of apoptosis, whereas both the populations are active in Fas-based cytotoxicity in coeliac disease Gut 49 380–386
M Iwamoto T Koji K Makiyama N Kobayashi PK Nakane (1996) ArticleTitleApoptosis of crypt epithelial cells in ulcerative colitis J Pathol 180 152–159
H Ueyama T Kiyohara N Sawada et al. (1998) ArticleTitleHigh Fas ligand expression on lymphocytes in lesions of ulcerative colitis Gut 43 48–55
JC Coffey MW Bennett JH Wang et al. (2001) ArticleTitleUpregulation of Fas-Fas-L (CD95/CD95L)-mediated epithelial apoptosis. A putative role in pouchitis? J Surg Res 98 27–32
T Lin T Brunner B Tietz et al. (1998) ArticleTitleFas ligand-mediated killing by intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Participation in intestinal graft-versus-host disease J Clin Invest 101 570–577
M Boirivant M Marini G Di Felice et al. (1999) ArticleTitleLamina propria T cells in Crohn’s disease and other gastrointestinal inflammation show defective CD2 pathway-induced apoptosis Gastroenterology 116 557–565
K Ina J Itoh K Fukushima et al. (1999) ArticleTitleResistance of Crohn’s disease T cells to multiple apoptotic signals is associated with a Bcl-2/Bax mucosal imbalance J Immunol 163 1081–1090
A Di Sabatino GR Corazza (2001) ArticleTitleSurviving too long in Crohn’s disease Gut 49 6–8
FD Lee (1993) ArticleTitleImportance of apoptosis in the histopathology of drug related lesions in the large intestine J Clin Pathol 46 118–122
PA Hall PJ Coates B Ansari D Hopwood (1994) ArticleTitleRegulation of cell number in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract J Cell Sci 107 3569–3577
J Gerdes H Lemke H Baisch HH Wacker U Schwab H Stein (1984) ArticleTitleCell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67 J Immunol 133 1710–1715
BM Gumbiner (1996) ArticleTitleCell adhesion Cell 84 345–357
SL Pender SP Tickle AJ Docherty D Howie NC Wathen TT MacDonald (1997) ArticleTitleA major role for matrix metalloproteinases in T cell injury in the gut J Immunol 158 1582–1590
K Yamada B Geiger (1997) ArticleTitleMolecular interactions in cell adhesion complexes Curr Opin Cell Biol 9 76–85
M Takeichi (1991) ArticleTitleCadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator Science 251 1451–1455
ML Hermiston JI Gordon (1995) ArticleTitleInflammatory bowel disease and adenomas in mice expressing a dominant negative N-cadherin Science 270 1203–1207
JC Adams FM Watt (1993) ArticleTitleRegulation of development and differentiation by the extracellular matrix Development 117 1183–1395
EJ Goetzl MJ Banda D Leppert (1996) ArticleTitleMatrix metalloproteinases in immunity J Immunol 156 1–4
SM Frisch H Francis (1994) ArticleTitleDisruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis J Cell Biol 124 619–626
WR Best JM Becktel JW Singleton F Kern (1976) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a Crohn’s disease activity index Gastroenterology 70 439–444
Y Gavrieli Y Sherman SA Ben-Sasson (1992) ArticleTitleIdentification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation J Cell Biol 119 493–501
J Jankowsky R McMenemin D Hopwood J Penston KG Wormsley (1991) ArticleTitleAbnormal expression of growth regulatory peptides in Barrett’s oesophagus Clin Sci 81 663–668
P Möller H Walczak S Riedl J Sträter PH Krammer (1996) ArticleTitlePaneth cells express high levels of CD95 ligand transcripts Am J Pathol 149 9–13
G Majno I Joris (1995) ArticleTitleApoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis. An overview of cell death Am J Pathol 146 3–15
F Autschbach G Schürmann L Qiao H Merz R Wallich SC Meuer (1995) ArticleTitleCytokine messenger RNA expression and proliferation status of intestinal mononuclear cells in noninflamed gut and Crohn’s disease Virchows Arch 426 51–60
D Seegert P Rosenstiel H Pfahler P Pfefferkorn S Nikolaus S Schreiber (2001) ArticleTitleIncreased expression of IL-16 in inflammatory bowel disease Gut 48 326–332
L Mazzucchelli C Hauser K Zgraggen et al. (1996) ArticleTitleDifferential in situ expression of the genes encoding the chemokines MCP-1 and RANTES in human inflammatory bowel disease J Pathol 178 201–206
TT MacDonald M Bajaj-Elliott SL Pender (1999) ArticleTitleT cells orchestrate intestinal mucosal shape and integrity Immunol Today 20 505–510
E Ierardi M Principi O Burattini et al. (2001) ArticleTitlePattern of apoptosis in Crohn’s disease Dig Liver Dis 33 614–615
JJ Mattapallil S Dondekar DR Canfield JV Solnick (2000) ArticleTitleA predominant T helper 1 type of immune response is induced early during acute Helicobacter pylori infection in Rhesus macaques Gastroenterology 118 307–315
A Doğan ZD Wang J Spencer (1995) ArticleTitleE-cadherin expression in intestinal epithelium J Clin Pathol 48 143–146
AM Hanby R Chinery R Poulsom RJ Playford M Pignatelli (1996) ArticleTitleDownregulation of E-cadherin in the reparative epithelium of the human gastrointestinal tract Am J Pathol 148 723–729
JA Jankowski FK Bedford RA Boulton et al. (1998) ArticleTitleAlterations in classical cadherins associated with progression in ulcerative and Crohn’s colitis Lab Invest 78 1155–1167
AJ Karayiannakis KN Syrigos J Efstathiou et al. (1998) ArticleTitleExpression of catenins and E-cadherin during epithelial restitution in inflammatory bowel disease J Pathol 185 413–418
J Strater U Wedding TF Barth K Koretz C Elsing P Moller (1996) ArticleTitleRapid onset of apoptosis in vitro follows the disruption of β1-integrin/matrix interactions in human colonic crypt cells Gastroenterology 110 1776–1784
UK Saarialho-Kere M Vaalamo P Puolakkainen K Airola WC Parks ML Karjalainen-Lindsberg (1996) ArticleTitleEnhanced expression of matrilysin, collagenase, and stromelysin-1 in gastrointestinal ulcers Am J Pathol 148 519–526
MD Baugh AP Hollander GS Evans (1998) ArticleTitleThe regulation of matrix metalloproteinase production in human colonic fibroblasts Ann NY Acad Sci 859 175–179
MD Baugh MJ Perry AP Hollander et al. (1999) ArticleTitleMatrix metalloproteinase levels are elevated in inflammatory bowel disease Gastroenterology 117 814–822
E Louis C Ribbens A Godon et al. (2000) ArticleTitleIncreased production of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 by inflamed mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease Clin Exp Immunol 120 241–246
B von Lampe B Barthel SE Coupland EO Riecken S Rosewicz (2000) ArticleTitleDifferential expression of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in colon mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease Gut 47 63–73
Z Sun X Wang R Wallen (1998) ArticleTitleThe influence of apoptosis on intestinal barrier integrity in rats Scand J Gastroenterol 33 415–422
JM Anderson (2000) ArticleTitleMaintaining a defense as the injured leave the field Gastroenterology 119 1783–1786
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Di Sabatino, A., Ciccocioppo, R., Luinetti, O. et al. Increased Enterocyte Apoptosis in Inflamed Areas of Crohn’s Disease. Dis Colon Rectum 46, 1498–1507 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-004-6802-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-004-6802-z