PURPOSE:
Bowel preparation with oral sodium phosphate can cause symptomatic dehydration and electrolyte disturbances. This randomized, controlled trial was designed to evaluate whether carbohydrate-electrolyte (E-Lyte®) solution enhanced bowel preparation and improved patient acceptance with oral sodium phosphate.
METHODS:
A total of 187 consecutive adults undergoing colonoscopy by two endoscopists were randomized to receive two packets of oral sodium phosphate (Fleet® Phospho-soda®) with or without additional supplement of a carbohydrate-electrolyte (E-Lyte®) solution. All patients and endoscopists completed a standardized questionnaire. Urine-specific gravity and serum biochemistry were randomly performed in 150 and 50 patients, respectively.
RESULTS:
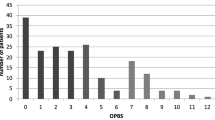
Ninety patients were randomized to have oral sodium phosphate with E-Lyte® supplements (Group 1) and 94 patients to sodium phosphate without E-Lyte® supplements (Group 2). The groups were similar in age and gender, indication for colonoscopy, and previous colonic surgery. Patients taking E-Lyte® supplement had significantly less dizziness (none, 80 vs. 56 percent; P < 0.001) and a trend toward less nausea (none, 70 vs. 56 percent; P = 0.05). All patients in Group 1 completed the bowel preparation as opposed to 3 percent of Group 2 being unable to complete the preparation. Hypokalemia was significantly more frequent (P = 0.008) in Group 2 patients without E-Lyte® supplements. More patients in Group 2 needed intravenous rehydration (11 vs. 4 percent). Differences in serum creatinine and urine-specific gravity suggested possibly a lesser degree of hypovolemia in patients taking E-Lyte® supplements. The quality of bowel cleansing in patients taking E-Lyte® supplements was considered better by both the endoscopists and patients.
CONCLUSIONS:
Carbohydrate-electrolyte (E-Lyte®) solution protects against hypokalemia, improves patient tolerability, and may enhance use of oral sodium phosphate as a bowel-preparation agent.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
SJ Vanner PH MacDonald WG Paterson RS Prentice LR DaCosta IT Beck (1990) ArticleTitleA randomized prospective trial comparing oral sodium phosphate with standard polyethylene glycol-based lavage solution (Golytely) in the preparation of patients for colonoscopy Am J Gastroenterol 85 422–7
SM Cohen SD Wexner SR Binderow et al. (1994) ArticleTitleProspective, randomized, endoscopic-blinded trial comparing precolonoscopy bowel cleansing methods Dis Colon Rectum 37 689–96
CW Hsu TF Imperiale (1998) ArticleTitleMeta-analysis and cost comparison of polyethylene glycol lavage versus sodium phosphate for colonoscopy preparation Gastrointest Endosc 48 276–82
BE Kolts WE Lyles SR Achem L Burton AJ Geller T MacMath (1993) ArticleTitleA comparison of the effectiveness and patient tolerance of oral sodium phosphate, castor oil and standard electrolyte lavage for colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy preparation Am J Gastroenterol 88 1218–23
J Tjandra P Tagkalidis (2002) ArticleTitleOral sodium phosphate solution is a superior colonoscopy preparation to sodium picosulphate Dis Colon Rectum 45 A53
K Yoshioka AB Connolly OA Ogunbiyi H Hasegawa DG Morton MR Keighley (2000) ArticleTitleRandomized trial of oral sodium phosphate compared with oral sodium picosulphate (picolax) for elective colorectal surgery and colonoscopy Dig Surg 17 66–70
T Huynh S Vanner W Paterson (1995) ArticleTitleSafety profile of 5-h oral sodium phosphate regimen for colonoscopy cleansing lack of clinically significant hypocalcaemia or hypovolaemia Am J Gastroenterol 90 104–7
ME Avery JD Snyder (1990) ArticleTitleOral therapy for acute diarrhea: the underused simple solution N Engl J Med 13 891–4
A Pinfield MD Stringer (1999) ArticleTitleRandomised trial of two pharmacological methods of bowel preparation for day case colonoscopy Arch Dis Child 80 181–3
S Klein CR Fleming (1998) Enteral and parenteral nutrition M Feldman BF Scharschmidt MH Sleisenger (Eds) Sleisenger and Fordtran’s gastrointestinal and liver disease WB Saunders Philadelphia 254–77
RJ Maughan JH Owen SM Shirreffs JB Leiper (1994) ArticleTitlePost-exercise rehydration in man: effects of electrolyte addition to ingested fluids Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 69 209–25
RL Barclay WT Depew SJ Vanner (2002) ArticleTitleCarbohydrate-electrolyte rehydration protects against intravascular volume contraction during colonic cleansing with orally administered sodium phosphate Gastrointest Endosc 56 633–8
JM Henderson JL Barnett DK Turgeon et al. (1995) ArticleTitleSingle-day, divided-dose oral sodium phosphate laxative versus intestinal lavage as preparation for colonoscopy: efficacy and patient tolerance Gastrointest Endosc 42 238–43
R Shaoul R Wolff J Seligmann Y Tal M Jaffe (2001) ArticleTitleSymptoms of hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia in an adolescent after the oral administration of sodium phosphate in preparation for a colonoscopy Gastrointest Endosc 53 650–2
KM Chow PK Li (2001) ArticleTitleA patient with severe hyperphosphataemia Postgrad Med J 77 473–84
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors thank Dr. Richard Hiscock for helping with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fleet® Phospho-soda® and E-Lyte® were supplied by CB Fleet Co., Inc., Lynchburg, VA.
About this article
Cite this article
Tjandra, J., Tagkalidis, P. Carbohydrate-Electrolyte (E-Lyte®) Solution Enhances Bowel Preparation With Oral Fleet® Phospho-soda®. Dis Colon Rectum 47, 1181–1186 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-004-0559-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-004-0559-2