Abstract
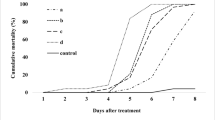
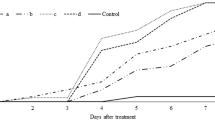
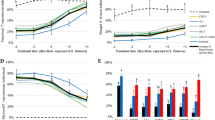
Two strains of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff) Sorokin and two strains of Beauveria bassiana (Ballsamo) Vuillemin were evaluated for their potential use as biological control agents against the tea termite Microtermes obesi Holmgren. The strains were screened for relative pathogenicity, and the median lethal time eliciting 50% mortality (LT50) was calculated. In general, the M. anisopliae strains were more virulent with lower LT50 values than B. bassiana strains. The LT50 values ranged from 1.6 to 3.7 days. The median lethal concentrations (LC50) of all the isolates were also determined. The M. anisopliae strains had low LC50 values compared to B. bassiana strains. The LC50 values ranged from 35 to 140 conidia per termite. The strains were also tested for survival under laboratory nest conditions. All the isolates exhibited the ability to grow, sporulate and produce an epizootic in treated nest material. Field applications of the isolates also produced promising results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed S, Ashraf MR, Hussain MA, Riaz MA (2009) Pathogenicity of isolates of Metarhizium anisopliae from Gujranwala (Pakistan) against Coptotermes heimi (Wasmann) (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Int J Agric Biol 11:707–711
Arora K, Arora SS (1995) Lindane as termiticide—a review. In: Singh Y (ed) Termite management in buildings. Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi, pp 56–59
Carruthers RI, Soper RS (1987) Fungal diseases. In: Fuxa JR, Tanada Y (eds) Epizootiology of insect diseases. Wiley, New York, pp 357–416
Choudhury P, Dutta BK, Bhattacharjee PC (2005) Control of termites in tea (Camellia sinensis L (O) Kuntze) plantations of Barak Valley. Int J Tea Sci 4:9–17
Chouvenc T, Su Nan-Yao, Robert A (2009)Susceptibility of seven termite species (Isoptera) to the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Sociobiology 54(3):723–748
Cowie RH, Logan JWM, Wood TG (1989) Termite (Isoptera) damage and control in tropical forestry with special reference to Africa and Indo-Malaysia: a review. Bull Entomol Res 79:173–184
Dong C, Zhang J, Huang H, Chen W, Hu Y (2009) Pathogenicity of new China variety of Metarhizium anisopliae (Manisopliae var.dcjhyium) to subterranean termite Odontotermes formosanus. Microbiol Res 164:27–35
Fernandes PM (1991) Controle microbiano de Conitermes cumulans (Kollar, 1832) utilizando Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. Metarhizium anisopliae Metsch.) Sorok. Ph.D. dissertation, ESALQ-University de Sao Paulo, Piracicaba, Brazil
Finney DJ (1971). Probit analysis, III edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, pp 1–333
Goettel MS, Inglis GD, Wright SP (2000) Fungi. In: Lacey LA, Kaya HK (eds) Field manual of techniques in invertebrate pathology : application and evaluation of pathogens for control of insects and other invertebrate pests. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 255–282
Goyal DD (1994) Anti-termite treatment in buildings. Construc Rep 1:5–8
Grace JK (1992) Termite distribution, colony size, and potential for damage. In: Robinson WH (ed) Proceedings of the national conference on urban entomology, College Park, MD, pp 67–76
Grace JK, Yates JR, Tamashiro M, Yamamoto RT (1993) Persistence of organochlorine insecticides for Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) control in Hawaii. J Econ Entomol 86:761–766
Gurusubramanian G, Tamuli AK, Ghosh RKB (1999) Susceptibility of Odontotermes obesus (Rambur) to Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. Insect Sci Appl 19:157–162
Hamill RL, Higgins CE, Boaz HE, Gorman M (1969) The structure of beauvericin, a new depsipeptide antibiotic toxic to Artemia salina. Tetrahedron Lett 49:4255–5258
Ignoffo CM (1992) Environmental factors affecting persistence of entomopathogens. Fla Entomol 75:516–625
Jones WE, Grace KJ, Tamashiro M (1996) Virulence of seven isolates of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae to Coptotermes formosanus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Environ Entomol 25(2):481–487
Khan KH, Jayaraj S, Gopalan M (1993) Muscaradine fungi for the biological control of Agroforestry termite Odontotermes obesus (Rambur). Insect Sci Appl 14(4):529–535
Kramm KR, West DF, Rockenbach PG (1982) Termite pathogens: transfer of the entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae between Reticulitermes species termites. J Invertebr Pathol 40:1–6
Lacey LA, Fransen JJ, Carruthers R (1996) Global distribution of naturally occurring fungi of Bemisia, their biologies and use as biological control agents. In: Gerling D, Mayer R (eds) Bemisia-1995: taxonomy, biology, damage, management. Intecept, Andover, pp 401–433
Lacey LA, Frutos R, Kaya HK, Vail P (2001) Insect pathogens as biological control agents: do they have a future? Biol Control 21:230–248
Lai PY, Tamashiro M, Fuji JK (1982) Pathogenicity of six strains of entomogenous fungi to Coptotermes formosans. J Invertebr Pathol 39:1–5
Lenz M (2005) Biological control in termite management: the potential of nematodes and fungal pathogens. In Chow-Yang L, William HR (eds) Proceedings of the fifth international conference on urban pests, Malaysia
Logan JWM, Cowie RH, Wood TG (1990) Termite (Isoptera) control in agriculture and forestry by non-chemical methods: a review. Bull Entomol Res 80:309–330
McCoy CW, Samson RA, Boucias DG (1988) Entomogenous fungi. In: Ignoffo CM (ed) CRC handbook of natural pesticides. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, pp 151–236
Milner RJ, Hodom DG, Glare TR (1984) Diurnal patterns of mortality in aphids infected by entomophthoran fungi. Entomol Exp Appl 36:37–42
Mullens BA (1985) Host age, sex and pathogen exposure level as factors in the susceptibility of Musca domestica to Entomopthora muscae. Entomol Exp Appl 37:33–39
Myles TG (2002) Alarm, aggregation, and defense by Reticulitermes flavipes in response to a naturally occurring isolate of Metarhizium anisopliae. Sociobiology 40:243–255
Nair KSS, Verma RV (1985) Some ecological aspects of the termite problem in young Eucalyptus plantations in Kerala, India. For Ecol Manag 12:287–303
Padmaja V, Kaur G (2001) Use of fungus Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. (Moniliales: Deuteromycetes) for controlling termites. Sci Curr 81(6):645–647
Pais M, Das BC, Ferron P (1981) Depspeptides from Metarhizium anisopliae. Phytochemistry 20:715–723
Pik-Kheng H, Choon-Fah J, Bong KJ, Amartalingam R (2009) Evaluation of Metarhizium anisopliae var. anisopliae (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycete) isolates and their effects on subterranean termite Coptotermes curvignathus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) American. J Agric Biol Sci 4(4):289–297
Sands WA (1962) The evaluation of insecticides as soil and mound poisons against termites in agricultural and forestry. Bull Entomol Res 53:179–192
Sands WA (1977) The role of termites in tropical agriculture. Outlook Agric 9(3):136–143
Sannasi A (1969) Apparent infections of queens and drones of the mound building termite Odontotermes obesus by Aspergillums flavus. J Invertebr Pathol 10:434–535
Sapna Bai N, Sasidharan TO, Remadevi OK, Rajan PD, Balachander M (2010) Virulence of Metarhizium isolates against the polyphagous defoliator pest, Spilarctia obliqua (Lepidoptera: Arctiidae). J Trop For Sci 22(1):74–80
Shah PA, Goettel MS (1999) Directory of microbial control products. Society for invertebrate pathology, Division of microbial control. http://www.sipweb.org/directory.html
Singha D (2009) Studies on the potential of biocontrol agents against the termite pests of tea in the agroclimatic conditions of Barak valley, Assam, India. Ph.D Thesis, Assam University, Silchar, India
Singha D, Singha B, Dutta BK (2006) Virulence of isolates of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff) Sorokin and Beauveria bassiana (Ballsamo)Vuillemin on tea termite Microcerotermes beesoni Snyder Barak valley of Assam. Ind J Entomol 68(1):66–70
Staples JA, Milner RJ (2000) A laboratory evaluation of the repellency of Metarhizium anisopliae conidia to Coptotermes lacteus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitdae). Sociobiology 36:133–146
Zoberi MH, Grace JK (1990) Isolation of the pathogen Beauveria bassiana from Reticulitermes flavipes (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Sociobiology 16:289–296
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the University Grants Commission, Govt. of India, for funding the research. We are also grateful to the Zoological survey of India, Kolkata for identifying the termites and the Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi and the Project Directorate of Biological Control, Bangalore for providing the fungal strains. We are also grateful to the reviewers for their valuable suggestions in improving the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Traugott.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singha, D., Singha, B. & Dutta, B.K. Potential of Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana in the control of tea termite Microtermes obesi Holmgren in vitro and under field conditions. J Pest Sci 84, 69–75 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-010-0328-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-010-0328-z