Abstract
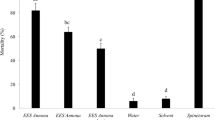
Toxicity by contact and by ingestion of lufenuron, flufenoxuron, lambda (λ)-cyhalothrin, cypermethrin, thiamethoxam and five entomopathogenic insecticides (three formulations of Beauveria bassiana, a compound containing spores of Metarhizium anisopliae var. acridum, and a mixture of Brevibacillus laterosporus, Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus chitinosporus) were evaluated on adults of the Eucalyptus snout-beetle Gonipterus scutellatus Gyllenhal (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) under laboratory conditions. By contact, entomopathogenic fungus B. bassiana EC and the pyrethroid λ-cyhalothrin exhibited the highest efficiency, achieving 100 and 97.5% mortality, respectively. By ingestion, the highest mortality was obtained by B. bassiana EC (100%) and thiamethoxam (95%). Flufenoxuron and lufenuron, bacteria mixture and M. anisopliae showed a weak toxicity. Furthermore, we found a sex-biased mortality, being males more affected. Due to the good performance and low risk to humans and environment, B. bassiana EC (strain PPRI 5339) appears to be the most promising product to promote an IPM programme in South Africa.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur FH, Yue B, Wilde GE (2004) Susceptibility of stored-product beetles on wheat and maize treated with thiamethoxam: effects of concentration, exposure interval, and temperature. J Stored Prod Res 40:527–546
Arzone A (1976) Un nemico dell’Eucalipto nuovo per l’Italia. L’Apicoltore Moderno 67:173–177
Atkinson PR (1995) Pests and diseases network. Institute for Commercial Forestry Research (ICFR) Bulletin 5/95
Atkinson PR (1997) Recommendations, practices and notes of the control of pests and diseases in commercial forestry in South Africa. Institute for Commercial Forestry Research (ICFR) Bulletin 1/97
Atkinson PR (1999) Eucalyptus snout beetle, Gonipterus scutellatus Gyll., and its control in South Africa through biological, cultural and chemical means. Institute for Commercial Forestry Research (ICFR) Bulletin 1/99
Batista-Filho A, Leite LG, Raga A, Sato ME (1995) Enhanced activity of Beauveria bassiana (Balls.) Vuill. associated with mineral oil against Cosmopolites sordidus (Germar) adults. An Soc Entomol Bras 24:405–408
Byrne FJ, Toscano NC, Urena AA, Morse JG (2007) Toxicity of systemic nenicotinoid insecticides to avocado thrips in nursery avocado trees. Pest Manag Sci 63:860–866
CABI/EPPO (1997) Gonipterus scutellatus. Distribution Maps of Plant Pests No. 344. CAB International, Wallingford
Cordero-Rivera A, Santolamazza-Carbone S, Andrés JA (1999) Life cycle and biological control of the Eucalyptus snout beetle (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) by Anaphes nitens (Hymenoptera, Mymaridae) in north-west Spain. Agric For Entomol 1:103–109
Davies PE, Cook LSJ (1993) Catastrofic macroinvertebrate drift and sublethal effect on brown trout, Salmo trutta, caused by cypermethrin spraying on a Tasmanian stream. Aquat Toxicol 27:201–224
DeBach P, Rosen D (1991) Biological control by natural enemies. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Devotto L, Cisternas E, Gerding M, Carrillo R (2007) Response of grassland soil arthropod community to biological and conventional control of a native moth: using Beauveria bassiana and lambda-cyhalothrin for Dalaca pallens (Lepidoptera: Hepialidae) suppression. Biocontrol 52:507–531
Elliott M, Janes NF (1978) Synthetic pyrethroids—a new class of insecticide. Chem Soc Rev 7:473–505
Hahn T, Liess M, Schulz R (2001) Effects of the hormone mimetic insecticide tebufenozide on Chironomus riparius larvae in two different exposure setups. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 49:171–178
Ham D (1999) New technology brings improved insect control. Aust Cottongrower 20:102–103
Hanks LM, Millar JG, Paine TD, Campbell CD (2000) Classical biological control of the Australian weevil Gonipterus scutellatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in California. Biol Control 29:369–375
Humeres E, Da Cruz IBM, De Oliveira AK (1999) Age and time exposure-related toxicity of fenthion to male and female Anastrepha fraterculus (Wied.) (Diptera: Tephritidae). An Soc Entomol Bras 28:1–6
Inglis GD, Johnson DL, Goettel MS (1996) Effect of bait substrate and formulation on infection of grasshopper nymphs by Beauveria bassiana. Biocontrol Sci Tech 6:35–315
Kassa A, Stephan D, Vidal S, Zimmermann G (2004) Laboratory and field evaluation of different formulations of Metarhizium anisopliae var. acridum submerged spores and aerial conidia for the control of locusts and grasshoppers. BioControl 49:63–81
Lanfranco D, Dungey HS (2001) Insect damage in Eucalyptus: a review of plantations in Chile. Aust Ecol 26:477–481
Lawson DS, Dumbar DM, White SM, Ngo N (1999) ACTARA™ 25 WG: control of cotton pests with a new neonicotinoid insecticide, thiamethoxam. In: Proceedings of the Beltwide cotton conferences, cotton insect research and control conference. National Cotton Council of America, Memphis, TN, USA, pp 1106–1110
Loch AD (2008) Parasitism of the Eucalyptus weevil, Gonipterus scutellatus Gyllenhal, by the egg parasitoid, Anaphes nitens Girault, in the Eucalyptus globulus plantations in southwestern Australia. Biol Control 47:1–7
Maienfisch PL, Gsell L, Rindlisbacher A (1999) Synthesis and insecticidal activity of CGA 293343—a novel broad spectrum insecticide. Pestic Sci 55:351–354
Mally CW (1924) The Eucalyptus snout-beetle (Gonipterus scutellatus. Gyll.). J Dept Agric Un S Afr 9:415–442
Meyling NV, Lübeck M, Eilenberg J, Rehner SA (2009) Community composition, host range and genetic structure of the fungal entomopathogen Beauveria in adjoining agricultural and seminatural habitats. Mol Ecol 18:1282–1293
Musser FR, Shelton AM (2003) Bt sweet corn and selective insecticides: impacts on pests and predators. J Econ Entomol 96:71–80
Nasr FN, Moein SIM (1997) New trend of the use of Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff) Sorokin and Verticillium indicum (Petch) Gams as entomopathogens to the termite Cryptotermes brevis (Walker) (Isoptera, Kalotermitidae). Anz Schadlingskd Pfl 70:13–16
Newenschwander P, Borgemeister C, Langewald J (2003) Biological control in IPM systems in Africa. CAB International, Wallingford
Nielsen AL, Shearer PW, Hamilton GC (2008) Toxicity of insecticides to Halyomorpha halys (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) using glass-vial bioassay. J Econ Entomol 101:1439–1442
OEPP/EPPO (2005) Data sheets on quarantine pests. Gonipterus gibberus and Gonipterus scutellatus. Bull OEPP/EPPO Bull 35:368–370
Parrella MP, Murphy BC (1998) Insect growth regulators. GrowerTalks 62:86–89
Peleg BA (1983) Effect of three insect growth regulators on larval development, fecundity and egg viability of the coccinellid, Chilocorus bipustulatus (Col., Coccinellidae). Entomophaga 28:117–121
Pérez-Otero R, Mansilla-Vázquez P, Rodríguez-Iglesias J (2003) Eficacia y efectos en laboratorio de diferentes insecticidas en el control del defoliador del eucalipto Gonipterus scutellatus y de su parasitoide Anaphes nitens. Bol San Veg Plagas 29:649–658
Pimentel D (2006) Amounts of pesticides reaching target pests: environmental impacts and ethics. J Agr Environ Ethics 8:17–29
Prior C, Jollands P, Le Patourel G (1988) Infectivity of oil and water formulations of Beauveria bassiana (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) to the cocoa weevil pest Pantorhytes plutus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Invertebr Pathol 52:66–72
Rehner SA, Buckley EP (2003) Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci from the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales). Mol Ecol 3:409–411
Richardson KF, Meakins RH (1986) Inter- and intra-specific variation in the susceptibility of eucalypts to the snout beetle Gonipterus scutellatus Gyll. (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). S Afr For J 139:21–31
Santolamazza-Carbone S (2002) Ecología del comportamiento del gorgojo del eucalipto Gonipterus scutellatus Gyllenhal y de su parasitoide Anaphes nitens Girault. Ph.D. Thesis. Universidad de Vigo, Spain
Santolamazza-Carbone S, Cordero Rivera A (1998) Sperm competition, cryptic female choice and prolonged mating in the Eucalyptus Snout-Beetle, Gonipterus scutellatus (Coleoptera, Curculionidae). Etologia 6:33–40
Santolamazza-Carbone S, Fernández de Ana-Magán FJ (2004) Testing of selected insecticides to assess the viability of the integrated pest management of the Eucalyptus snout-beetle Gonipterus scutellatus in north-west Spain. J Appl Entomol 128:620–627
Scher HB, Rodson M, Lee KS (1998) Microencapsulation of pesticides by interfacial polymerization utilizing isocyanate or aminoplast chemistry. Pestic Sci 54:394–400
Shah PA, Pell JK (2003) Entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 61:413–423
Shearer PW, Usmani KA (2001) Sex-related response to organophosphorus and carbamate insecticides in adult Oriental fruit moth, Grapholita molesta. Pest Manag Sci 57:822–826
Shida O, Takagi H, Kadowaki K, Komagata K (1996) Proposal for two new genera, Brevibacillus gen. nov. and Aneurinibacillus gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:939–946
Siddall JB (1976) Insect growth regulators and insect control: a critical appraisal. Environ Health Perspect 14:119–126
Staal GB (1975) Insect growth regulators with juvenile hormone activity. Annu Rev Entomol 20:417–460
Strasser H, Vey A, Butt TM (2000) Are there any risks in using entomopathogenic fungi for pest control, with particular reference to the bioactive metabolites of Metarhizium, Tolypocladium and Beauveria species? Biocontrol Sci Tech 10:717–735
Teder T, Tammaru T (2005) Sexual size dimorphism within species increases with body size in insects. Oikos 108:321–334
Tillman PG, Mulrooney JE (2000) Effect on selected insecticides on the natural enemies Coleomegilla maculata and Hippodamia convergens (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), Geocoris punctipes (Hemiptera: Lygaeidae), and Bracon mellitor, Cardiochiles nigriceps, and Cotesia marginiventris (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) in cotton. J Econ Entomol 93:1638–1643
Tillman PG, Mulrooney JE, Mitchell W (1998) Susceptibility of selected beneficial insects to DPX-MP062. In: Proceedings, Beltwide cotton conferences, vol 2, 5–9 January, 1998, San Diego, CA, USA. National Cotton Council of America, Memphis, TN, pp 1112–1114
Tooke FGC (1935) The eucalyptus snout beetle. Extent to which different kinds of Eucalyptus are attacked. Farming in S Afr 10:174
Tooke FGC (1955) The Eucalyptus Snout-Beetle, Gonipterus scutellatus Gyll. A study of its ecology and control by biological means. Entomol Mem Dept Agric Un S Afr 3:1–282
Tribe GD (1984) Eucalyptus snout beetle in S.E. Transvaal. For News 4:22
Tribe GD (2005) The present status of Anaphes nitens (Hymenoptera: Mymaridae), an egg parasitoid of the Eucalyptus snout beetle Gonipterus scutellatus, in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. S Afr For J 203:49–54
Van Den Bosch R (1971) Biological control of insects. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 2:45–66
Vandekerkhove B, De Clercq P (2004) Effects of an encapsulated formulation of lambda-cyhalothrin on Nezara viridula and its predator Podisus maculiventris (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Fla Entomol 87:112–118
Zimmermann G (2007) Review on safety of the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and Beauveria brongniartii. Biocontrol Sci Technol 17:553–596
Acknowledgements
We thank the companies (Syngenta S.A., BASF S.A., Biological Control Products S.A., Plant Health Products S.A. and Microbial Solutions S.A.) that kindly provided insecticides samples tested in our study. We are grateful to Gifty Hammond for her assistance with insect sexing. We also thank the late Ben Eisenberg, Mike van der Linde and Hennie Groeneveld (University of Pretoria) for their statistical assistance and the University of Pretoria for the use of various facilities during the course of this investigation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Brownbridge.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Echeverri-Molina, D., Santolamazza-Carbone, S. Toxicity of synthetic and biological insecticides against adults of the Eucalyptus snout-beetle Gonipterus scutellatus Gyllenhal (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Pest Sci 83, 297–305 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-010-0298-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-010-0298-1