Abstract
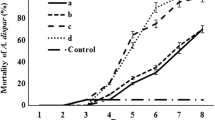
The insecticidal activity of an entomopathogenic fungus, Isaria farinosa on pine bark-weevil (Pissodes punctatus) at different life stages underwent laboratory testing. Larvae, pupae and adults of Pissodes punctatus were exposed to a range of concentrations of fungal conidia in suspension for 5 s; mean mortality and LC50 values were calculated. The results showed I. farinosa can effectively infect larvae, pupae and adult pine bark-weevils, and the highest mean mortalities at each life stage can exceed 88%. The mean mortalities increased with higher concentrations of I. farinosa. Larvae were most susceptible with LC50 1.2 × 106 conidia ml−1 (15 days), pupae (30 days) exhibited the second largest effects, and adults (15 days) with LC50 1.72 × 106 and 1.99 × 106 conidia ml−1, respectively, at end of the experiments. This suggests that I. farinosa could be a potential bio-control agent against the pine bark-weevil.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adili, Shi DM (2000) Research on degradation rule of affecting power of PaeciIomyces farinosus after successive cultures. J Xinjiang Agric Univ 23(3):48–49 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Anderson TE, Roberts DW, Soper RS (1988) Use of Beauveria bassiana for suppression of Colorado potato beetle in New York State (Coleoptera:Chrysomelidae). Environ Entomol 17:140–145
Ayyasamy R, Baskaran P (2005) Effect of temperature and relative humidity on radial growth and sporulation of Paecilomyces farinosus. J Food Agric Environ 3(1):137–138
Chai XS, Liang SX (1990) The biological characters of Pissodes punctatus and its control. Entomol Knowl 27(6):352–354 (in Chinese)
Chen ZA, Feng HY, Shi LC, Liu YG, Pan LC, Wang GN, Fang YJ (2000) Evaluation of Metarhizium anisopliae for control of Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus in the field. Chin J Biol Contr 16(2):53–55 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deng JH, Wu XF, Zhuang H, Hong YD, Wang HL (2005) Infection effect of Paecilomyces sp on Myzus nicotianae (Blackman). Tob Sci Technol 3:46–48 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Duan ZY, Lei GL, Wang LP, Ji M (1998) Preliminary study on harm characteristics of Pissodes sp. Yunnan For Sci Tech 3:81–85 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ferron P (1981) Pest control by the fungi Beauveria and Metarhizium. In: Burges HD (ed) Microbial control of pests and plant diseases 1970–1980. Academic Press, London, pp 465–482
Hallsworth JE, Naresh M (1999) Water and temperature relations of growth of the entomogenous fungi Beauveria bassiana, Metarhizium anisopliae, and Paecilomyces farinosus. J Invertebr Pathol 74:261–266. doi:10.1006/jipa.1999.4883
Jia CS (2006) Calculating the LC50 of insecticides with software SPSS. Chin Bull Entomol 43(3):414–417 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Liu JH, Xiao YS, Lou ZF, Xie KL, Li RB (2005) The relationship between occurrence of Pissodes punctatus pest and the growth status of host trees. J Southwest For Coll 26(2):53–55 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Maniania NK, Sithanantham S, Ekesi S, Ampong-Nyarko K, Baumgartner J, Löhr B, Matoka CM (2003) A field trial of the entomogenous fungus Metarhizium anisopliae for control of onion thrips, Thrips tabaci. Crop Prot 22:553–559. doi:10.1016/S0261-2194(02)00221-1
Mohammed SA, Abdel-Basit BMM, Rana MJ (2003) Distribution, occurrence and characterization of entomopathogenic fungi in agricultural soil in the Palestinian area. Mycopathologi 156(3):235–244. doi:10.1023/A:1023339103522
Sun SF (2003) A study on bio-control of Paecilomyces farinosus on Cyllorhynehites ursulus and Curculio bimaculatus. Yunnan For Sci Tech 2:57–59 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang SY, Zhao ML, Shi YQ (1997) Isolation and identification of Paecilomyces farinosus from Anoplophora glabripennis. For Pest Dis 4:76–77 (in Chinese)
Wang HL, Li LS, Yang L, Zuo TX (2002) A study on Tomicus piniperda control by Paecilomyces farinosus Brown et Smith. J Southwest For Coll 22(3):39–41 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wei JN, Kuang RP (2002) Biological control of coffee stem borers, Xylotrechus quardripes and Acalolepta cervinus, by Beauveria Bassiana preparation. Entomol Sin 9(2):43–50
Wu WD, Chen MJ, Chen DM (1993) A study on using PaeciIomyces farinosus to control Dendrolimus punctatus in Southern China. J Fujian Coll For 13(2):176–183 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang B, Li TS, Liu CY, Yao JP, Wu TL (2005) Studies on the impact of rotate speed of rocking bed, initial inoculum and initial pH value on mycelial biomass of Paecilomyces farinosus. J Yunnan Univ 27(3):267–271 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang S, Zhuang H, Hong YD, Chai SC, Li YH (2007) Infection of Paecilomyces farinosus on Pissodes punctatus. For Pest Dis 26(1):39–40 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yao JH, Zhong LZ, Li YD, Chai SQ, Xie KL, Ma P (2003) Experiment to HulinshenII against Pissodes punctatus in forest fields. For Pest Dis 5:21–22 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ze SZ, Zhou N, Liu HP, Chen P, Li HR (2006) Production process of Paecilomyces farinosus, an entomopathogenic fungus. J W China For Sci 35(1):112–116 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhao RX, Wu JW (1991) The control of pine caterpillar (Dendrolimus tabulaeformis and D. spectabilis) with Paecilomyces farinosus and its epizootic problems. Sci Silvaec Sin 27(3):119–228 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zukowski K, Bajan C (1997) Laboratory determination of the activity of insecticidal fungus Paecilomyces farinosus in reducing the numbers of cockroaches Blattella germanica L. Rocz Panstw Zakl Hig 48(2):133–138
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our sincere thanks to Mr. Duan Zhaoyao for rearing experimental insects, and as well to Ms. Hong Yingdi for isolation and culturing of fungus strain tested in this study. Many thanks to Ms. Even Pay for editing of manuscript. Our work is supported by Yunnan Provincial Key Technology Research and Development Grant (No. 2003NG12).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. J. Storer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Zhuang, H., Li, Y. et al. Insecticidal efficacy of Isaria farinosa in different life stages of Pissodes punctatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J Pest Sci 82, 321–325 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-009-0256-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-009-0256-y