Abstract
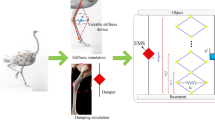
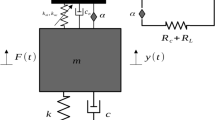
This paper presents a new device integrating a nonlinear vibration absorber with a levitation magnetoelectric energy harvester for whole-spacecraft systems. This device effectively reduces vibration and has a stronger energy harvesting capability than the existing systems. It harvests energy from a wide frequency range and has a high output voltage. The harvested energy is determined by magnetic field strength, excitation frequency, and resistive load. The change in the magnetic field strength has the least impact on the output voltage. The vibration reduction effects and harvested energy of the system are analyzed with an approximate analytical method that combines the harmonic balance approach and the pseudo-arclength continuation algorithm. The results of the Runge–Kutta method are nearly consistent with those of the approximate analytical method. Moreover, the effects of the excitation frequency, resistive load, and parameters of the nonlinear energy sink on the system vibration response and energy harvesting are analyzed.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilke PS, Johnson CD, Fosness ER. Whole-spacecraft passive launch isolation. J Spacecr Rockets. 1998;35(5):690–4.
Johnson CD, Wilke PS, Darling KR. Multi-axis whole-spacecraft vibration isolation for small launch vehicles. Proc SPIE. 2001;4331:153–61.
Liu LK, Zheng GT, Huang WH. Octo-strut vibration isolation platform and its application to whole spacecraft vibration isolation. J Sound Vib. 2006;289(4–5):726–44.
Liu LK, Liang L, Zheng GT, Huang WH. Dynamic design of octostrut platform for launch stage whole-spacecraft vibration isolation. J Spacecr Rockets. 2005;42(4):654–62.
Hu Q, Cao J, Zhang Y. Robust backstepping sliding mode attitude tracking and vibration damping of flexible spacecraft with actuator dynamics. J Aerosp Eng. 2009;22(2):139–52.
Vakakis AF, McFarland DM, Bergman LA, Manevitch LI, Gendelman O. Isolated resonance captures and resonance capture cascades leading to single-or multi-mode passive energy pumping in damped coupled oscillators. J Vib Acoust. 2004;126(2):235–44.
Vakakis AF. Inducing passive nonlinear energy sinks in vibrating systems. J Vib Acoust. 2001;123(3):324–32.
Lu Z, Wang Z, Zhou Y, Lu X. Nonlinear dissipative devices in structural vibration control: a review. J Sound Vib. 2018;423:18–49.
Vakakis AF, Gendelman O. Energy pumping in nonlinear mechanical oscillators ii: resonance capture. J Appl Mech. 2001;68(1):42–8.
Georgiades F, Vakakis AF, Kerschen G. Broadband passive targeted energy pumping from a linear dispersive rod to a lightweight essentially non-linear end attachment. Int J Non-Linear Mech. 2007;42(5):773–88.
Ahmadabadi ZN, Khadem SN. Nonlinear vibration control of a cantilever beam by a nonlinear energy sink. Mech Mach Theory. 2012;50:134–49.
Chen JE, Zhang W, Yao MH, Liu J. Vibration suppression for truss core sandwich beam based on principle of nonlinear targeted energy transfer. Compos Struct. 2017;171:419–28.
Gourc E, Michon G, Seguy S, Berlioz A. Experimental investigation and design optimization of targeted energy transfer under periodic forcing. J Vib Acoust. 2014;136(2):021021.
Zang J, Chen LQ. Complex dynamics of a harmonically excited structure coupled with a nonlinear energy sink. Acta Mech Sin. 2017;33(4):801–22.
Dai HL, Abdelkefi A, Wang L. Usefulness of passive non-linear energy sinks in controlling galloping vibrations. Int J Non-Linear Mech. 2016;81:83–94.
Haris A, Motato E, Mohammadpour M, Theodossiades S, Rahnejat H, O’Mahony M, Vakakis AF, Bergman LA, McFarland DM. On the effect of multiple parallel nonlinear absorbers in palliation of torsional response of automotive drivetrain. Int J Non-Linear Mech. 2017;96:22–35.
Yang B, Lee C, Xiang W, Xie J, He JH, Kotlanka RK, Low SP, Feng H. Electromagnetic energy harvesting from vibrations of multiple frequencies. J Micromech Microeng. 2009;19(3):035001.
Torres EO, Rincón-Mora G. Electrostatic energy-harvesting and battery-charging CMOS system prototype. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap. 2009;56(9):1938–48.
Li P, Wen Y, Huang X, Yang J, Wen J, Qiu J, Zhu Y, Yu M. Wide-bandwidth high-sensitivity magnetoelectric effect of magnetostrictive/piezoelectric composites under adjustable bias voltage. Sens Actuators A Phys. 2013;201:164–71.
Ferrari M, Ferrari V, Guizzetti M, Andò B, Baglio S, Trigona C. Improved energy harvesting from wideband vibrations by nonlinear piezoelectric converters. Procedia Chem. 2009;1(1):1203–6.
Tao K, Tang L, Wu J, Lye SW, Chang H, Miao J. Investigation of multimodal electret-based mems energy harvester with impact-induced nonlinearity. J Microelectromech Syst. 2018;27(2):276–88.
Zhou S, Chen W, Malakooti MH, Cao J, Inman DJ. Design and modeling of a flexible longitudinal zigzag structure for enhanced vibration energy harvesting. J Intell Mater Syst Struct. 2017;28(3):367–80.
Liu H, Gudla S, Hassani FA, Heng CH, Lian Y, Lee C. Investigation of the nonlinear electromagnetic energy harvesters from hand shaking. IEEE Sens J. 2015;15(4):2356–64.
Zhou S, Zuo L. Nonlinear dynamic analysis of asymmetric tristable energy harvesters for enhanced energy harvesting. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2018;61:271–84.
Chtiba MO, Choura S, Nayfeh AH, El-Borgi S. Vibration confinement and energy harvesting in flexible structures using collocated absorbers and piezoelectric devices. J Sound Vib. 2010;329(3):261–76.
Ahmadabadi ZN, Khadem SE. Nonlinear vibration control and energy harvesting of a beam using a nonlinear energy sink and a piezoelectric device. J Sound Vib. 2014;333(19):4444–57.
Fang ZW, Zhang YW, Li X, Ding H, Chen LQ. Integration of a nonlinear energy sink and a giant magnetostrictive energy harvester. J Sound Vib. 2017;391:35–49.
Fang ZW, Zhang YW, Li X, Ding H, Chen LQ. Complexification-averaging analysis on a giant magnetostrictive harvester integrated with a nonlinear energy sink. J Vib Acoust. 2017;140(2):021009.
Kremer D, Liu K. A nonlinear energy sink with an energy harvester: transient responses. J Sound Vib. 2014;333(20):4859–80.
Kremer D, Liu K. A nonlinear energy sink with an energy harvester: harmonically forced responses. J Sound Vib. 2017;410:287–302.
Zhu Y, Zu JW, Guo L. A magnetoelectric generator for energy harvesting from the vibration of magnetic levitation. IEEE Trans Magn. 2012;48(11):3344–7.
Dai X, Wen Y, Li P, Yang J, Zhang G. Modeling, characterization and fabrication of vibration energy harvester using Terfenol-D/PZ. Sens Actuators A Phys. 2009;156(2):350–8.
Yang K, Zhang YW, Ding H, Yang TZ, Li Y, Chen LQ. Nonlinear energy sink for whole-spacecraft vibration reduction. J Vib Acoust. 2017;139(2):021011.
Ding H, Zhu MH, Chen LQ. Nonlinear vibration isolation of a viscoelastic beam. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018;92(2):325–49.
Ding H, Tang YQ, Chen LQ. Frequencies of transverse vibration of an axially moving viscoelastic beam. J Vib Control. 2017;23(20):3504–14.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 11772205), the Training Project of Liaoning Provincial Higher Education Institutions in Domestic and Overseas (Project No. 2018LNGXGJWPY-YB008), and the Scientific Research Fund of Liaoning Provincial Education Department (Project No. L201703).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YW., Wang, SL., Ni, ZY. et al. Integration of a Nonlinear Vibration Absorber and Levitation Magnetoelectric Energy Harvester for Whole-Spacecraft Systems. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 32, 298–309 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-019-00081-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-019-00081-y