Abstract
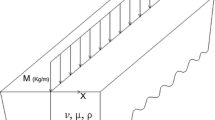
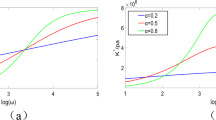
By introducing the equivalent stiffness of an elastic half-space interacting with a Timoshenko beam, the displacement solution of the beam resting on an elastic half-space subjected to a moving load is presented. Based on the relative relation of wave velocities of the half-space and the beam, four cases with the combination of different parameters of the half-space and the beam, the system of soft beam and hard half-space, the system of sub-soft beam and hard half-space, the system of sub-hard beam and soft half-space, and the system of hard beam and soft half-space are considered. The critical velocities of the moving load are studied using dispersion curves. It is found that critical velocities of the moving load on the Timoshenko beam depend on the relative relation of wave velocities of the half-space and the beam. The Rayleigh wave velocity in the half-space is always a critical velocity and the response of the system will be infinite when the load velocity reaches it. For the system of soft beam and hard half-space, wave velocities of the beam are also critical velocities. Besides the shear wave velocity of the beam, there is an additional minimum critical velocity for the system of sub-soft beam and hard half-space. While for systems of (sub-) hard beams and soft half-space, wave velocities of the beam are no longer critical ones. Comparison with the Euler-Bernoulli beam shows that the critical velocities and response of the two types of beams are much different for the system of (sub-) soft beam and hard half-space but are similar to each other for the system of (sub-) hard beam and soft half space. The largest displacement of the beam is almost at the location of the load and the displacement along the beam is almost symmetrical if the load velocity is smaller than the minimum critical velocity (the shear wave velocity of the beam for the system of soft beam and hard half-space). The largest displacement of the beam shifts behind the load and the asymmetry of the displacement along the beam increases with the increase of the load velocity due to the damping and wave radiation. The displacement of the beam at the front of the load is very small if the load velocity is larger than the largest wave velocity of the beam and the half space. The results of the present study provide attractive theoretical and practical references for the analysis of ground vibration induced by the high-speed train.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dieterman, H.A. and Metrikine, A.V., The equivalent stiffness of a half-space interacting with a beam. Critical velocities of a moving load along the beam. Eur. J. Mech., A/Solids, Vol.15 No.1, 1996, 67–90.
Kenney, J.T., Steady-state vibrations of beam on elastic foundation for moving load, Journal of Appl. Mech., 76, 1954, 359–364.
Achenbach, J.D. and Sun, C.T., Moving load on a flexibly supported Timoshenko beam, Int. J. Solids Structures, Vol.1, 1965, 355–370.
Kerr, A.D., The continuously supported rail subjected to an axial force and a moving load, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 14, 1972, 71–78.
Xie, W.P., Hu, J.W. and Xu, J., Dynamic response of track-ground systems under high velocity moving load, Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, Vol.21, No.7, 2002, 1075–1078 (in Chinese).
Chen, Y.M., Wang, C.J., Ji, M.X. and Chen, R.P., Train-induced ground vibration and deformation, In: Chen, Y.M. and Hirokazu Takemiya ed., Environmental Vibration Prediction, Monitoring and Evaluation. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2003, 158–174.
Filippov, A.P., Steady-state vibrations of an infinite beam on elastic half-space subjected to a moving load, Izvestija AN SSSR OTN Mehanika I Mashinostroenie, 6, 1961, 97–105 (translated from Russian).
Labra, J.J., An axially stressed railroad track on an elastic continuum subjected to a moving load, Acta Mechanica, 22, 1975, 113–129.
Dieterman, H.A. and Metrikine A.V., Steady-state displacements of a beam on an elastic half-space due to a uniformly moving constant load, Eur. J. Mech., A/Solids, Vol.16 No.2, 1997, 295–306.
Wang, C.M., Yang T.Q. and Lam K.Y, Viscoelastic Timoshenko beam solutions from Euler-Bernoulli solutions, J. Engng. Mech., Vol.123, No.7, 1997, 746–748.
Suiker, A.S.J., Borst, R. de, and Esveld, C., Critical behavior of a Timoshenko beam-half plane system under a moving load, Archive of Appl. Mech., 68, 1998, 158–168.
Cowper, G.R., The shear coefficient in Timoshenko’s beam theory, J. Appl. Mech., Vol.33, 1966, 335–340.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.50538010), the Doctoral Education of the State Education Ministry of China (No.20040335083) and Encouragement Fund for Young Teachers in University of Ministry of Education.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Wang, C. Steady-state response of a Timoshenko beam on an elastic half-space under a moving load. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 19, 26–39 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-006-0604-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-006-0604-x