Abstract
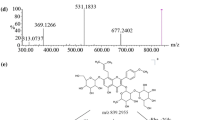
Timosaponin B-II (TB-II), a representative furostanol saponin in Rhizoma anemarrhenae, has been used as an emperor herb in many Chinese herbal formulas to treat diabetes and senile dementia. However, its metabolism and tissue distribution had not been investigated so far. In this work, a sensitive and specific high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry method was applied for the identification of TB-II and its major metabolites in in-vivo and in-vitro samples. Rat urine, feces, plasma and tissues were collected after oral administration of TB-II at a single dose of 300 mg kg−1. Furthermore, TB-II was incubated in artificial gastric juice (AGJ) and artificial intestinal juice (AIJ). As a result, 19 metabolites were detected and identified by comparing their HPLC behavior and MSn spectra profile with those of the parent drug. Moreover, the structures of its five metabolites were identified by using the standards prepared by the acid hydrolysis of TB-II. In addition to the parent drug, 14, 12, 6, 1, 1 and 7 metabolites were detected in rat urine, feces, plasma, heart, kidney and liver, respectively, while no metabolites or the parent drug were found in rat brain, spleen and lung. Seven metabolites appeared in AIJ incubation samples, but the parent drug was absent. Nine metabolites along with the parent drug were observed in AGJ incubation samples. The biotransformation pathways of TB-II mainly included dehydration, deglycosylation, hydroxylation, oxidation and E-ring cleavage. This is the first comprehensive investigation of the in-vivo and in-vitro metabolism of TB-II. The result provided important information for further pharmacological research on TB-II.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagumo S, Kishi S, Inoue T, Nagai M (1991) Yakugaku Zasshi 111(6):306–310
Nakashima N, Kimura I, Kimura M, Matsuura H (1993) J Nat Prod 56(3):345–350
Ma CH, Fan MS, Tang YH, Li ZX, Sun ZL, Ye G, Huang CG (2008) Biomed Chromatogr 22:835–850
Ma CH, Wang LX, Tang YH, Fan MS, Xiao HB, Huang CG (2008) Biomed Chromatogr 22:1066–1083
Lu WQ, Oiu Y, Li TJ, Tao X, Sun LN, Chen WS (2011) Clin Exp Pharmacol P 38:430–434
Kang LP, Zhang J, Cong Y, Li B, Xiong CQ, Zhao Y, Tan DW, Yu HS, Yu ZY, Cong YW, Liu C, Ma BP (2012) Planta Med 78:611–616
Lu WQ, Oiu Y, Li TJ, Tao X, Sun LN, Chen WS (2009) Arch Pharm Res 32:1301–1308
Xiao SZ, Xu ME, Ge YK, Xiao GF (2006) Biomed Environ Sci 19:185–191
Li TJ, Qiu Y, Yang PY, Rui YC, Chen WS (2007) Neurosci Lett 421:147–151
Deng Y, Ma BP, Cong YW, Shen YX, Zhang JJ, Shen YJ (2009) Chin Pharmacol Bull 25(2):244–247
Lu MZ, Zhang ZQ, Yi J, Chen WS, Hou ZH, Li TJ (2010) J Pharm Pract 28:283–287
Cai F, Sun LN, Gao SH, Yang Y, Yang Q, Chen WS (2008) J Pharm Biomed Anal 48:1411–1416
Cai F, Xu W, Wei H, Sun LN, Gao SH, Yang Q, Feng J, Zhang F, Chen WS (2010) J Chromatogr B 878:1845–1854
Liu ZR, Liu M, Qi YP, Zhu ZY, Chai YF, Yuan C, Lin Y (2013) J Sep Sci 36:1659–1666
Liu ZR, Dong X, Ding X, Chen XF, Lv L, Li YY, Chai YF (2013) J Chromatogr B 926:28–35
Feng Y, Chen BT, Lin AH, Liu YM (2014) J Chromatogr B 965:119–126
Wu B, Liu ZY, Fan MS, Sun ZL, Jiang WX, Huang CG (2012) Chin Chem Lett 23:332–334
Guo J, Xu CH, Xue R, Jiang WX, Wu B, Huang CG (2014) Arch Pharm Res. doi:10.1007/s12272-014-0431-4
Xiao Y, Cao JH, Zhao SW, Jiang DX, Zhang D (2011) West China J Pharm Sci 26(4):389–390
Appolpnova SA, Shpak AV, Semenov VA (2004) J Chromatogr B 800:281–289
Liu ZR, Zhu DL, Lv L, Li YY, Dong X, Zhu ZY, Chai YF (2012) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 26:1955–1964
Kang LP, Zhang J, Cong Y, Li B, Xiong CQ, Zhao Y, Tan DW, Yu HS, Yu ZY, Cong YW, Liu C, Ma BP (2012) Planta Med 78:611–616
He XJ, Qiao AM, Wang XH, Liu B, Jiang MM, Su LN, Yao XS (2006) Steroids 71:828–833
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this research was provided by a grant from the Key Program and General Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 81030065 and 81274055).
Compliance with ethical standards
We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed. All authors involved have no commercial association or other arrangement that might pose or imply a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article. All of the animal care and experimental procedures were approved by the Animal Ethical Committee of Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica (Shanghai, China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Y. Jia and Z. Fu contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Fu, Z., Li, Z. et al. In-vivo and In-vitro Metabolism Study of Timosaponin B-II Using HPLC-ESI-MSn . Chromatographia 78, 1175–1184 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2927-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-015-2927-6