Abstract
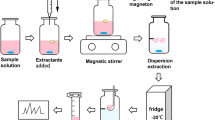
Solid-phase extraction followed by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction (SPE-DLLME) technique has been developed as a new analytical approach for extracting, cleaning up and preconcentrating benzaldehyde, a toxic oxidation product of the widely used preservative and co-solvent benzyl alcohol, in injectable formulation solutions. SPE of benzaldehyde from samples was carried out using C18 sorbent. After the elution of benzaldehyde from the sorbent by using acetonitrile, DLLME technique was performed on the obtained solution. Benzaldehyde was preconcentrated by using DLLME technique. Thus, 1.5 mL acetonitrile extract (disperser solvent) and 55.0 µL 1,2-dichloroethane (extraction solvent) were added to 5 mL ultra pure water and a DLLME technique was applied. Several variables that govern the proposed technique were studied and optimized. Under optimum conditions, the method detection limit (LOD) of benzaldehyde calculated as three times the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) was 0.08 µg L−1. The relative standard deviation (RSD) for four replicates was 5.8 %. The calibration graph was linear within the concentration range of 0.5–500 µg L−1 for benzaldehyde. The proposed method has been successfully applied to the analysis of the benzaldehyde in injectable formulation solutions (diclofenac, vitamin B-complex and voltaren) and the relative recoveries were between 88 and 92 % and show that matrix has a negligible effect on the performance of the proposed method.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moreton RC (2001) Handbook of pharmaceutical excipients, 3rd edn. American pharmaceutical Association and pharmaceutical press, Washington
Kazamifard AG, Moore DE, Mohammadi A (2002) J Pharm Biomed Anal 30:257–262
Jardine DS, Rogers J (1989) Pediatrics 83:153–160
Hiller JL, Benda GI, Rahatzad M, Allen JR, Culver DH, Carlson CV, Reynolds JW (1986) Pediatrics 77:500–506
The British pharmacopoeia (2012) British pharmacopoeia, HMSO, London
USP commission, (2001) The United States pharmacopoeia 24 and the National Formulary 19, Rockville, MD, USA.
Rezaee M, Assadi Y, Hosseini MRM, Aghaee E, Ahmadi F, Berijani S (2006) J Chromatogr A 1116:1–9
Rahnama Kozani R, Assadi Y, Shemirani F, Milani Hosseini MR, Jamali MR (2007) Talanta 72:387–393
Rezaee M, Yamini Y, Shariati S, Esrafili A, Shamsipur M (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:1511–1514
Rezaee M, Yamini Y, Faraji M (2010) J Chromatogr A 1217:2342–2357
Melwanki MB, Fuh MR (2008) J Chromatogr A 1207:24–28
Ebrahimzadeh H, Yamini Y, Kamarei F (2009) Talanta 79:1472–1477
Garcia-Lopez M, Rodriguez I, Cela R (2007) J Chromatogr A 1166:9–15
Rezaee M, Yamini Y, Khanchi A, Faraji M, Saleh A (2010) J. Hazard. Mater 178:766–770
Mashayekhi HA, Rezaee M, Garmaroudi SS, Montazeri N, Ahmadi SJ (2011) Anal Sci 27:865–868
Fattahi N, Samadi S, Assadi Y, Hosseini MRM (2007) J Chromatogr A 1169:63–69
Zhao RS, Diao CP, Chen QF, Wang X (2009) J Sep Sci 32:1069–1074
Liu X, Li J, Zhao Z, Zhang W, Lin K, Huang C, Wang X (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:2220–2226
Montes R, Rodriguez I, Ramil M, Rubi E, Cela R (2009) J Chromatogr A 1216:5459–5466
Alves ACH, Goncalves MMPB, Bernardo MMS, Mendes BS (2011) J Sep Sci. 34:2475–2481
Yan H, Qiao J, Wang H, Yang G, Row KH (2011) Analyst 136:2629–2634
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by Shahrekord University through a research fund. The authors were also partially supported by the Center of Excellence for Mathematics, Shahrekord University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haddadi, H., Rezaee, M., Semnani, A. et al. Application of Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction for the Determination of Benzaldehyde in Injectable Formulation Solutions. Chromatographia 77, 951–955 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-014-2701-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-014-2701-1