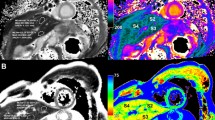
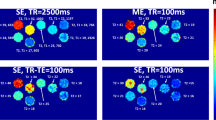
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of a range of parameter settings on T1 measurement stability in the portal vein using the T1-mapping sequences Look-Locker (LL) and Modified Look-Locker inversion recovery (MOLLI).
Materials and methods
Ten different versions of LL and MOLLI sequences were tested and compared to a reference sequence provided by the MR manufacturer. Ten healthy volunteers were imaged multiple times on two separate scan days at 3T. The mean T1 values and coefficient of variation (CoV) were calculated for each of the ten sequences and compared to the reference sequence.
Results
Six of the tested sequences had T1 values close to the reference sequence; among those, three sequences achieved lower CoV than the reference sequence. Lowest CoV was achieved using a non-triggered LL sequence with 5 beat readout and a 45o flip angle (mean T1 1733 ms ± 89 ms, CoV 1.3% ± 0.58%).
Conclusion
T1-measurements in the hepatic portal vein can be performed with high precision using either MOLLI or LL sequences provided that LL sampling duration is sufficiently long and flip angle sufficiently high. The advantage of constant timing outweighed the advantage of ECG-triggering.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ganong WF (1999) Review of medical physiology, 19th edn. Appleton & Lange, Stamford
Shen Y, Goerner FL, Snyder C, Morelli JN, Hao D, Hu D, Li X, Runge VM (2015) T1 relaxivities of gadolinium-based magnetic resonance contrast agents in human whole blood at 1.5, 3, and 7 T. Invest Radiol 50(5):330–338
Liu P, Chalak LF, Krishnamurthy LC, Mir I, Peng SL, Huang H, Lu H (2016) T1 and T2 values of human neonatal blood at 3 Tesla: dependence on hematocrit, oxygenation, and temperature. Magn Reson Med 75(4):1730–1735
Zhang X, Petersen ET, Ghariq E, De Vis JB, Webb AG, Teeuwisse WM, Hendrikse J, van Osch MJ (2013) In vivo blood T(1) measurements at 1.5 T, 3 T, and 7 T. Magn Reson Med 70(4):1082–1086
Piechnik SK, Ferreira VM, Lewandowski AJ, Ntusi NA, Banerjee R, Holloway C, Hofman MB, Sado DM, Maestrini V, White SK, Lazdam M, Karamitsos T, Moon JC, Neubauer S, Leeson P, Robson MD (2013) Normal variation of magnetic resonance T1 relaxation times in the human population at 1.5 T using ShMOLLI. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 15(13):11
Varela M, Hajnal JV, Petersen ET, Golay X, Merchant N, Larkman DJ (2011) A method for rapid in vivo measurement of blood T1. NMR Biomed 24(1):80–88
Treibel TA, Nasis A, Fontana M, Maestrini V, Castelletti S, Bhuva AN, Rosmini S, Abdel-Gadir A, Bulluck H, Kellman P, Piechnik SK, Robson MD, Moon J (2015) An instantaneous ECV with no blood sampling: using native blood T1 for hematocrit is as good as standard ECV. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 17(1):Q129
Look DC, Locker DR (1970) Time saving in measurement of NMR end EPR relaxation times. Rev Sci Instrum 41:250–251
Messroghli DR, Radjenovic A, Kozerke S, Higgins DM, Sivananthan MU, Ridgway JP (2004) Modified Look-Locker inversion recovery (MOLLI) for high-resolution T 1 mapping of the heart. Magn Reson Med 52(1):141–146
Qin Q, Strouse JJ, van Zijl PC (2011) Fast measurement of blood T 1 in the human jugular vein at 3 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 65(5):1297–1304
Li W, Liu P, Lu H, Strouse JJ, van Zijl PC, Qin Q (2016) Fast measurement of blood T 1 in the human carotid artery at 3T: accuracy, precision, and reproducibility. Magn Reson Med 77(6):7
Vassiliou V, Heng EL, Nyktari E, Greiser A, Firmin D, Pennell DJ, Gatehouse P, Prasad SK (2015) Effect of temperature and heart rate variability on Phantom T1 maps. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 17(1):W24
Scheffler K, Lehnhardt S (2003) Principles and applications of balanced SSFP techniques. Eur Radiol 13(11):2409–2418
Deichmann RH, Haase A (1992) Quantification of T1 Values by SNAPSHOT-FLASH NMR Imaging. J Magn Reson 96(3):608–612
Taylor AJ, Salerno M, Dharmakumar R, Jerosch-Herold M (2016) T1 mapping: basic techniques and clinical applications. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 9(1):67–81
Kellman P, Hansen MS (2014) T1-mapping in the heart: accuracy and precision. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 16(1):2
Kalavagunta C, Michaeli S, Metzger GJ (2014) In-vitro Gd-DTPA relaxometry studies in oxygenated venous human blood and aqueous solution at 3 and 7T. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 9(2):169–176
Shimada K, Nagasaka T, Shidahara M, Machida Y, Tamura H (2012) In vivo measurement of longitudinal relaxation time of human blood by inversion-recovery fast gradient-echo MR imaging at 3T. Magn Reson Med Sci 11(4):265–271
Wu W-C, Jain V, Li C, Giannetta M, Hurt H, Wehrli FW, Wang DJJ (2010) In vivo venous blood T(1) measurement using inversion recovery true-FISP in children and adults. Magn Reson Med 64(4):1140–1147
Zhang X, Petersen ET, Ghariq E, Vis JB, Webb AG, Teeuwisse WM, Hendrikse J, Osch MJP (2013) In vivo blood T1 measurements at 1.5 T, 3 T, and 7 T. Magn Reson Med 70(4):1082–1086
McRobbie DW (2007) MRI from picture to proton, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gallix BP, Taourel P, Dauzat M, Bruel JM, Lafortune M (1997) Flow pulsatility in the portal venous system: a study of Doppler sonography in healthy adults. Am J Roentgenol 169(1):141–144
Acknowledgements
Grant support: this project is funded by the Research Council of Norway.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SASV design and planning of the study, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of manuscript, and critical revision. PKH design and planning of the study, drafting of manuscript, and critical revision. AB design and planning of the study, drafting of manuscript, and critical revision. MA-M design and planning of the study, drafting of manuscript, and critical revision. CH design and planning of the study, drafting of manuscript, and critical revision. THS design and planning of the study, drafting of manuscript, and critical revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

10334_2018_731_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
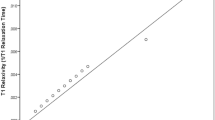
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of the apparent T1 and CoV depending on the method of analyzation. Y-axis are measurements made by the method described in the methods section. X-axis are measurements made in parametric maps. As evident from the figure, the measurements are well comparable between the two methods of analyzation.

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vatnehol, S.A.S., Hol, P.K., Bjørnerud, A. et al. Precision of T1-relaxation time measurements in the hepatic portal vein: influence of measurement technique and sequence parameters. Magn Reson Mater Phy 32, 359–368 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-018-00731-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-018-00731-1