Abstract
Object
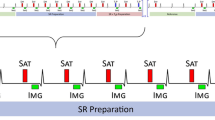
The objective was to improve the temporal resolution in black-blood CINE tissue phase mapping sequences at high field MR systems. The temporal resolution is limited due to SAR constraints causing idle times into the sequence. The aim was to avoid these idle times and therefore providing an increased number of heart phases.
Materials and methods
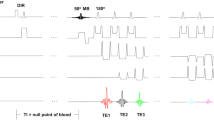
Thirteen volunteers were enrolled in this study. Each volunteer underwent different myocardial short-axis scans comprising scans with application of both presaturation pulses, with alternating application of presaturation pulses and with an attenuation of the excitation angle. The last two approaches enable a SAR reduction or increased temporal resolution. The contrast to noise ratio (CNR) between myocardium and blood and the influence on the measured tissue motion were investigated.
Results
High CNR between myocardium and blood could be obtained with the application of alternating presaturation-pulses. Reduction of the flip angle of the presaturation-pulses provided reduced CNR relative to both the original and the alternated presaturation-pulses approach. More details of the myocardial motion were observed with increased temporal resolution.
Conclusion
It is feasible to increase the temporal resolution at high field strength by reducing the SAR with either alternating presaturation-pulses or decreased flip angle of these pulses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drangova M, Zhu Y, Pelc NJ (1997) Effect of artifacts due to flowing blood on the reproducibility of phase-contrast measurements of myocardial motion. J Magn Reson Med 7: 664–668
Felmlee J, Ehman R (1987) Spatial presaturation: a method for suppressing flow artifacts and improving depiction of vascular anatomy in MR imaging. Radiology 164: 559–564
Delfino JG, Johnson KR, Eisner RL, Eder S, Leon AR, Oshinski JN (2008) Three-directional myocardial Phase-Contrast tissue velocity MR imaging with Navigator-Echo gating: in vivo and in vitro study. Radiology 246: 917–925
Jung B, Schneider B, Markl M, Saurbier B, Geibel A, Hennig J (2004) Measurement of left ventricular velocities: phase contrast MRI velocity mapping versus tissue-doppler-ultrasound in healthy volunteers. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 6: 777–783
Petersen SE, Jung BA, Wiesmann F, Selvanayagam JB, Francis JM, Hennig J, Neubauer S, Robson MD (2006) Myocardial tissue phase mapping with cine phase-contrast mr imaging: regional wall motion analysis in healthy volunteers. Radiology 238: 816–826
Nayak KS, Rivas PA, Pauly JM, Scott GC, Kerr AB, Hu BS, Nishimura DG (2001) Real-time black-blood MRI using spatial presaturation. J Magn Reson Med 13: 807–812
Hennig J, Schneider B, Peschl S, Markl M, Laubenberger TKJ (1998) Analysis of myocardial motion based on velocity measurements with a black blood prepared segmented gradient-echo sequence: Methodology and applications to normal volunteers and patients. J Magn Reson Med 8: 868–877
Bradley WG (1988) Carmen lecture. Flow phenomena in MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol 150: 983–994
Mayo J, Culham J, MacKay A, Aikins D (1989) Blood MR signal suppression by preexcitation with inverting pulses. Radiology 173: 269–271
Edelman R, Chien D, Kim D (1991) Fast selective black blood MR imaging. Radiology 181: 655–660
Reichenbach JR, Venkatesan R, Schillinger DJ, Kido DK, Haacke EM (1997) Small vessels in the human brain: MR venography with deoxyhemoglobin as an intrinsic contrast agent. Radiology 204: 272–277
Frahm J, Merboldt KD, Hanicke W, Haase A (1985) Stimulated echo imaging. J Magn Reson Med 64: 81–93
Frahm J, Hanicke W, Bruhn H, Gyngell ML, Merboldt KD (1991) High-speed STEAM MRI of the human heart. Magn Reson Med 22: 133–142
Fahmy AS, Pan L, Stuber M, Osman NF (2006) Correction of through-plane deformation artifacts in stimulated echo acquisition mode cardiac imaging. Magn Reson Med 55: 404–412
Basha TA, Ibrahim EH, Weiss RG, Osman NF (2009) Cine cardiac imaging using black-blood steady-state free precession (BB-SSFP) at 3T. J Magn Reson Med 30: 94–103
Koktzoglou I, Li D (2007) Diffusion-prepared segmented steady-state free precession: application to 3D black-blood cardiovascular magnetic resonance of the thoracic aorta and carotid artery walls. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 9: 33–42
Sirol M, Itskovich VV, Mani V, Aguinaldo JGS, Fallon JT, Misselwitz B, Weinmann H, Fuster V, Toussaint J, Fayad ZA (2004) Lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques detected by gadofluorine-enhanced in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 109: 2890–2896
Pell GS, Lewis DP, Branch CA (2003) Pulsed arterial spin labeling using TurboFLASH with suppression of intravascular signal. Magn Reson Med 49: 341–350
Bornstedt A, Bernhardt P, Hombach V, Kamenz J, Spiess J, Subgang A, Rasche V (2008) Local excitation black blood imaging at 3T: application to the carotid artery wall. Magn Reson Med 59: 1207–1211
Miller S, Simonetti OP, Carr J, Kramer U, Finn JP (2002) MR imaging of the heart with cine true fast imaging with steady-state precession: influence of spatial and temporal resolutions on left ventricular functional parameters. Radiology 223: 263–269
Inoue Y, Nomura Y, Nakaoka T, Watanabe M, Kiryu S, Okubo T, Ohtomo K (2005) Effect of temporal resolution on the estimation of left ventricular function by cardiac MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 23: 641–645
Jung B, Föll D, Böttler P, Petersen S, Hennig J, Markl M (2006) Detailed analysis of myocardial motion in volunteers and patients using high-temporal-resolution MR tissue phase mapping. J Magn Reson Imaging 24: 1033–1039
Jung B, Zaitsev M, Hennig J, Markl M (2006) Navigator gated high temporal resolution tissue phase mapping of myocardial motion. Magn Reson Med 55: 937–942
Haacke EM, Brown RW, Thompson MR, Venkatesan R (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging: physical principles and sequence design. Wiley, New York
Pelc NJ, Bernstein MA, Shimakawa A, Glover GH (1991) Encoding strategies for three-direction phase-contrast MR imaging of flow. J Magn Reson Imaging 1: 405–413
Souza SP, Szumowski J, Dumoulin CL, Plewes DP, Glover G (1988) SIMA: simultaneous multislice acquisition of MR images by hadamard-encoded excitation. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12: 1026–1030
Delfino JG, Bhasin M, Cole R, Eisner RL, Merlino J, Leon AR, Oshinski JN (2006) Comparison of myocardial velocities obtained with magnetic resonance phase velocity mapping and tissue doppler imaging in normal subjects and patients with left ventricular dyssynchrony. J Magn Reson Imaging 24: 304–311
Wang Y, Rossman PJ, Grimm RC, Riederer SJ, Ehman RL (1996) Navigator-echo-based real-time respiratory gating and triggering for reduction of respiration effects in three-dimensional coronary MR angiography. Radiology 198: 55–60
Bellenger NG, Gatehouse PD, Rajappan K, Keegan J, Firmin DN, Pennell DJ (2000) Left ventricular quantification in heart failure by cardiovascular MR using prospective respiratory navigator gating: comparison with breath-hold acquisition. J Magn Reson Imaging 11: 411–417
Fradkin M, Ciofolo C, Mory B, Hautvast G, Breeuwer M (2008) Comprehensive segmentation of cine cardiac mr images. In: Metaxas DN, Axel L, Fichtinger G, Székely G (eds) MICCAI (1), vol 5241 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, pp 178–185
Hautvast G, Lobregt S, Breeuwer M, Gerritsen F (2006) Automatic contour propagation in cine cardiac magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 25: 1472–1482
Walker PG, Cranney GB, Scheidegger MB, Waseleski G, Pohost GM, Yoganathan AP (1993) Semiautomated method for noise reduction and background phase error correction in MR phase velocity data. J Magn Reson Imaging 3: 521–530
Zerhouni EA, Parish DM, Rogers WJ, Yang A, Shapiro EP (1988) Human heart: tagging with MR imaging—a method for noninvasive assessment of myocardial motion. Radiology 169: 59–63
Foo TK, Bernstein MA, Aisen AM, Hernandez RJ, Collick BD, Bernstein T (1995) Improved ejection fraction and flow velocity estimates with use of view sharing and uniform repetition time excitation with fast cardiac techniques. Radiology 195: 471–478
Markl M, Hennig J (2001) Phase contrast MRI with improved temporal resolution by view sharing: k-space related velocity mapping properties. Magn Reson Imaging 19: 669–676
Bernstein MA, King KF, Zhou XJ (2004) Handbook of MRI pulse sequences. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lutz, A., Bornstedt, A., Manzke, R. et al. SAR reduced black-blood cine TPM for increased temporal resolution at 3T. Magn Reson Mater Phy 24, 127–135 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-010-0242-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-010-0242-7