Abstract
Objectives
Histopathology of prostate needle biopsies (PNBs) is an important part in the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment evaluation of prostate cancer. The determination of metabolite levels in the same biopsies may have additional clinical value. Here, we demonstrate the use of non-destructive high resolution magic angle spinning (HRMAS) proton NMR Spectroscopy for the assessment of metabolic profiles of prostate tissue in PNBs as commonly obtained in standard clinical practice.
Materials and methods
PNBs that were taken routinely from 48 patients suspected of having prostate cancer were subjected to HRMAS proton NMR spectroscopy. Subsequent histopathology of the same biopsies classified the tissue either as cancer (n = 10) or benign (n = 30).
Results
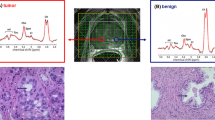
Some practical aspects of this assessment were evaluated, such as typical spectral contamination caused by the PNB procedure. Significant metabolic differences were found between malignant and benign tissue using a small set of ratio’s involving signals of choline compounds, citrate and lactate. Moreover, significant correlations were observed between choline, total choline, and citrate over creatine signal ratios and the Gleason scores of tumor in PNBs and of tumor in the whole prostate.
Conclusion
This preliminary study indicates that HRMAS NMR of routinely obtained PNBs can provide detailed metabolic information of intact prostate tissue with clinical relevance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thornbury JR, Ornstein DK, Choyke PL, Langlotz CP, Weinreb JC (2001) Prostate cancer: what is the future role for imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176: 17–22
Gao X, Porter AT, Grignon DJ, Pontes JE, Honn KV (1997) Diagnostic and prognostic markers for human prostate cancer. Prostate 31: 264–281
Deshmukh N, Foster CS (2002) Grading prostate cancer. In: Foster CS, Bostwick DG(eds) Pathology of the prostate. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 191–227
Matsumoto T, Mochida O, Kumazawa J, Kinjo M, Sagiyama K (2002) Critical assessment of inflammatory lesions of the prostate, including cytopathologic appearances and diagnosis. In: Foster CS, Bostwick DG(eds) Pathology of the prostate. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 56–65
Nickel JC, True LD, Krieger JN, Berger RE, Boag AH, Young ID (2001) Consensus development of a histopathological classification system for chronic prostatic inflammation. BJU Int 87: 797–805
Helpap B (2002) Benign prostatic hyperplasia. In: Foster CS, Bostwick DG(eds) Pathology of the Prostate. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp 66–113
Schiebler ML, Miyamoto KK, White M, Maygarden SJ, Mohler JL (1993) In vitro high resolution 1H-spectroscopy of the human prostate: benign prostaic hyperplasia, normal peripheral zone and adenocarcinoma. Magn Reson Med 29: 285–291
Cornel EB, Smits GA, Oosterhof GO, Karthaus HF, Schalken JA, Heerschap A (1993) Characterization of human prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia and normal prostate by in vitro 1H and 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Urol 150: 2019–2024
Kurhanewicz J, Dahiya R, MacDonald JM, Chang LH, James TL, Narayan P (1993) Citrate alterations in primary and metastatic human prostatic adenocarcinomas: 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy and biochemical study. Magn Reson Med 29: 149–157
Hahn P, Smith IC, Leboldus L, Littman C, Somorjai RL, Bezabeh T (1997) The classification of benign and malignant human prostate tissue by multivariate analysis of 1H magnetic resonance spectra. Cancer Res 57: 3398–3401
van der Graaf M, Schipper R, Oosterhof G, Schalken J, Verhofstad A, Heerschap A (2000) Proton MR spectroscopy of prostatic tissue focused on the detection of spermine, a possible biomarker of malignant behavior in prostate cancer. MAGMA 10: 153–159
Tomlins AM, Foxall PJD, Lindon JC, Lynch MJ, Spraul M, Everett JR, Nicholson JK (1998) High resolution magic angle spinning H-1 nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of intact prostatic hyperplastic and tumour tissues. Anal Commun 35: 113–115
Cheng LL, Wu C, Smith MR, Gonzalez RG (2001) Non-destructive quantitation of spermine in human prostate tissue samples using HRMAS 1H NMR spectroscopy at 9.4 T. FEBS Lett 494: 112–116
Swanson MG, Vigneron DB, James JK, Kurhanewicz J (2002) 1H HR-MAS investigations of four potential markers for prostate cancer. Proc Int Soc Mag Reson 9: 2336
Fitch WL, Detre G, Holmes CP (1994) High resolution 1H NMR in solid-phase organic synthesis. J Org Chem 59: 7955–7956
Smith ICP, Blandford DE (1998) Diagnosis of cancer in humans by 1H NMR of tissue biopsies. Biochem Cell Biol 76: 472–476
Huhn Stephen D, Szabo Christina M, Gass Jerome H, Manzi Adriana E (2004) Metabolic profiling of normal and hypertensive rat kidney tissues by hrMAS-NMR spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem 378: 1511–1519
Meiboom S, Gill D (1958) Modified Spin-echo Method for measuring nuclear relaxation times. Rev Sci Instrum 29: 688–691
Bancroft JD, Stevens A, Turner DR (1996) Theory and practice of histopathological techniques. Churchill Livingstone, New York, p 101
Swanson GM, Vigneron DB, Tabatabai ZL, Males RG, Schmitt L, Carroll PR, James JK, Hurd RE, Kurhanewicz J (2003) Proton HR-MAS spectroscopy and quantitative pathologic analysis of MRI/3D-MRSI-targeted postsurgical prostate tissues. Magn Reson Med 50: 944–954
Swanson MG, Zektzer AS, Tabatabai ZL, Simko J, Jarso S, Keshari KR, Schmitt L, Carroll PR, Shinohara K, Vigneron DB, Kurhanewicz J (2006) Quantitative analysis of prostate metabolites using 1H HR-MAS spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 55: 1257–1264
Wu CL, Taylor JL, He W, Zepeda AG, Halpern EF, Bielecki A, Gonzalez RG, Cheng LL (2003) Proton high-resolution magic angle spinning NMR analysis of fresh and previously frozen tissue of human prostate. Magn Reson Med 50: 1307–1311
Wind RA, Hu JZ, Rommereim DN (2001) High-resolution 1H NMR spectroscopy in organs and tissues using slow Magic Angle Spinning. Magn Reson Med 46: 213–218
Taylor JL, Wu CL, Cory D, Gonzalez RG, Bielecki A, Cheng LL (2003) High-Resolution Magic Angle Spinning Proton NMR Analysis of Human Prostate Tissue With Slow Spinning Rates. Magn Reson Med 50: 627–632
Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Nelson SJ, Hricak H, MacDonald JM, Konety B, Narayan P (1995) Citrate as an in vivo marker to discriminate prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia and normal prostate peripheral zone: detection via localized proton spectroscopy. Urology 45: 459–466
Heerschap A, Jager GJ, van der Graaf M, Barentsz JO, de la Rosette JJMCH, Oosterhof GON, Ruijter ETG, Ruijs SHJ (1997) In vivo proton MR spectroscopy reveals altered metabolite content in malignant prostate tissue. Anticancer Res 17: 1455–1460
Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Males RG, Swanson MG, Yu KK, Hricak H (2000) The prostate: MR imaging and spectroscopy. Present and future. Radiol Clin North Am 38: 115–138
Shah N, Sattar A, Benanti M, Hollander S, Cheuck L (2006) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy as an imaging tool for cancer: a review of the literature. J Am Osteopath Assoc 106(1): 23–7
Futterer JJ, Scheenen TW, Heijmink SW, Huisman HJ, Hulsbergen-Vande Kaa CA, Witjes JA, Heerschap A, Barentsz JO (2007) Standardized threshold approach using threedimensional proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in prostate cancer localization of the entire prostate. Invest Radiol 42(2):116–122
Lynch MJ, Nicholson JK (1997) Proton MRS of human prostatic fluid: correlations between citrate, spermine, and myo-inositol levels and changes with disease. Prostate 30: 248–255
Costello LC, Franklin RB (2006) The clinical relevance of the metabolism of prostate cancer; zinc and tumor suppression: connecting the dots. Mol Cancer 5: 17
Kim J-w, Dang CV (2006) Cancer’s molecular sweet tooth and the Warburg effect. Cancer Res 66: 8927–8930
Golman K, In‘t Zandt R, Thaning M (2006) Real-time metabolic imaging. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(30): 11270–11275
Stoyanova R, Swanson MG, Vigneron DB, Kurhanewicz J, Brown TR (2002) Metabolite Profiles Associated with Prostate Tissue Subcomponents, Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med, 10
Zakian KL et al (2005) Correlation of proton MR spectroscopic imaging with gleason score based on step-section pathologic analysis after radical prostatectomy. Radiology 234(3): 804– 814
Kurhanewicz J, Swanson MG, Nelson SJ, Vigneron DB (2002) Combined magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopic imaging approach to molecular imaging of prostate cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 16(4):451–463. Review
Podo F (1999) Tumour phospholipid metabolism. NMR Biomed 12(7):413–439. Review
Glunde K, Jacobs MA, Bhujwalla ZM (2006) Choline metabolism in cancer: implications for diagnosis and therapy. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 6(6): 821–829
Cheng LL, Burns MA, Taylor JL, He W, Halpern EF, McDougal WS, Wu CL (2005) Metabolic Characterization of Human Prostate Cancer with Tissue Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Cancer Res 65: 3030–3035
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Albert Verhofstad died before publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Asten, J.J.A., Cuijpers, V., Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C. et al. High resolution magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy for metabolic assessment of cancer presence and Gleason score in human prostate needle biopsies. Magn Reson Mater Phy 21, 435–442 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0156-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0156-9