Abstract
Introduction
The effect of the acoustic scanner noise produced by gradient coil switching on the auditory evoked BOLD signal represents a well-known problem in auditory functional MRI (FMRI). In this paper, a new low-noise echo-planar imaging (EPI) sequence is presented that is optimized for auditory FMRI measurements.
Methods
The sequence produces a narrow-band acoustic frequency spectrum by using a sinusoidal readout echo train and a constant phase encoding gradient. This narrow band is adapted to the frequency response function of the MR scanner by varying the switching frequency of the sinusoidal readout gradient.
Results
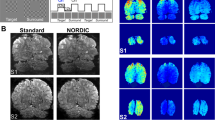
Compared to a manufacturer-provided standard EPI sequence, the acoustic noise reduction amounts to up to 20 dBA. Using a simple block design paradigm contrasting presentation of a pure tone during ON blocks and “silence” (absence of the tone) during OFF blocks, the new low-noise sequence was evaluated and compared to the standard EPI sequence. Statistical parametric mapping (SPM) resulted in higher levels of significance of auditory activation for the low-noise sequence.
Discussion
These findings strongly suggest that the low-noise sequence may generate enhanced BOLD contrasts compared to the standard EPI sequences commonly used in FMRI.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bandettini PA, Jesmanowicz A, Van Kylen J, Birn RM, Hyde JS (1998) Functional MRI of brain activation induced by scanner acoustic noise. Magn Reson Med 39: 410–416
Elliott MR, Bowtell RW, Morris PG (1999) The effect of scanner sound in visual, motor, and auditory functional MRI. Magn Reson 41: 1230–1235
Brummett RE, Talbot JM, Charuhas P (1988) Potential hearing loss resulting from MR imaging. Radiology 169: 539–540
Quirk ME, Letendre AJ, Ciottone RA, Lingley JF (1989) Anxiety in patients undergoing MR imaging. Radiology 170: 463–466
Mansfield P, Glover PM, Beaumont J (1998) Sound generation in gradient coil structures for MRI. Magn Reson Med 39: 539–550
Edelstein WA, Hedeen RA, Mallozzi RP, El Hamamsy SA, Ackermann RA, Havens TJ (2002) Making MRI quieter. Magn Reson Imaging 20: 155–163
Schad LR, Bock M, Müller E, Lorenz WJ (1995) Echo planar imaging on a standard 1.5 Tesla imager. Z Med Phys 5: 205–207
Shellock FG, Ziarati M, Atkinson D, Chen DY (1998) Determination of gradient magnetic field induced acoustic noise associated with the use of Echo Planar and three-dimensional, fast spin Echo techniques. J Magn Reson Imaging 8: 1154–1157
Price DL, De Wilde JP, Papadaki AM, Curran JS, Kitney RI (2001) Investigation of acousic noise on 15 MRI scanners from 0.2T to 3T. J Magn Reson Imaging 13: 228–293
Counter SA, Olofsson A, Grahn HF, Borg E (1997) MRI acoustic noise: sound pressure and frequency analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging 7: 606–611
Foster JR, Hall DA, Summerfield AQ, Palmer AR, Bowtell RW (2000) Sound-level measurements and calculations of safe noise dosage during EPI at 3 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 12: 157–163
Zwicker E, Fastl H (2001) Psychoacoustics. Facts and models, 2nd edn. Springer, Heidelberg
Scheffler K, Bilecen D, Schmid N, Tschopp K, Seelig J (1998) Auditory cortical responses in hearing subjects and unilateral deaf patients as detected by functional magnetic resonance imaging. Cereb Cortex 8: 156–163
Hall DA, Haggard MP, Akeroyd MA, Palmer AR, Summerfield AQ, Elliott MR, Gurney EM, Bowtell RW (1999) Sparse temporal sampling in auditory fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp 7: 213–223
Ravicz ME, Melcher JR (2001) Isolating the auditory system from acoustic noise during functional magnetic resonance imaging: examination of noise conduction through the ear canal, head, and body. J Acoust Soc Am 109: 216–231
Mansfield P, Haywood B (2000) Principles of active acoustic control in gradient coil design. Magn Reson Mater Phy 10: 147–151
Cho ZH, Chung ST, Chung JY, Park SH, Kim JS, Moon CH, Hong IK (1998) A new silent magnetic resonance imaging using a rotating DC gradient. Magn Reson Imaging 39: 317–321
Katsunuma A, Takamori H, Sakakura Y, Hamamura Y, Ogo Y, Katayama R (2002) Quiet MRI with novel acoustic noise reduction. Magn Reson Mater Phys 13: 139–144
Chambers J, Akeroyd MA, Summerfield AQ, Palmer AR (2001) Active control of the volume acquisition noise in functional magnetic resonance imaging: method and psychoacoustical evaluation. J Acoust Soc Am 110: 3041–3054
Hennel F, Girard F, Loenneker T (1999) Silent MRI with soft gradient pulses. Magn Reson Med 42: 6–10
Hennel F (2001) Fast spin echo and fast gradient echo MRI with low acoustic noise. J Magn Reson Imaging 13: 960–966
Tomasi DG, Ernst T (2003) Fast spin echo and fast gradient echo MRI with low acoustic noise. J Magn Reson Imaging 13: 960–966
Oesterle C, Hennel F, Hennig J (2001) Quiet imaging with interleaved spiral read-out. Magn Reson Imaging 19: 1333–1337
Seifritz E, Di Salle F, Esposito F, Herdener M, Neuhoff JG, Scheffler K (2006) Enhancing BOLD response in the auditory system by neurophysiologically tuned fMRI sequence. Neuroimage 29: 1013–1022
Hedeen RA, Edelstein WA (1997) Characterization and prediction of gradient acoustic noise in MR imagers. Magn Reson Med 37: 7–10
Schomberg H, Timmer J (1995) The gridding method for image reconstruction by Fourier transform. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 14: 597–607
Sekihara K, Kohno H (1987) New reconstruction technique for echo-planar imaging to allow combined use of odd and even numbered echoes. Magn Reson Med 5: 485–491
Schmitt F, Stehling MK, Turner R (1998) Echo planar imaging—theory, thechnique and application. Springer, Heidelberg
O’Sullivan JD (1985) A fast sinc function gridding algorithm for Fourier inversion in computer tomography. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 4: 200–207
Egan JP, Hake HW (1950) On the masking pattern of a simple auditory stimulus. J Acoust Soc Am 22: 622–630
Wegel RL, Lane CE (1924) The auditory masking of one sound by another and its probable relation to the dynamics of the inner ear. Phys Rev 23: 266–285
Bornert P, Aldefeld B, Eggers H (2000) Reversed spiral MR imaging. Magn Reson Med 44: 479–484
Jakob PM, Schlaug G, Griswold M, Lovblad KO, Thomas R, Ives JR, Matheson JK, Edelman RR (1998) Functional burst imaging. Magn Reson Med 40: 614–621
Schwarzbauer C, Davis MH, Rodd JM, Johnsrude I (2006) Interleaved silent steady state (ISSS) imaging: a new sparse imaging method applied to auditory fMRI. Neuroimage 29: 774–782
Diesch E, Struve M, Rupp A, Ritter S, Hülse M, Flor H (2004) Enhancement of steady-state auditory evoked magnetic fields in tinnitus. Eur J Neurosci 19: 1093–1104
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmitter, S., Diesch, E., Amann, M. et al. Silent echo-planar imaging for auditory FMRI. Magn Reson Mater Phy 21, 317–325 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0132-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0132-4