Abstract
Purpose
Chemotherapy increases survival in breast cancer patients. Consequently, cerebral metastases have recently become a significant clinical problem, with an incidence of 30–40% among breast carcinoma patients. As this phenomenon cannot be studied longitudinally in humans, models which mimic brain metastasis are needed to investigate its pathogenesis. Such models may later be used in experimental therapeutic approaches.
Material and methods/results
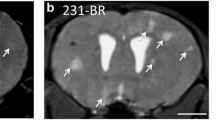
We report a model in which 69% of the animals (9/13 BALB/c nude mice) developed MR-detectable abnormal masses in the brain parenchyma within a 20 to 62-day time window post intra-carotid injection of 435-Br1 human cells. The masses detected in vivo were either single (7 animals) or multiple (2 animals). Longitudinal MR (MRI/MRS) studies and post-mortem histological data were correlated, revealing a total incidence of experimental brain metastases of 85% in the cases studied (11/13 animals). ADC maps perfectly differentiated edema and/or CSF areas from metastasis. Preliminary MRS data also revealed additional features: decrease in N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) was the first MRS-based marker of metastasis growth in the brain (micrometastasis); choline-containing compounds (Cho) rose and creatine (Cr) levels decreased as these lesions evolved, with mobile lipids and lactate also becoming visible. Furthermore, MRS pattern recognition-based analysis suggested that this approach may help to discriminate different growth stages.
Conclusions
This study paves the way for further in vivo studies oriented towards detection of different tumor progression states and for improving treatment efficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADC:
-
Apparent diffusion coefficient
- ASCII:
-
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
- CBF:
-
Cerebral blood flow
- CBV:
-
Cerebral blood volume
- CE-T1 MRI:
-
Contrast-enhanced T1 MRI
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- DMEM/F12:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium with nutrient mixture F12 Ham
- d_PI:
-
Days post-injection
- DWI:
-
Diffusion weighted imaging
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- GUI:
-
Graphical user interface
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin–eosin
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- ic :
-
Intracarotid
- ip :
-
Intraperitoneal
- LB:
-
Line broadening
- HBSS:
-
Hanks’ balanced salt solution
- 1H MRS:
-
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- ML:
-
Mobile lipids
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- MTX:
-
Matrix size
- MSME:
-
multi-slice multi-echo
- NEX:
-
Number of averages
- OCT:
-
Tissue freezing medium
- PCNA:
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- PRESS:
-
Point resolved spectroscopy
- RARE:
-
Rapid acquisition by relaxation enhancement
- sc :
-
Subcutaneous
- SNR:
-
Signal to noise ratio
- SPF:
-
Specific pathogen free
- TAT:
-
Total acquisition time
- TE:
-
Echo time
- TR:
-
Repetition time
- VAPOR:
-
Variable pulse power and optimized relaxation delays
- Δν 1/2 :
-
MRS peak width at half height
- Δ:
-
Big delta
- δ :
-
Small delta
References
International Agency for Research on Cancer (WHO). http://www.iarc.fr/. Accessed: 16 Oct, 2007
Weil RJ, Palmieri DC, Bronder JL, Stark AM, Steeg PS (2005) Breast cancer metastasis to the central nervous system. Am J Pathol 167: 913–920
Sierra A (2005) Metastases and their microenvironments: linking pathogenesis and therapy. Drug Resist Updat 8: 247–257
Carey LA, Ewend MG, Metzger R, Sawyer L, Dees EC, Sartor CI, Moore DT, Graham ML (2004) Central nervous system metastases in women after multimodality therapy for high risk breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 88: 273–280
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC (2002) Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer 2: 563–572
Zhang RD, Fidler IJ, Price JE (1991) Relative malignant potential of human breast cancer carcinoma cell lines established from pleural effusions and a brain metastasis. Invas Metast 11: 204–215
Schackert G, Fidler IJ (1988) Development of in vivo models for studies of brain metastasis. Int J Cancer. 41: 589–594
Schackert G, Price JE, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ (1989) Unique patterns of brain metastasis produced by different human carcinomas in athymic nude mice. Int J Cancer 44: 892–897
Dome B, Timar J, Paku S (2003) A novel concept of glomeruloid body formation in experimental cerebral metastases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62: 655–661
Leenders W, Kusters B, Pikkemaat J, Wesseling P, Ruiter D, Heerschap A, Barentsz J, de Waal RM (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor-A determines detectability of experimental melanoma brain metastasis in GD-DTPA-enhanced MRI. Int J Cancer 105: 437–443
Yoneda T, Williams PJ, Hiraga T, Niewolna M, Nishimura R (2001) A bone-seeking clone exhibits different biological properties from the MDA-MB-231 parental human breast cancer cells and a brain-seeking clone in vivo and in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 16: 1486–1495
Heyn C, Ronald JA, Ramadan SS, Snir JA, Barry AM, MacKenzie LT, Mikulis DJ, Palmieri D, Bronder JL, Steeg PS, Yoneda T, MacDonald IC, Chambers AF, Rutt BK, Foster PJ (2006) In vivo MRI of cancer cell fate at the single-cell level in a mouse model of breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Magn Reson Med 56: 1001–1010
Howe FA, Opstad KS (2003) 1H MR spectroscopy of brain tumors and masses. NMR Biomed 16: 123–131
Griffin JL, Kauppinen RA (2007) A metabolomics perspective of human brain tumours. FEBS J 274: 1132–1139
Griffin JL, Kauppinen RA (2007) Tumour metabolomics in animal models of human cancer. J Proteome Res 6: 498–505
Tate AR, Griffiths JR, Martinez-Perez I, Moreno A, Barba I, Cabañas ME, Watson D, Alonso J, Bartumeus F, Isamat F, Ferrer I, Vila F, Ferrer E, Capdevila A, Arús C (1998) Towards a method for automated classification of 1H MRS spectra from brain tumors. NMR Biomed 11: 177–191
Sierra A, Price JE, Garcia-Ramirez M, Mendez O, Lopez L, Fabra A (1997) Astrocyte-derived cytokines contribute to the metastatic brain specificity of breast cancer cells. Lab Invest 77: 357–368
Paris S, Sesboue R (2004) Metastasis models:the green fluorescent revolution?. Carcinogenesis 25: 2285–2292
Schmidt CM, Settle SL, Keene JL, Westlin WF, Nickols GA, Griggs DW (1999) Characterization of spontaneous metastasis in an aggressive breast carcinoma model using flow cytometry. Clin Expr Metastasis 17: 537–544
Al-Attar SA, Pollex RL, Robinson JF, Miskie BA, Walcarius R, Rutt BK, Hegele RA (2006) Semi-automated segmentation and quantification of adipose tissue in calf and thigh by MRI: a preliminary study in patients with monogenic metabolic syndrome. BMC Med Imaging 6: 11–19
García-Martín ML, Martinez GV, Raghunand N, Sherry AD, Zhang S, Gillies RJ (2006) High resolution pH(e) imaging of rat glioma using pH-dependent relaxivity. Magn Reson Med 55: 309–315
Navarro-Vazquez A, Cobas JC, Sardina FJ, Casanueva J, Diez E (2004) A graphical tool for the prediction of vicinal proton-proton 3J(HH) coupling constants. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 44: 1680–1685
Interpret Project: http://azizu.uab.es/INTERPRET/. Accessed: 16 Oct 2007
Tate AR, Underwood J, Acosta DM, Julià-Sapé M, Majós C, Moreno-Torres A, Howe FA, van der Graaf M, Lefournier V, Murphy MM, Loosemore A, Ladroue C, Wesseling P, Luc Bosson J, Cabañas ME, Simonetti AW, Gajewicz W, Calvar J, Capdevila A, Wilkins PR, Bell BA, Rémy C, Heerschap A, Watson D, Griffiths JR, Arús C (2006) Development of a decision support system for diagnosis and grading of brain tumours using in vivo magnetic resonance single voxel spectra. NMR Biomed 19: 411–434
Pilheu FR, Fefer SA (1961) Mandibular metastasis secondary to a cancer of the breast. Sem Med 118: 95–97
van der Waal RI, Buter J, van der Waal I (2003) Oral metastases: report of 24 cases. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 41: 3–6
Guise TA, Kozlow WM, Heras-Herzig A, Padalecki SS, Yin JJ, Chirgwin JM (2005) Molecular mechanisms of breast cancer metastases to bone. Clin Breast Cancer 5: S46–53
Sasaki A, Yoneda T, Terakado N, Alcalde RE, Suzuki A, Matsumura T (1998) Experimental bone metastasis model of the oral and maxillofacial region. Anticancer Res 18: 1579–1584
Bandyopadhyay A, Elkahloun A, Baysa SJ, Wang L, Sun LZ (2005) Development and gene expression profiling of a metastatic variant of the human breast cancer MDA-MB-435 cells. Cancer Biol Ther 4: 168–174
Kirsch M, Schackert G, Black PM (2000) Angiogenesis, metastasis, and endogenous inhibition. J Neurooncol 50: 173–180
Kauppinen RA (2002) Monitoring cytotoxic tumor treatment response by diffusion magnetic resonance imaging and proton spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 15: 6–17
Sun Y, Mulkern RV, Schmidt K, Doshi S, Albert MS, Schmidt NO, Ziu M, Black P, Carrol R, Kieran MW (2004) Quantification of water diffusion and relaxation times of human U87 tumors in a mouse model. NMR Biomed 17: 399–404
Lu S, Ahn D, Johnson G, Cha S (2003) Peritumoral diffusion tensor imaging of high-grade gliomas and metastatic brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: 937–941
García-Martín ML, Herigault G, Rémy C, Farion R, Ballesteros P, Coles JA, Cerdán S, Ziegler A (2001) Mapping extracellular pH in rat brain gliomas in vivo by 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging: comparison with maps of metabolites. Cancer Res 61: 6524–6531
Rémy C, Arús C, Ziegler A, Lai ES, Moreno A, Le Fur Y, Decorps M (1994) In vivo, ex vivo, and in vitro one- and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of an intracerebral glioma in rat brain: assignment of resonances. J Neurochem 62: 166–179
Barba I, Cabañas ME, Arús C (1999) The relationship between nuclear magnetic resonance-visible lipids, lipid droplets, and cell proliferation in cultured C6 cells. Cancer Res 59: 1861–1868
Rémy C, Fouilhe N, Barba I, Sam-Lai E, Lahrech H, Cucurella MG, Izquierdo M, Moreno A, Ziegler A, Massarelli R, Decorps M, Arús C (1997) Evidence that mobile lipids detected in rat brain glioma by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance correspond to lipid droplets. Cancer Res 57: 407–414
Ross DT, Scherf U, Eisen MB, Perou CM, Rees C, Spellman P, Iyer V, Jeffrey SS, Van de Rijn M, Waltham M, Pergamenschikov A, Lee JC, Lashkari D, Shalon D, Myers TG, Weinstein JN, Botstein D, Brown PO (2000) Systematic variation in gene expression patterns in human cancer cell lines. Nat Genet 24: 227–235
Diekman C, Simões RV, Pohman R, Cerdán S, Arús C (2006) Proton chemical shift imaging of mouse brain tumors at 7T. Bruker SpinReport. 2006; 157:18–21 http://www.bruker-biospin.com/spin_report.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simões, R.V., Martinez-Aranda, A., Martín, B. et al. Preliminary characterization of an experimental breast cancer cells brain metastasis mouse model by MRI/MRS. Magn Reson Mater Phy 21, 237–249 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0114-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0114-6