Abstract
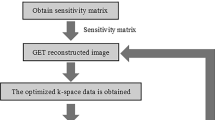
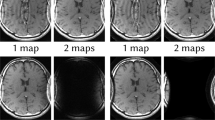
Parallel imaging techniques, which in principle represent procedures of unfolding a reduced dataset, are well known and well established in MR imaging. This paper presents a further application of one particular reconstruction method, the SENSE algorithm, considered from a different point of view to remove potential foldover in conventional images acquired with multiple receive coils. Based on the coil sensitivity information, a body coverage map in the excited plane is calculated. This is used together with the measured raw data in a SENSE-type reconstruction to optimize the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) as well as to remove foldover reliably by unfolding the image to a larger field of view. The reconstruction is performed automatically, without any user interaction, and does not affect data acquisition. Based on phantom and in vivo studies, which retain high image quality after the removal, the potential and limits of this approach are discussed, also taking into account future scanner hardware that will support a large number of parallel receiver channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sodickson DK, Manning WJ (1997) Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn Reson Med 38:591–603
Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P (1999) SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 42:952–962
Roemer PB, Edelstein WA, Hayes CE, Souza SP, Mueller OM (1990) The NMR phased array. Magn Reson Med 16:192–225
Singh S, Brody WR (1993) Projection presaturation III accurate selective excitation or presaturation of the regions of tailored shape in the presence of short-T1 species. J Magn Res B 101:52–62
Goldfarb J, Shinnar M (2002) Field-of-view restrictions for artifact-free SENSE imaging. In: Proceedings ISMRM, p 2412
Weiger M, Pruessmann KP, Boesiger P (2002) 2D SENSE for faster 3D MRI. MAGMA 14:10–19
Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Boesiger P (2000) Sensitivity encoded MRI. Medica Mundi 44(2):10–16
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (2002) Numerical Recipes in C. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kellman P, Dyke CK, Aletras AH, McVeigh ER, Arai AE (2004) Artifact suppression in imaging of myocardial infarction using B1-weighted phased-array combined phase-sensitive inversion recovery dagger. Magn Reson Med 51:408–412
Sodickson DK, McKenzie CA (2001) A generalized approach to parallel magnetic resonance imaging. Med Phys 28:1629–1643
Sodickson DK et al. (2004) Twelve- to sixteen-fold accelerations of contrast-enhanced MRA using highly parallel MRI with a 32-element array. In: Proceedings ISMRM, 327
Lin FH, Kwong KK, Belliveau JW, Wald LL (2004) Parallel imaging reconstruction using automatic regularization. Magn Reson Med 51:559–567
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgement The authors would like to thank Romhild Hoogeveen from Philips Medical Systems in Best, Netherlands, for helpful discussions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winkelmann, R., Börnert, P., Nehrke, K. et al. Efficient foldover suppression using SENSE. MAGMA 18, 63–68 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-004-0081-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-004-0081-5