Abstract
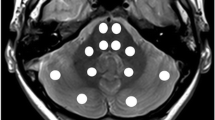
We previously reported cerebellar and putaminal transverse relaxation time (T2) differences in children with ADHD and in adults with childhood trauma. As brain T2 can be altered by deoxyhemoglobin concentration ([dHb]) and because [dHb] is proportional to regional cerebral blood volume (rCBV), at steady state we attributed those differences to rCBV changes. Studies in other species have established a correlation between T2 and rCBV; however this has yet to be demonstrated in human brain. Echo planar imaging (EPI) T2 relaxometry and dynamic susceptibility-contrast (DSC) MRI were used to measure T2 and rCBV in 11 healthy adults. Significant T2-rCBV correlations were observed in both cerebellar vermis and putamen (r=0.759,p=0.007;r=0.782,p=0.004, respectively). These correlations predict 9±3% and 10±3% rCBV changes, respectively, for each 1-msec change in T2. Consequently, brain T2 measurements may be useful for estimating steady-state rCBV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tankard CF, Waldstein SR, Siegel EL, Holder LE, Lefkowitz D, Anstett F, Katzel LI (2003) Cerebral blood flow and anxiety in older men: an analysis of resting anterior asymmetry and prefrontal regions. Brain Cogn 52:70–78
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ (2003) Positron emission tomography and single-photon emission computed tomography in substance abuse research. Semin Nucl Med 33:114–128
Schweitzer JB, Lee DO, Hanford RB, Tagamets MA, Hoffman JM, Grafton ST, Kilts CD (2003) A positron emission tomography study of methylphenidate in adults with ADHD: Alterations in resting blood flow and predicting treatment response. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:967–973
Videbech P, Ravnkilde B, Pedersen TH, Hartvig H, Egander A, Clemmensen K, Rasmussen NA, Andersen F, Gjedde A, Rosenberg R (2002) The Danish PET/depression project: clinical symptoms and cerebral blood flow. A regions-of-interest analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand 106:35–44
Kwong KK, Belliveau JW, Chesler DA, Goldberg IE, Weisskoff RM, Poncelet BP, Kennedy DN, Hoppel BE, Cohen MS, Turner R, et al. (1992) Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of human brain activity during primary sensory stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5675–5679
Kumari V, Gray JA, Ffytche DH, Mitterschiffthaler MT, Das M, Zachariah E, Vythelingum GN, Williams SCR, Simmons A, Sharma T (2003) Cognitive effects of nicotine in humans: an fMRI study. Neuroimage 19:1002–1013
Xi ZX, Wu GH, Stein EA, Li SJ (2002) GABAergic mechanisms of heroin-induced brain activation assessed with functional MRI. Magn Reson Med 48:838–843
Kaufman MJ, Levin JM, Maas LC, Kukes TJ, Villafuerte RA, Dostal K, Lukas SE, Mendelsohn JH, Cohen BM, Renshaw PF (2001) Cocaine-induced cerebral vasoconstriction differs as a function of sex and menstrual cycle phase. Biol Psychiatry 49:774–781
Cohen ER, Ugurbil K, Kim SG (2002) Effect of basal conditions on the magnitude and dynamics of the blood oxygenation level-dependent fMRI response. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:1042–1053
Belliveau JW, Rosen BR, Kantor HL, Rzedzian RR, Kennedy DN, McKinstry RC, Vevea JM, Cohen MS, Pykett IL, Brady TJ (1990) Functional cerebral imaging by susceptibility-contrast NMR. Magn Reson Med 14:538–546
Levin JM, Kaufman MJ, Ross MH, Mendelson JH, Maas LC, Cohen BM, Renshaw PF (1995) Sequential dynamic susceptibility contrast MR experiments in human brain: residual contrast agent effect, steady state, and hemodynamic perturbation. Magn Reson Med 34:655–663
Teicher MH, Anderson CM, Polcari A, Glod CA, Maas LC, Renshaw PF (2000) Functional deficits in basal ganglia of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder shown with functional magnetic resonance imaging relaxometry. Nat Med 6:470–473
Pitkanen A, Laakso M, Kalviainen R, Partanen K, Vainio P, Lehtovirta M, Riekkinen P, Soininen H (1996) Severity of hippocampal atrophy correlates with the prolongation of MRI T2 relaxation time in temporal lobe epilepsy but not in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 46:1724–1730
Chen JC, Hardy PA, Clauberg M, Joshi JG, Parravano J, Deck JH, Henkelman RM, Becker LE, Kucharczyk W (1989) T2 values in the human brain: comparison with quantitative assays of iron and ferritin. Radiology 173:521–526
Chen JC, Hardy PA, Kucharczyk W, Clauberg M, Joshi JG, Vourlas A, Dhar M, Henkelman RM (1993) MR of human postmortem brain tissue: correlative study between T2 and assays of iron and ferritin in Parkinson and Huntington disease. AJNR: Am J Neuroradiology 14:275–281
Grubb RL, Jr., Raichle ME, Eichling JO, Ter-Pogossian MM (1974) The effects of changes in PaCO2 on cerebral blood volume, blood flow, and vascular mean transit time. Stroke 5:630–639
Thulborn KR, Waterton JC, Matthews PM, Radda GK (1982) Oxygenation dependence of the transverse relaxation time of water protons in whole blood at high field. Biochim Biophys Acta 714:265–270
Jezzard P, Heineman F, Taylor J, DesPres D, Wen H, Balaban RS, Turner R (1994) Comparison of EPI gradient-echo contrast changes in cat brain caused by respiratory challenges with direct simultaneous evaluation of cerebral oxygenation via a cranial window. NMR Biomed 7:35–44
Punwani S, Ordidge RJ, Cooper CE, Amess P, Clemence M (1998) MRI measurements of cerebral deoxyhaemoglobin concentration [dHb]–correlation with near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). NMR Biomed 11:281–289
Ulatowski JA, Oja JM, Suarez JI, Kauppinen RA, Traystman RJ, van Zijl PC (1999) In vivo determination of absolute cerebral blood volume using hemoglobin as a natural contrast agent: an MRI study using altered arterial carbon dioxide tension. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 19:809–817
Anderson CM, Teicher MH, Polcari A, Renshaw PF (2002) Abnormal T2 relaxation time in the cerebellar vermis of adults sexually abused in childhood: potential role of the vermis in stress-enhanced risk for drug abuse. Psychoneuroendocrinology 27:231–244
Anderson CM, Polcari A, Lowen SB, Renshaw PF, Teicher MH (2002) Effects of methylphenidate on functional magnetic resonance relaxometry of the cerebellar vermis in boys with ADHD. Am J Psychiatry 159:1322–1328
Silveri MM, Anderson CM, McNeil JF, Diaz CI, Lukas SE, Mendelsohn JH, Renshaw PF, Kaufman MJ (2004) Oral methylphenidate challenge selectively decreases putaminal T2 in healthy subjects. Drug Alcohol Depend 76:173–180
Rohan ML, Eskesen JG, Anderson CM, Kaufman MJ, Renshaw PF (2004) TE stepping with EPI: reliable relaxometry ISMRM, Kyoto, JA 993
Maas LC, Frederick BD, Renshaw PF (1997) Decoupled automated rotational and translational registration for functional MRI time series data: the DART registration algorithm. Magn Reson Med 37:131–139
Duvernoy HM (1995) The human brain stem and cerebellum: surface, structure, vascularization, and three-dimensional sectional anatomy with MRI. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
West GB, Brown JH, Enquist BJ (1997) A general model for the origin of allometric scaling laws in biology. Science 276:122–126
Kavec M, Usenius JP, Tuunanen PI, Rissanen A, Kauppinen RA (2004) Assessment of cerebral hemodynamics and oxygen extraction using dynamic susceptibility contrast and spin echo blood oxygenation level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging: applications to carotid stenosis patients. Neuroimage 22:258–267
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anderson, C., Kaufman, M., Lowen, S. et al. Brain T2 relaxation times correlate with regional cerebral blood volume. MAGMA 18, 3–6 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-004-0076-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-004-0076-2