Abstract
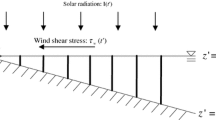
Thermal stratification is one of the important features in closed water bodies, which primarily depend on meteorological conditions, and has strong impact on the ecological environment in lakes or reservoirs. Data monitored in 3 days were analyzed for factors that affect heat mixing processes to examine the diurnal stratification cycles in the Shikinawa Lake, a study area in Fukuoka prefecture, Japan. We found that wind speeds and directions played an important role in the thermal mixing in the lake. High solar heating mainly caused stratification state, but with less effect under stronger wind action. Development of mixed layer depth in a natural lake due to wind-induced flow and thermal convection were calculated. Functional relationships between entrainment rate and Richardson number or Wedderburn number were found and represented in this paper. Besides, heats exchanged at the air–water interface and energy stored in the water column were also analyzed and discussed.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charpa SC (1998) Surface water quality modeling. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 560–589
Chu CR, Soong CK (1997) Numerical simulation of wind-induced entrainment in a stably stratified water basin. J Hydraulic Res 35(1):21–41
De Bruin HAR (1978) A simple model for shallow lake evaporation. J Appl Meteorol 17:1132–1134
Ford DE, Johnson LS (1986) An assessment of reservoir mixing process. Technical Report E-86-7, US Army Engineers Waterways Experiment Station, Vicksburg, MS
Hamagami K, Mori K, Hirai Y (2008) Inhomogeneous cooling process in a closed density stratified water body. Trans of JSIDRE No 256:47–54
Kranenburg C (1984) Wind-induced entrainment in a stably stratified fluid. J Fluid Mech 145:253–273
Martin JL, McCutcheon SC (1998) Hydrodynamic and transport for water quality modeling. Lewis Publisher, pp 355–420
Mori K, Tohara Y, Kato O (1989) Experiment study on entrainment rate of density interface due to a wind induced current. Transaction of JSIDRE, pp 85–93
Scott A, Condie, Webster IT (2002) Stratification and circulation in a shallow turbid waterbody. Environ Fluid Mech 2:177–196
Spigel RH, Imberger J (1980) The classification of mixed-layer dynamics of lakes of small to medium size. J Phys Oceanogr 10:1104–1121
Tuan NV, Cong VC, Mori K (2008) Characteristic of water quality in the Shikinawa Lake, Fukuoka, Japan. J Int Assoc Lowland Technol 10–2:1–9
Wu J (1973) Wind-induced turbulent entrainment across a stable density interface. J Fluid Mech 61:275–287
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tuan, N.V., Hamagami, K., Mori, K. et al. Mixing by wind-induced flow and thermal convection in a small, shallow and stratified lake. Paddy Water Environ 7, 83–93 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-009-0158-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-009-0158-x