Abstract
Objective
The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of Casticin on proliferation inhibition of human cervical cancer HeLa cells in vitro and to unravel the associated mechanisms.
Methods
Human cervical HeLa cells were cultured in vitro. The inhibitory effect of Casticin on the viability of human cervical cancer HeLa cells was evaluated by the MTT assay. The colony formation ability was detected by plate colony formation assay. Distribution of cell cycle was analyzed by flow cytometry. The protein expression levels were analyzed by Western blot.
Results
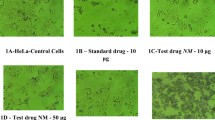
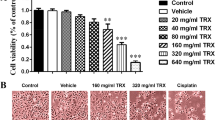
Casticin significantly inhibited the growth of human cervical cancer HeLa cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner, and the IC50 was 2.82 μg/mL. The colony-forming rate was reduced drastically compared with control group (P < 0.05). The cells were markedly arrested at G2/M phase after the treatment of Casticin for 48 h. Western blot showed that the expression of p21 protein was up-regulated and protein level of Cyclin B1 was depressed by Casticin in a concentration dependent manner.
Conclusion
Casticin could inhibit the cell growth and lead to cell arrest in human cervical cancer HeLa cells, and the down-regulation of Cyclin B1 protein expression and activation of p21 protein might contribute to Casticin induced cell arrest in human cervical cancer HeLa cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin S, Zhang H, Han T, et al. In vivo effect of Casticin on acute inflammation. J Chin Integ Med (Chinese), 2007, 5: 573–576.
Hu Y, Xin HL, Zhang QY, et al. Anti-nociceptive and anti-hyperprolactinemia activities of Fructus Viticis and its effective fractions and chemical constituents. Phytomedicine, 2007, 14: 668–674.
Shen JK, Du HP, Yang M, et al. Casticin induces leukemic cell death through apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe. Ann Hematol, 2009, 88: 743–752.
Hu Y, Hou TT, Zhang QY, et al. Evaluation of the estrogenic activity of the constituents in the fruits of Vitex rotundifolia L. for the potential treatment of premenstrual syndrome. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2007, 59: 1307–1312.
Xiao H, Gong WJ, Cao JP, et al. Influence of CDK1 and CDK2 siRNA interference on tumor cell cycle and cell apoptosis. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2009, 8: 371–374.
Haïdara K, Zamir L, Shi QW, et al. The flavonoid Casticin has multiple mechanisms of tumor cytotoxicity action. Cancer Lett, 2006, 242: 180–190.
Kobayakawa J, Sato-Nishimori F, Moriyasu M, et al. G2-M arrest and antimitotic activity mediated by Casticin, a flavonoid isolated from Viticis Fructus (Vitex rotundifolia Linne fil.). Cancer Lett, 2004, 208: 59–64.
Li WX, Cui CB, Cai B, et al. Flavonoids from Vitex trifolia L. inhibit cell cycle progression at G2/M phase and induce apoptosis in mammalian cancer cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res, 2005, 7: 615–626.
Suzuki T, Urano T, Miki Y, et al. Nuclear cyclin B1 in human breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic factor. Cancer Sci, 2007, 98: 644–651.
Buchynska LG, Nesina IP, Yurchenko NP, et al. Expression of p53, p21WAF1/CIP1, p16INK4A and Ki-67 proteins in serous ovarian tumors. Exp Oncol, 2007, 29: 49–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a grant from Hunan Provincial Health Department Research Fund (No. B2007-116).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, J., Bai, J., Sheng, X. et al. Proliferation inhibition of human cervical cancer HeLa cells by Casticin in vitro. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 10, 47–50 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-011-0711-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-011-0711-0