Abstract
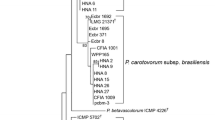
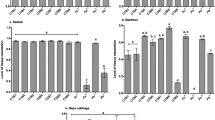
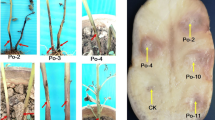
Dark brown, necrotic pods with extensive water-soaked lesions caused by plant pathogenic bacteria were found on okra plants in different fields in Malaysia in 2010. PCR amplification of the pectate lyase (pel) gene and amplification of the 16S–23S rRNA (ITS) with G1 and L1 primers produced 434-, 535- and 570-bp fragments, respectively. From the similarity between the results of biochemical tests and their equivalency with standard bacteriological sources, PCR-based pel gene, and RFLP analysis of the ITS-PCR products, all isolates were identified as Pectobacterium carotovorum. This is the first report of P. carotovorum in okra from Malaysia.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AVA (2001) Diagnostic records of the Plant Health Diagnostic Services. Plant Health Centre, Agri-food & Veterinary Authority, Singapore
Avrova AO, Hyman LJ, Toth RL, Toth IK (2002) Application of amplified fragment polymorphism fingerprinting for taxonomy and identification of the soft rot bacteria Erwinia carotovora and Erwinia chrysanthemi. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1499–1508
Darrasse A, Priou S, Kotoujansky A, Bertheau Y (1994) PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism of a pel gene as a tool to identify Erwinia carotovora in relation to potato diseases. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1437–1443
Gardan L, Gouy C, Christen R, Samson R (2003) Elevation of three subspecies of Pectobacterium carotovorum to species level: Pectobacterium atrosepticum sp. nov., Pectobacterium betavasculorum sp. nov., and Pectobacterium wasabiae sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:381–391
Garibaldi A, Battman DF (1971) Pectic enzymes produced by Erwinia chrysanthemi and their effects on plant tissue. Physiol Plant Pathol 1:25–40
Hauben L, Moore ERB, Vauterin L, Steenackers M, Mergaert J, Verdonck L, Swings J (1998) Phylogenetic position of phytopathogens within the Enterobacteriaceae. Syst Appl Microbiol 21:384–397
Kotoujansky A (1987) Molecular genetics of pathogenesis by soft rot erwinias. Annu Rev Phytopathol 25:405–430
Kwon SW, Go SJ, Kang HW, Ryu JC, Jo JK (1997) Phylogenetic analysis of Erwinia species based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:1061–1067
Lelliot RA, Dickey RS (1984) Genus VII. Erwinia Winslow, Broadhurst, Buchanan, Krumwiede, Rogers and Smith 1920, 209. In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. Williams & Wilkins Co., Baltimore, pp 469–476
Luzzatto T, Yishay M, Lipsky A, Ion A, Belausov E, Yedidia I (2007) Efficient, long-lasting resistance against the soft rot bacterium Pectobacterium carotovorum in calla lily provided by the plant activator methyl jasmonate. Plant Pathol 56:692–701
Nazerian E, Sijam K, Mior Ahmad ZA, Vadamalai G (2011) First report of cabbage soft rot caused by Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum in Malaysia. Plant Dis 95:491
Pérombelon MCM, Kelman A (1980) Ecology of the soft rot erwinias. Annu Rev Phytopathol 18:361–387
Schaad NW, Jones JB, Chun W (eds) (2001) Laboratory guide for identification of plant pathogenic bacteria, 3rd edn. American Phytopathological Society Press, St. Paul
Somchai B, Somchai W, Vanida T (1987) Longevity of Erwinia carotovora pv. carotovora from some cruciferous plants in soil. Research report 1984: Fruit, vegetable, mushroom, ornamental plants, coconut, oil palm, drug plant and spice crops. Department of Agriculture, Bangkok, pp 151–152
Toth IK, Hyman LJ, Grevesse C, Pérombelon MCM (1996) An update on Erwinia diagnostics. In: Proceedings of crop protection in northern Britain. Scottish Crop Institute, Invergowrie, Dundee, Scotland, UK pp 331–336
Toth IK, Avrova AO, Hyman LJ (2001) Rapid identification and differentiation of the soft rot erwinias by 16S–23S intergenic transcribed spacer-PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism analyses. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4070–4076
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nazerian, E., Sijam, K., Meor Ahmad, Z.A. et al. Characterization of Pectobacterium carotovorum causing a new soft rot disease on okra in Malaysia. J Gen Plant Pathol 77, 292–294 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-011-0322-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10327-011-0322-1