Abstract
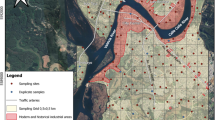
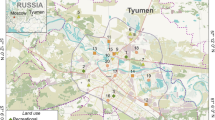
As part of a harmonised assessment of urban soils (http://www.urbsoil.paisley.ac.uk), we investigated the variability of metal content in soils from Aveiro (Portugal) and Glasgow (UK). Samples were collected from parks and other public open spaces in each city. Metal content (Al, Ca, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn) and basic soil parameters (texture, CEC, pH, organic matter) were determined and data investigated using principal component analysis (PCA). The two cities differ in absolute levels of metal content reflecting industrial and historical development. Factors identified by PCA included anthropogenic (Cu, Pb, Zn), soil properties and geology, which explain variability when data were assessed based on metal content, soil properties and land use. This study highlights the contribution from geological background even in strongly urbanised environments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boudia N, Halley R, Kennedy G, Lambert J, Gareau L, Zayed J (2006) Manganese concentrations in the air of the Montreal (Canada) subway in relation to surface automobile traffic density. Science of the total environment 366:143–147
Davidson C, Nordon A, Urquhart G, Ajmone-Marsan F, Biasioli M, da Costa Duarte A, Díaz-Barrientos E, Grcman H, Hodnik A, Hossack I, Hursthouse A, Ljung K, Madrid L, Otabbong E, Rodrigues S (2007) Assessing inter-laboratory variability in the measurement of potentially toxic elements in urban soils within the EU URBSOIL project. Int J Environ Anal Chem 87:589–601
Facchinelli A, Sacchi E, Mallen L (2001) Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ Pollut 114:313–324
Gee GW, Bauder JW (1986) Particle-size analysis in methods of soil analysis, Part 1. In: Page AL (ed) Physical and mineralogical methods, Agronomy series 9. American Society of Agronomy, Madison
Glasgow City Council 2006, http://www.glasgow.gov.uk/en/AboutGlasgow/
Hipkin JA (1988) Title soils around Glasgow and the Firth of Clyde. Macaulay Land Use Research Institute, Aberdeen
Hursthouse AS (2001) The relevance of speciation in the remediation of soils and sediments contaminated by metallic elements: an overview and examples from Central Scotland, UK. J Environ Monitor 3(1):46–60
INE, 2002 INE (“Instituto Nacional de Estatística”), 2002. “Censos 2001, Resultados definitivos”. [online] URL: http://www.ine.pt/prodserv/censos_definit/censos_definit.asp Accessed 16 December 2002
Ljung K, Otabbong E, Selinus O (2006) Natural and anthropogenic metal inputs to soils in urban Uppsala, Sweden. Environ Geochem Health 28:353–364
Madrid L, Diaz-Barrientos E, Ruiz-Cortés E, Reinoso R, Biasioli M, Davidson CM, Duarte AC, Grcman H, Hossack I, Hursthouse A, Kralj T, Ljung K, Otabbong E, Rodrigues S, Urquhart GJ, Ajmone-Marsan F (2006) Potentially toxic metals in urban soils of six European cities: a pilot study on selected parks. J Environ Monitor 8:1158–1165
Pouyat R, Yesilonis I, Russel-Anelli J, Neerchal N (2007) Soil chemical and physical properties that differentiate land-use and cover types. Soil Sci Soc Am 71:1010–1019
Acknowledgment
The URBSOIL project was supported by the EU FP5, Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development Program, under contract EVK4-CT-2001-00053.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rodrigues, S., Urquhart, G., Hossack, I. et al. The influence of anthropogenic and natural geochemical factors on urban soil quality variability: a comparison between Glasgow, UK and Aveiro, Portugal. Environ Chem Lett 7, 141–148 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-008-0149-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-008-0149-y