Abstract
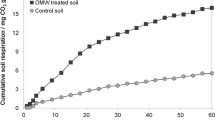
Olive mill wastewaters are toxic for plants and microbes due to their high polyphenol content. We studied the effect of agricultural soil as a natural catalyst to promote polyphenol oxidation and polymerization, and in turn detoxify olive mill wastewaters. We show that model polyphenols are fully converted in soil slurries. Their products show no toxicity to the growth of a typical soil bacterium, Bacillus cereus, and reduced phytotoxicity in germination tests with English cress seeds. Those findings are promising for the sustainable treatment of olive wastewater in aerated soil slurries.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allouche N, Fki I, Sayadi S (2004) Toward a high yield recovery of antioxidants and purified hydroxytyrosol from olive mill wastewaters. J Agric Food Chem 52:267–273. DOI 10.1021/jf034944u
Ardi MR, Colarieti ML, Toscano G, Greco G (2004) Polyphenol removal from olive mill wastewaters by catalytic soil components. In: Hoikkala A, Soidinsalo O (eds) Polyphenols communications 2004. (XXII International conference on polyphenols 25–28 august 2004, Helsinki, Finland) Gummerus Printing, Jyväskylä, pp 735–736
Capasso R, Cristinzio G, Evidente A, Scognamiglio F, (1992) Isolation, spectroscopy and selective phytotoxic effects of polyphenols from vegetable waste waters. Phytochemistry 31:4125–4128. DOI 10.1016/0031-9422(92)80426-F
Colarieti ML, Toscano G, Greco G (2002) Soil-catalyzed polymerization of phenolics in polluted waters. Water Res 36:3015–3022. DOI 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00002-7
Colarieti ML, Toscano G, Ardi MR, Greco G (2006) Abiotic oxidation of catechol by soil metal oxides. J Hazard Mater (in press). DOI 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.054
Gianfreda L, Rao MA, Sannino F, Saccomandi F, Violante A (2002) Enzymes in soil: properties, behavior and potential applications. In: Violante A, Huang PM, Bollag J-M, Gianfreda L (eds) Soil mineral-organic matter-microorganism interactions and ecosystem health, Developments in Soil Science, vol. 28B. Elsevier Science BV, pp 301–327
Sparks DL (ed) (1996) Methods of soil analysis Part 3: chemical methods (Soil Science Society of America Book Series No. 5). American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI
Pérez J, De la Rubia T, Moreno J, Martínez J (1992) Phenolic content and antibacterial activity of olive oil waste waters. Environ Toxicol Chem 11:489–495
Rozzi A, Maipei F (1996) Treatment and disposal of olive mill effluents. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 38:135–144. DOI 10.1016/S0964-8305(96)00042-X
Spandre R, Dellomonaco G (1996) Polyphenols pollution by olive mill waste waters, Tuscany, Italy. J Environ Hydrol 4:1–13
Wang TSC, Huang PM, Chou C-H, Chen J-H (1986) The role of soil minerals in the abiotic polymerization of phenolic compounds and formation of humic substances. In: Huang PM, Schnitzer M (eds) Interactions of soil minerals with natural organics and microbes. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, pp 251–281
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported financially by the European Union, INCO-MED contract no. ICA3-2002-10021 “New Technologies for Olive Mill Waste Water Detoxification and Product Recovery” and by the Italian Ministry for University and Research, PRIN 2004 prot. 2004099359/002 “Removal of polyphenols from olive mill wastewaters by soil natural catalysts.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colarieti, M.L., Toscano, G. & Greco, G. Toxicity attenuation of olive mill wastewater in soil slurries. Environ Chem Lett 4, 115–118 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-006-0050-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-006-0050-5