Abstract
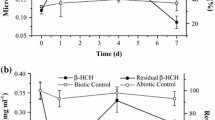
For elucidation of the metabolism of the endocrine disruptor nonylphenol by Sphingomonas sp. strain TTNP3, the degradation of an isomer of nonylphenol, 4(2′,6′-dimethyl-2′-heptyl)-phenol, has been studied. As in the case of 4(3′,5′-dimethyl-3′-heptyl)-phenol, the metabolism of this nonylphenol isomer leads to the formation of the NIH-shifted product 2(2′,6′-dimethyl-2′-heptyl)-1,4-benzenediol (NIH: National Institute of Health), but also to the alkoxy derivative 4(2′,6′-dimethylheptan-2′-yloxy)phenol as additional metabolite. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report describing the formation of alkoxyphenol as a degradation product of nonylphenol. Additionally, these results provide for the first time evidence for slight differences in the biodegradation of the isomers of nonylphenol.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corvini PFX, Vinken R, Hommes G, Schmidt B, Dohmann M (2004a) Degradation of the radioactive and non-labelled branched 4(3′,5′-dimethyl-3′-heptyl)-phenol nonylphenol isomer by Sphingomonas TTNP3. Biodegradation 15:9–18
Corvini PFX, Vinken R, Hommes G, Mundt M, Meesters R, Schröder HF, Hollender J, Schmidt B (2004b) Microbial degradation of a single branched isomer of nonylphenol by Sphingomonas TTNP3. Water Sci Technol 50(5):195–202
Corvini PFX, Meesters R, Schäffer A, Schröder HF, Vinken R, Hollender J (2004c) Degradation of a nonylphenol single isomer by Sphingomonas sp. strain TTNP3 leads to a hydroxylation-induced migration product. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6897–6900
Giger W, Ahel M, Koch M, Laubscher HU, Schaffner C, Schneider J (1987) Behaviour of alkylphenolpolyethoxylate surfactants and of nitrilotriacetate in sewage treatment. Water Sci Technol 19:449–460
Soto AM, Justica H, Wray JW, Sonnenschein C (1991) Para-nonylphenol: an estrogenic xenobiotic released from polystyrene. Environ Health Perspect 92:167–173
Van Ginkel CG (1996) Complete degradation of xenobiotic surfactants by consortia of aerobic microorganisms. Biodegradation 7:151–164
Vinken R, Schmidt B, Schäffer A (2002) Synthesis of tertiary 14C-labelled nonylphenol isomers. J Label Compd Radiopharm 45:1253–1263
Vinken R, Höllrigl-Rosta A, Schmidt B, Schäffer A, Corvini PFX (2004) Bioavailability of a nonylphenol isomer in dependence on the association to dissolved humic substances. Water Sci Technol 50(5):285–291
Wheeler TF, Heim JR, LaTorre MR, Janes B (1997) Mass spectral characterization of p-nonylphenol isomers using high-resolution capillary GC–MS. J Chromatogr Sci 35:19–30
Ying GG, Kookana RS, Dillon P (2003) Sorption and degradation of selected five endocrine disrupting chemicals in aquifer material. Water Res 37:3785–3791
Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. W. Verstraete and Dr. N. Boon (LabMet, University Ghent, Belgium) for the S. TTNP3 strain. The assistance of M. Meindorf is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corvini, P.F.X., Elend, M., Hollender, J. et al. Metabolism of a nonylphenol isomer by Sphingomonas sp. strain TTNP3. Environ Chem Lett 2, 185–189 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-004-0094-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-004-0094-3