Abstract
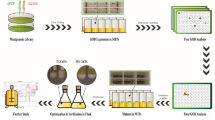
This work proposed a new method which applied image processing and support vector machine (SVM) for screening of mold strains. Taking Monascus as example, morphological characteristics of Monascus colony were quantified by image processing. And the association between the characteristics and pigment production capability was determined by SVM. On this basis, a highly automated screening strategy was achieved. The accuracy of the proposed strategy is 80.6 %, which is compatible with the existing methods (81.1 % for microplate and 85.4 % for flask). Meanwhile, the screening of 500 colonies only takes 20–30 min, which is the highest rate among all published results. By applying this automated method, 13 strains with high-predicted production were obtained and the best one produced as 2.8-fold (226 U/mL) of pigment and 1.9-fold (51 mg/L) of lovastatin compared with the parent strain. The current study provides us with an effective and promising method for strain improvement.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobson LF, O’Cleirigh CC, O’Shea DG (2008) The influence of morphology on geldanamycin production in submerged fermentations of Streptomyces hygroscopicus var. geldanus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(5):859–866. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1493-3
Elmayergi H, Scharer J, Moo-Young M (1973) Effects of polymer additives on fermentation parameters in a culture of A. niger. Biotechnol Bioeng 15(5):845–859. doi:10.1002/bit.260150503
Ford A, Roberts A (1998) Colour space conversions. Westminster University, London, pp 1–31. http://147.228.63.6/research/night_road/westminster.pdf. Accessed 9 Jan 2016
Fu YQ, Yin LF, Jiang R et al (2015) Effects of calcium on the morphology of Rhizopus oryzae and l-lactic acid production. In: Advances in applied biotechnology. Springer, Berlin, pp 233–243
General T, Prasad B, Kim HJ et al (2014) Saccharina japonica, a potential feedstock for pigment production using submerged fermentation. Biotechnol Bioprocess 19(4):711–719. doi:10.1007/s12257-013-0709-2
Ha M, Yang Y, Wang C (2013) A new support vector machine based on type-2 fuzzy samples. Soft Comput 17(11):2065–2074. doi:10.1007/s00500-013-1122-7
Hama S, Onodera K, Yoshida A et al (2005) Improved production of phospholipase A 1 by recombinant Aspergillus oryzae through immobilization to control the fungal morphology under nutrient-limited conditions. Biochem Eng J 96:1–6. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2014.12.013
He Y, Shao Y, Chen F (2014) Efficient gene targeting in ligase IV-deficient Monascus ruber M7 by perturbing the non-homologous end joining pathway. Fungal Biol 118:846–854. doi:10.1016/j.funbio.2014.07.003
Hirayama E, Sugiyama T, Hisamoto H et al (2000) Visual and colorimetric lithium ion sensing based on digital color analysis. Anal Chem 72(3):465–474. doi:10.1021/ac990588w
Jones C, Lonergan G, Mainwaring D (1995) Acid phosphatase positional correlations in solid surface fungal cultivation: a fractal interpretation of biochemical differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 208(3):1159–1165. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1995.1455
Kumar MS, Kumar PM, Sarnaik HM et al (2000) A rapid technique for screening of lovastatin-producing strains of Aspergillus terreus by agar plug and Neurospora crassa bioassay. J Microbiol Methods 40(1):99–104. doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(99)00135-9
Liu X, Fang H, Chen Z (2014) A novel cost function based on decomposing least-square support vector machine for Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy system identification. IET Control Theory Appl 8(5):338–347. doi:10.1049/iet-cta.2013.0707
Liu Y, Li R, Li C et al (2014) Application of BP neural network and support vector machine to the accumulated temperature interpolation. J Arid Land Resour Environ 28(5):158–165
McIntyre M, Müller C, Dynesen J et al (2001) Metabolic engineering of the morphology of Aspergillus. Metab Eng 73:103–128. doi:10.1007/3-540-45300-8_6
Mostafa ME, Abbady MS (2014) Secondary metabolites and bioactivity of the Monascus pigments review article. Global J Biotechnol Biochem 9:1–13. http://idosi.org/gjbb/gjbb9(1)14/1.pdf. Accessed 9 Jan 2016
Papagianni M (2004) Fungal morphology and metabolite production in submerged mycelial processes. Biotechnol Adv 22(3):189–259. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2003.09.005
Pohn B, Gerlach J, Scheideler M et al (2007) Micro-colony array based high throughput platform for enzyme library screening. J Biotechnol 129(1):162–170. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.11.002
Rajwa B, Venkatapathi M, Ragheb K et al (2008) Automated classification of bacterial particles in flow by multiangle scatter measurement and support vector machine classifier. Cytom Part A 73:369–379. doi:10.1002/cyto.a.20515
Tan J, Chu J, Wang Y et al (2014) High-throughput system for screening of Monascus purpureus high-yield strain in pigment production. Bioresour Bioprocess 1(1):1–7. doi:10.1186/s40643-014-0016-6
Treskatis SK, Orgeldinger V, Wolf H et al (1997) Morphological characterization of filamentous microorganisms in submerged cultures by on-line digital image analysis and pattern recognition. Biotechnol Bioeng 53(2):191–201. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19970120)53:2<191:AID-BIT9>3.0.CO;2-J
Viscarra Rossel RA, Minasny B, Roudier P et al (2006) Colour space models for soil science. Geoderma 133(3–4):320–337. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2005.07.017
Wang JJ, Lee CL, Pan TM (2004) Modified mutation method for screening low citrinin-producing strains of Monascus purpureus on rice culture. J Agric Food Chem 52(23):6977–6982. doi:10.1021/jf049783o
Wang J, Bai Z, Yang P (2014) Simulation and prediction of ion transport in the reclamation of sodic soils with gypsum based on the support vector machine. Sci World J. doi:10.1155/2014/805342
Wimpenny J, Wilkinson T, Peters A (1995) Monitoring microbial colony growth using image-analysis techniques. Binary-Comput Microb 7(1):14–18
Wongjewboot I, Kongruang S (2011) pH stability of ultrasonic Thai isolated Monascus purpureus pigments. Int J Biosci Biochem Bioinforma 1:79–83
Yang K, Wang JF, Li XJ et al (2001) Strain selection of Metarrhizium anisopliae by image analysis of colony morphology for consistency of steroid biotransformation. Biotechnol Bioeng 75(1):53–62. doi:10.1002/bit.1164
Zhang J, Wang YL, Lu LP et al (2014) Enhanced production of Monacolin K by addition of precursors and surfactants in submerged fermentation of Monascus purpureus 9901. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 61(2):202–207. doi:10.1002/bab.1154
Zhao QH, Ha MH, Peng GB et al (2009) Support vector machine based on half-suppressed fuzzy c-means clustering. In: Machine learning and cybernetics, 2009 international conference on 2009. IEEE, pp 1236–1240. doi:10.1109/ICMLC.2009.5212363
Zhu K, Song X, Xue D (2014) A roller bearing fault diagnosis method based on hierarchical entropy and support vector machine with particle swarm optimization algorithm. Measurement 47:669–675. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2013.09.019
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Open Funding Project of the National Key Laboratory of Biochemical Engineering (No. 2013KF-01), and the National High Technology Research and Development Program (863 Program, 2012AA021302).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Ml., Wang, L., Yang, Zx. et al. High-throughput screening of high Monascus pigment-producing strain based on digital image processing. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43, 451–461 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1729-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1729-z