Abstract
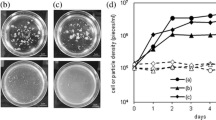
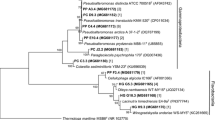
A bacterial strain capable of hydrolyzing sulfate ester bonds of p-nitrophenyl sulfate (pNPS) and agar was isolated from the coast area of Qingdao, China. It was identified as Marinomonas based on its 16S rRNA gene sequence and named as Marinomonas sp. FW-1. An arylsulfatase with a recovery of 13 % and a fold of 12 was purified to a homogeneity using ion exchange and gel filtration chromatographies. The enzyme was composed of a single polypeptide chain with the molecular mass of 33 kDa estimated using SDS-PAGE. The optimal pH and temperature of arylsulfatase were pH 9.0 and 45, respectively. Arylsulfatase was stable over pH 8–11 and at temperature below 55 °C. The K m and V max of this enzyme for the hydrolysis of pNPS were determined to be 13.73 and 270.27 μM/min, respectively. The desulfation ratio against agar from red seaweed Gelidium amansii and Gracilaria lemaneiformis were 86.11 and 89.61 %, respectively. There was no difference between the DNA electrophoresis spectrum on the gel of the arylsulfatase-treated G. amansii agar and that of the commercial agarose. Therefore, this novel alkaline arylsulfatase might have a great potential for application in enzymatic conversion of agar to agarose.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan GG, Johnson PG, Lay Y, Sarkanen KV (1971) Marine polymers; part 1. A new procedure for the fractionation of agar. Carbohydr Res 17:234–236
Amott S (1974) The agarose double helix and its function in agarose gel structure. J Mol Biol 90:269–284. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(74)90372-6
Araki CH (1937) Acetylation of agar like substance of Gelidium amansii. J Chem Soc Jpn 58:1138–1150
Beil S, Kehrli H, Peter J, Staudenmann W, Cook AM, Leisinger T, Kertesz MA (1995) Purification and characterization of the arylsulfatase synthesized by Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO during growth in sulfate-free medium and cloning of the arylsulfatase gene (atsA). Eur J Biochem 229:385–394. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20479.x
Benkovic SJ, Vergara EV, Hevey RC (1971) Purification and properties of an arylsulfatase from Aspergillus oryzae. J Biol Chem 246:4826–4933
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Byun D-S, Kim D-S, Samuel Godber J (2004) Isolation and characterization of marine bacterium producing arylsulfatase. J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:1134–1141
Cregut M, Rondags E (2013) New insights in agar biorefinery with arylsulphatase activities. Process Biochem 48:1861–1871. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2013.09.020
Dodgson KS, Price RG (1963) A note on the determination of the ester sulfate content of sulfated polysaccharides. Biochem J 84:350–356
Duckworth M, Yaphe W (1971) The structure of agar. Part 1 Fractionation of a complex mixture of polysaccharides. Carbohydr Res 16:189–197
Guiseley KB (1970) The relationship between methoxyl content and gelling temperature of agarose. Carbohydr Res 13:247–256
Guiseley KB, Kirpatrick FH, Provonchee RB, Dumais MM, Nochumson S (1993) A further fractionation of agarose. Hydrobiologia 260(261):505–511
Henderson MJ, Milazzo FH (1979) Arylsulfatase in Salmonella typhimurium: detection and influence of carbon source and tyramine on its synthesis. J Bacteriol 139:80–87
Jansen HJ, Hart CA, Rhodes JM, Saunders JR, Smalley JW (1999) A novel mucin-sulphatase activity found in Burkholderia cepacia and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol 48:551–557
Kertesz MA (1999) Riding the sulfur cycle–metabolism of sulfonates and sulfate esters in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24:135–175
Kim JH, Byun DS, Godber JS, Choi JS (2004) Purification and characterization of arylsulfatase from Sphingomonas sp. AS6330. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:553–559. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1463-8
Kim D-E, Kim K-H, Bae Y-J, Lee J-H, Jang Y-H, Nam S-W (2005) Purification and characterization of the recombinant arylsulfatase cloned from Pseudoalteromonas carrageenovora. Protein Expr Purif 39:107–115. doi:10.1016/j.pep.2004.09.007
Laas T (1972) Agar derivation for chromatography, electrophoresis and gel-bound enzymes. J Chromatogr 66:347–355
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. doi:10.1038/227680a0
Lim J-M, Jang Y-H, Kim H-R, Kim YT, Choi TJ, Kim JK, Nam S-W (2004) Overexpression of arylsulfatase in E. coli and its application to desulfatation of agar. J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:777–782
Lineweaver H, Burke D (1934) The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J Am Chem Soc 56:658–666
Lonnerdal B, Lass T (1976) Improved agarose for immunoelectrophoresis. Anal Biochem 72:527–532
Miech C, Dierks T, Selmer T, von Figura K, Schmidt B (1998) Arylsulfatase from Klebsiella pneumoniase carries a formylglycine generated from a serine. J Biol Chem 273:4835–4837. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.9.4835
Okamura H, Yamada T, Murooka Y, Harada T (1976) Purification and properties of arylsulfatase of Klebsiella aerogenes identity of the enzymes formed by non-repressed and de-repressed synthesis. Agric Biol Chem 40:2071–2076
Sambrook J, Russel DW (2001) Molecular cloning. In: Argentine J, Irwin N, Janssen KA, Curtis S, Zierler M, Dickerson M, Sialiano I, Mclnerny N, Brown D, Schaefer S, deBruin D, Atkeson E, Weiss D, Curtis MD (eds) A laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Singe SJ, Tanguay RL, Riggs AD (1989) Use of Chelex to improve the PCR signal from a small number of cells. Amplification 3:11–16
Skriptsova AV, Shevchenko NM, Zvyagintseva TN et al (2010) Monthly changes in the content and monosaccharide composition of fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida (Laminariales, Phaeophyta). J Appl Phycol 22:79–86. doi:10.1007/s10811-009-9438-5
Ueki T, Sawada Y, Fukangawa Y, Oki T (1995) A new type of Streptomyces arylsulfatase with high affinity to the sulfuryl moiety of the substrate. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 59:1069–1075
Yoy AB, Trudinger PA (1970) The biochemistry of inorganic compounds of sulfur. University Press, Cambridge
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Grant of the National Science Foundation of China (No. 31201298), the Grant of National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2013BAB01B01), and the Grant of Public Science and Technology Research Funds Projects of Ocean (No. 201405040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Duan, D., Xu, J. et al. Characterization of a novel alkaline arylsulfatase from Marinomonas sp. FW-1 and its application in the desulfation of red seaweed agar. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 42, 1353–1362 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1625-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-015-1625-6