Abstract
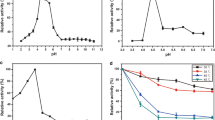
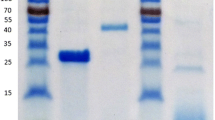
In the recent past, much research has been applied to the development of Aspergillus, most notably A. niger and A. oryzae, as hosts for recombinant protein production. In this study, the potential of another species, Aspergillus vadensis, was examined. The full length gDNA encoding two plant biomass degrading enzymes, i.e. α-l-arabinofuranosidase (abfB) (GH54) and endo-1,4-β-d-glucanase (eglA) (GH12) from A. vadensis were successfully expressed using the gpdA promoter from A. vadensis. Both enzymes were produced extracellularly in A. vadensis as soluble proteins and successfully purified by affinity chromatography. The effect of culture conditions on the expression of abfB in A. vadensis was examined and optimised to give a yield of 30 mg/L when grown on a complex carbon source such as wheat bran. Characterization of the purified α-l-arabinofuranosidase from A. vadensis showed an optimum pH and temperature of pH 3.5 and 60 °C which concur with those previously reported for A. niger AbfB. Comparative analysis to A. niger AbfA demonstrated interesting differences in temperate optima, pH stability and substrate specificities. The endo-1,4-β-d-glucanase from A. vadensis exhibited a pH and temperature optimum of pH 4.5 and 50 °C, respectively. Comparative biochemical analysis to the orthologous EglA from A. niger presented similar pH and substrate specificity profiles. However, significant differences in temperature optima and stability were noted.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agger T, Spohr AB, Carlsen M, Nielsen J (1998) Growth and product formation of Aspergillus oryzae during submerged cultivations: verification of a morphologically structured model using fluorescent probes. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:321–329
Alias NI, Mahadi NM, Murad AMA, Bakar FDA, Rabu A, Illias RM (2011) Expression optimisation of recombinant α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Aspergillus niger ATCC 120120 in Pichia pastoris and its biochemical characterisation. Afr J Biotechnol 10:6700–6710
Battaglia E, Benoit I, Gruben BS, de Vries RP (2010) Plant cell wall derived sugars as substrates for fungi and industry. In: Jenkins PT (ed) The sugar industry and cotton crops. Nova Science Publishers, New York
Bedford MR, Classen HL (1991) The influence of dietary xylanase on intestinal viscosity and molecular weight distribution of carbohydrates in rye-fed broiler chicks. Prog Biotechnol 7:361–370
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V, Henrissat B (2009) The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37:5
Carlsen M, Spohr AB, Nielsen J, Villadsen J (1996) Morphology and physiology of an alpha-amylase producing strain of Aspergillus oryzae during batch cultivations. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:266–276
Christov LP, Szakacs G, Balakrishnan H (1999) Production, partial characterization and use of fungal cellulase-free xylanases in pulp bleaching. Process Biochem 34:511–517
Coutinho PM, Andersen MR, Kolenova K, vanKuyk PA, Benoit I, Gruben BS et al (2009) Post-genomic insights into the plant polysaccharide degradation potential of Aspergillus nidulans and comparison to Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus oryzae. Fungal Genet Biol 46(Suppl 1):S161–S169
Culleton H, McKie V, de Vries RP (2013) Physiological and molecular aspects of degradation of plant polysaccharides by fungi: what have we learned from Aspergillus? Biotechnol J 8:884–894
Culleton H, Bouzoid O, McKie V, de Vries RP (2014) New promoters to improve heterologous protein production in Aspergillus vadensis. Curr Biotechnol 3:1–8
Davies RW (1994) Heterologous gene expression and protein secretion in Aspergillus. Prog Ind Microbiol 29:527–560
de Bekker C, Wiebenga A, Aguilar G, Wosten HA (2009) An enzyme cocktail for efficient protoplast formation in Aspergillus niger. J Microbiol Methods 76:305–306
de Vries RP, Visser J (2001) Aspergillus enzymes involved in degradation of plant cell wall polysaccharides. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:497–522
de Vries RP, Burgers K, van de Vondervoort PJ, Frisvad JC, Samson RA, Visser J (2004) A new black Aspergillus species, A. vadensis, is a promising host for homologous and heterologous protein production. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3954–3959
Finkelstein D (1987) Improvement of enzyme production in Aspergillus. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 53:349–352
Flipphi MJ, van Heuvel M, van der Veen P, Visser J, de Graaff LH (1993) Cloning and characterization of the abfB gene coding for the major α-l-arabinofuranosidase (ABF B) of Aspergillus niger. Curr Genet 24:525–532
Foreman PK, Brown D, Dankmeyer L, Dean R, Diener S, Dunn-Coleman NS et al (2003) Transcriptional regulation of biomass-degrading enzymes in the filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei. J Biol Chem 278:31988–31997
Frey-Wyssling A (1954) The fine structure of cellulose microfibrils. Science 119:80–82
Gomes J, Gomes II, Terler K, Gubala N, Ditzelmuller G, Steiner W (2000) Optimisation of culture medium and conditions for α-l-arabinofuranosidase production by the extreme thermophilic eubacterium Rhodothermus marinus. Enzyme Microb Technol 27:414–422
Gruben BS (2012) Novel transcriptional activators of Aspergillus involved in plant biomass utilization: Utrecht University
Hasper AA, Dekkers E, van Mil M, van de Vondervoort PJ, de Graaff LH (2002) EglC, a new endoglucanase from Aspergillus niger with major activity towards xyloglucan. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1556–1560
Kusters-van Someren MA, Harmsen JA, Kester HC, Visser J (1991) Structure of the Aspergillus niger pelA gene and its expression in Aspergillus niger and Aspergillus nidulans. Curr Genet 20:293–299
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lagopodi AL, Ram AFJ, Lamers GEM, Punt PJ, Van den Hondel CAMJJ, Lugtenberg BJJ et al (2002) Novel aspects of tomato root colonization and infection by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici revealed by confocal laser scanning microscopic analysis using the green fluorescent protein as a marker. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:172–179
Mai V, Wiegel J, Lorenz WW (2000) Cloning, sequencing, and characterization of the bifunctional xylosidase-arabinosidase from the anaerobic thermophile Thermoanaerobacter ethanolicus. Gene 247:137–143
Margolles-Clark E, Tenkanen M, Nakari-Setala T, Penttila M (1996) Cloning of genes encoding α-l-arabinofuranosidase and β-xylosidase from Trichoderma reesei by expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3840–3846
Miyazaki K (2005) Hyperthermophilic α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Thermotoga maritima MSB8: molecular cloning, gene expression, and characterization of the recombinant protein. Extremophiles 9:399–406
Mullaney E, Hamer J, Roberti K, Yelton MM, Timberlake W (1985) Primary structure of the trpC gene from Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet MGG 199:37–45
Peraza L, Ortiz MA, Peberdy JF, Aguilar G (2003) Growth and pectinase production by Aspergillus Mexican strain protoplast regenerated under acidic stress. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 111:15–27
Poutanen K (1997) Enzymes: an important tool in the improvement of the quality of cereal foods. Trends Food Sci Technol 8:300–306
Punt PJ, Dingemanse MA, Kuyvenhoven A, Soede RDM, Pouwels PH, van den Hondel CAMJJ (1990) Functional elements in the promoter region of the Aspergillus nidulans gpdA gene encoding glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Gene 93:101–109
Punt PJ, van Biezen N, Conesa A, Albers A, Mangnus J, van den Hondel C (2002) Filamentous fungi as cell factories for heterologous protein production. Trends Biotechnol 20:200–206
Quay DHX, Bakar FDA, Rabu A, Said M, Illias RM, Mahadi NM, Hassan O, Murad AMA (2011) Overexpression, purification and characterization of the Aspergillus niger endoglucanase, EglA, in Pichia pastoris. Afr J Biotechnol 10:2101–2111
Remond C, Plantier-Royon R, Aubry N, Maes E, Bliard C, O’Donohue MJ (2004) Synthesis of pentose-containing disaccharides using a thermostable α-l-arabinofuranosidase. Carbohydr Res 339:2019–2025
Rémond C, Ferchichi M, Aubry N, Plantier-Royon R, Portella C, O’Donohue MJ (2002) Enzymatic synthesis of alkyl arabinofuranosides using a thermostable α-l-arabinofuranosidase. Tetrahedron Lett 43:9653–9655
Rombouts FM, Voragen AGJ, Searle-van Leeuwen MF, Geraeds CCJM, Schols HA, Pilnik W (1988) The arabinanases of Aspergillus niger—purification and characterisation of two α-l-arabinofuranosidases and an endo-1,5-α-l-arabinanase. Carbohydr Polym 9:25–47
Saha BC (2003) Hemicellulose bioconversion. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:279–291
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Molecular Cloning
Shi P, Li N, Yang P, Wang Y, Luo H, Bai Y et al (2010) Gene cloning, expression, and characterization of a family 51 α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Streptomyces sp. S9. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:707–718
van Peij NN, Gielkens MM, de Vries RP, Visser J, de Graaff LH (1998) The transcriptional activator XlnR regulates both xylanolytic and endoglucanase gene expression in Aspergillus niger. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3615–3619
Wang L, Ridgway D, Gu T, Moo-Young M (2005) Bioprocessing strategies to improve heterologous protein production in filamentous fungal fermentations. Biotechnol Adv 23:115–129
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no commercial or financial conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Culleton, H., McKie, V.A. & de Vries, R.P. Overexpression, purification and characterisation of homologous α-l-arabinofuranosidase and endo-1,4-β-d-glucanase in Aspergillus vadensis . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 1697–1708 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1512-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1512-6